Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
通过拉取请求 (PR) 工作流程,开发人员可以从对等和自动化工具那里获得对其代码的反馈。 非微软工具和服务还可以通过使用 PR 状态 API 参与 PR 工作流。 本文介绍如何使用 Azure Functions 创建自定义分支策略来验证 Azure DevOps Git 存储库中的 PR。 即使工作负荷增长,Azure Functions 也无需预配和维护服务器。 它们提供高度可靠性和安全性的完全托管计算平台。
有关 PR 状态的详细信息,请参阅 使用拉取请求状态自定义和扩展拉取请求工作流。
先决条件
| 类别 | 要求 |
|---|---|
| 组织 | Azure DevOps 中的一个组织,包含一个 Git 存储库。 |
| Azure Function | 一个 Azure 函数,它实现了与 Azure DevOps 集成的无服务器事件驱动解决方案,以创建自定义分支策略并自动执行 PR 验证。 |
| 服务挂钩 | 为 PR 事件配置服务挂钩,以便在拉取请求发生变化时通知 Azure 函数。 |
| 身份验证 | 使用具有代码(状态)作用域的 Microsoft Entra ID 令牌来获得更改 PR 状态的权限。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Microsoft Entra 身份验证。 |
创建用于侦听 Azure Repos 事件的基本 Azure 函数
创建第一个 Azure 函数。 然后,修改示例中的代码,如下所示:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(HttpRequestMessage req, TraceWriter log)
{
try
{
log.Info("Service Hook Received.");
// Get request body
dynamic data = await req.Content.ReadAsAsync<object>();
log.Info("Data Received: " + data.ToString());
// Get the pull request object from the service hooks payload
dynamic jObject = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(data.ToString());
// Get the pull request id
int pullRequestId;
if (!Int32.TryParse(jObject.resource.pullRequestId.ToString(), out pullRequestId))
{
log.Info("Failed to parse the pull request id from the service hooks payload.");
};
// Get the pull request title
string pullRequestTitle = jObject.resource.title;
log.Info("Service Hook Received for PR: " + pullRequestId + " " + pullRequestTitle);
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
log.Info(ex.ToString());
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError);
}
}
为 PR 事件配置服务挂钩
服务挂钩是一项 Azure DevOps 功能,可在发生某些事件时向外部服务发出警报。 在此示例中,为 PR 事件设置了一个服务挂钩,当拉取请求发生变化时,Azure 函数会收到通知。 为了在拉取请求更改时接收 POST 请求,请为服务挂钩提供 Azure 函数 URL。
对于此示例,配置两个服务钩子。 第一个用于 拉取请求创建事件,第二个用于 拉取请求更新事件。
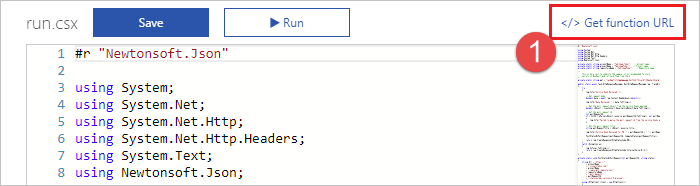
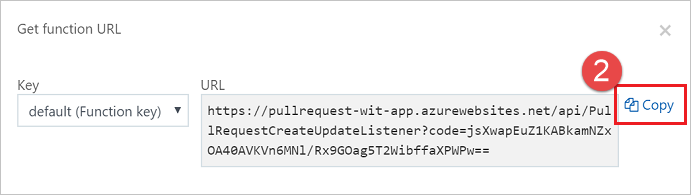
通过单击 Azure 函数视图中的 “获取函数 URL ”并复制 URL,从 Azure 门户获取函数 URL。
转到 Azure DevOps 中的项目,例如
https://dev.azure.com/<your organization>/<your project name>在导航菜单中,将鼠标悬停在 齿轮 上,然后选择 服务挂钩。

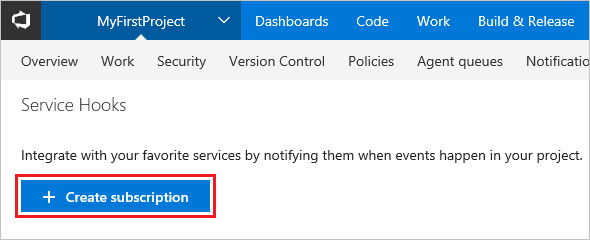
如果这是您的第一个服务挂钩,请选择“+ 创建订阅”。
如果已配置其他服务挂钩,请选择绿色加号
(+)以创建新的服务挂钩订阅。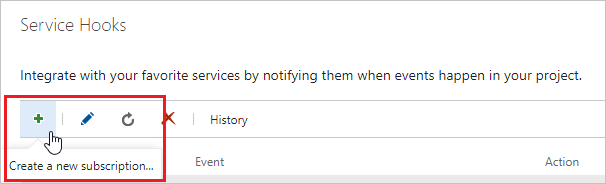
在“新建服务挂钩订阅”对话框中,从服务列表中选择“Web 挂钩”,然后选择“下一步”。
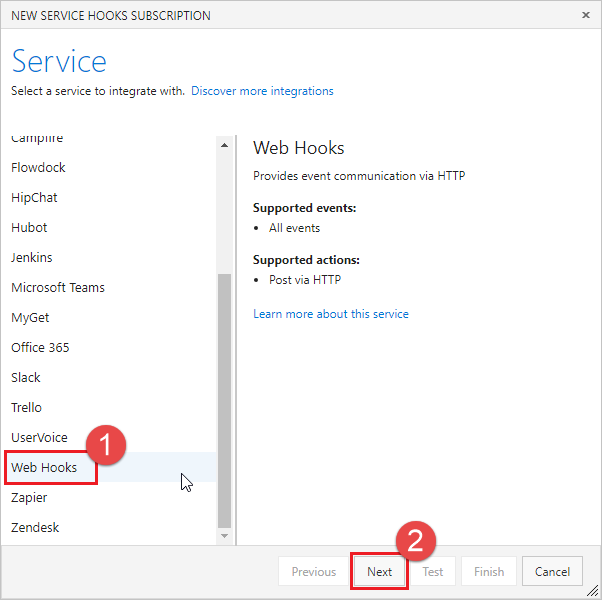
从事件触发器列表中选择“已创建拉取请求”,然后选择“下一步”。
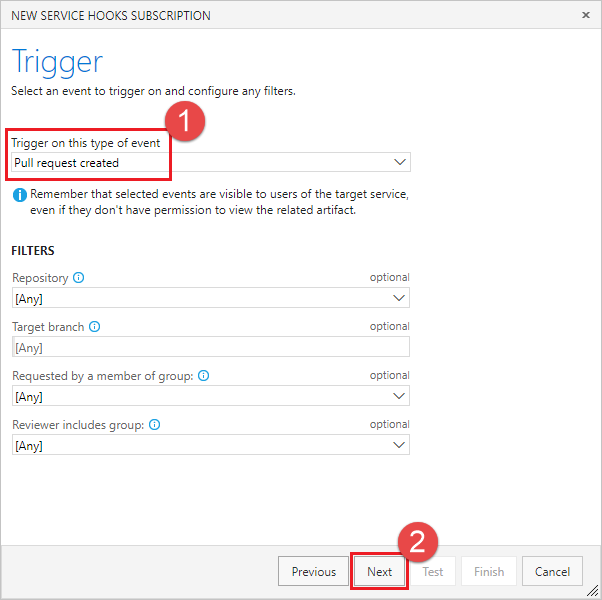
在“操作页面”中,在 URL 框中输入您在步骤 1 中复制的 URL。 选择 测试 来将测试事件发送到您的服务器。
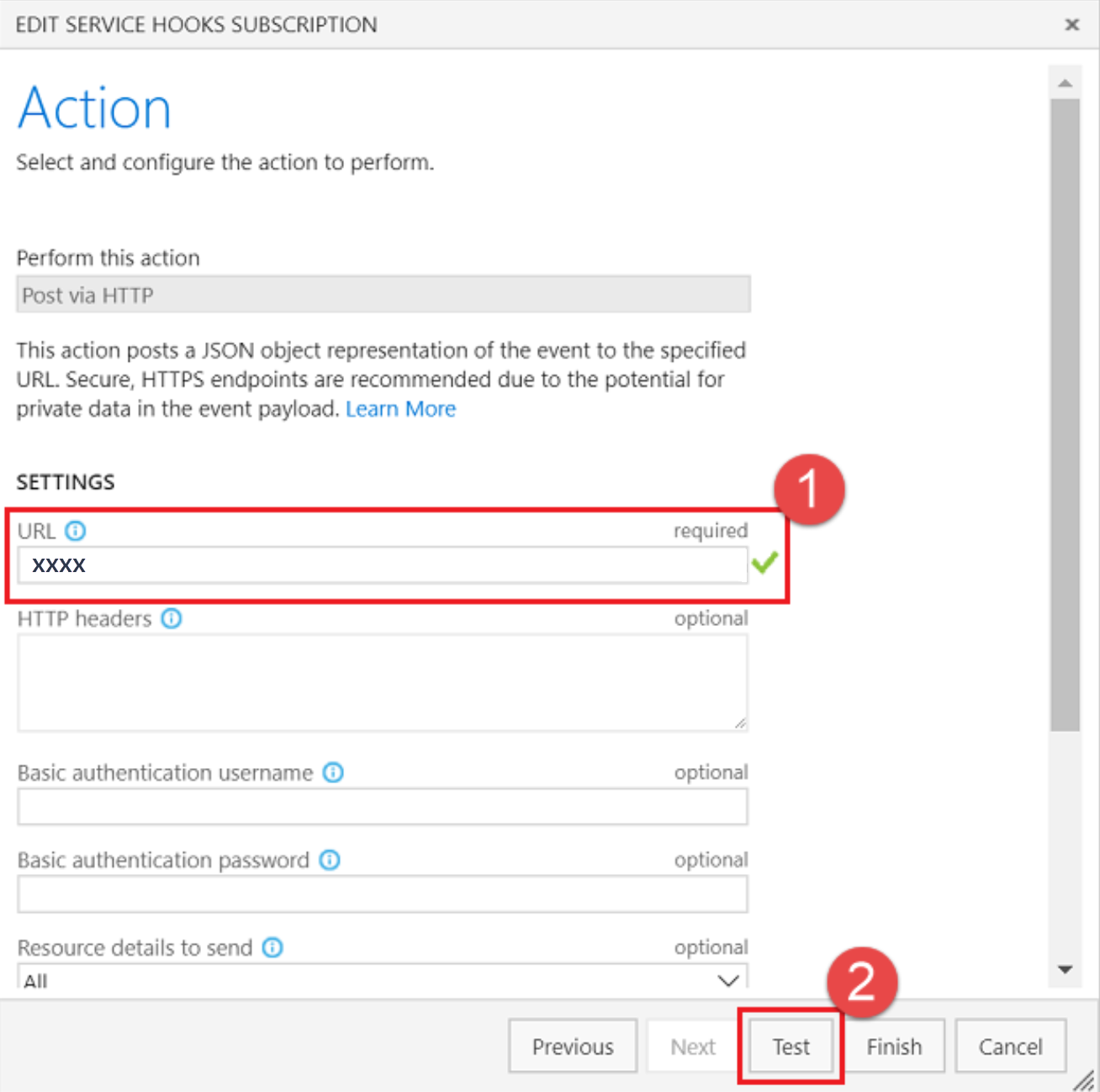
在 Azure 函数的日志窗口中,您会看到传入请求
POST返回了200 OK,表示您的函数已接收到服务挂钩事件。HTTP Requests ------------- POST / 200 OK在“测试通知”窗口中,选择“响应”选项卡以查看来自服务器的响应的详细信息。 应会看到来自服务器的响应。
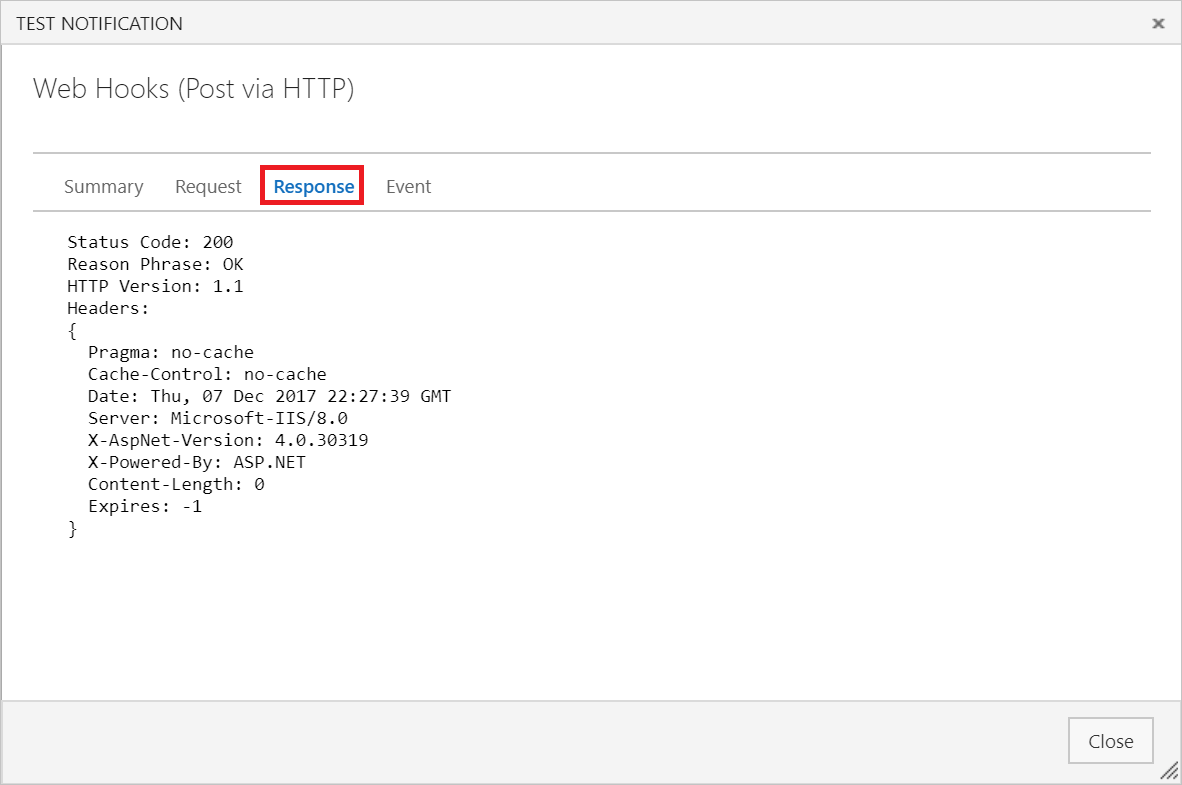
关闭“测试通知”窗口,然后选择“完成”以创建服务挂钩。
再次完成步骤 2-8,但这次是配置“已更新拉取请求”事件。
重要
请务必执行上述步骤两次,为“已创建拉取请求”事件和“已更新拉取请求”事件创建服务挂钩。
创建拉取请求以验证 Azure 函数是否收到通知。
将状态发布到 PR
现在,服务器可以在创建新 PR 时接收服务挂钩事件,请将其更新,以便将状态回发 PR。 可以使用服务挂钩发布的 JSON 有效负载来确定要在 PR 上设置的状态。
更新 Azure 函数的代码,类似于以下示例。
请确保使用组织名称、项目名称、存储库名称和Microsoft Entra ID 令牌更新代码。 若要具有更改 PR 状态的权限,令牌需要 vso.code_status 范围,可以通过Microsoft Entra 身份验证获取该范围。
重要
此示例代码将令牌存储在代码中,从而简化示例。 建议将机密存储在 Azure Key Vault 中,并使用托管标识从那里检索机密,以提高安全性。
此示例检查 PR 标题,以查看用户是否通过在标题中添加 WIP 来表明 PR 是否尚在进行中。 如果是这样,示例代码将更改发布回 PR 的状态。 用以下代码替换您 Azure 函数中的代码,此代码将更新返回给 PR 的状态。
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
private static string organizationName = "[Organization Name]"; // Organization name
private static string projectName = "[Project Name]"; // Project name
private static string repositoryName = "[Repo Name]"; // Repository name
/*
This is here just to simplify the sample, it is recommended to store
secrets in Azure Key Vault and retrieve them using managed identity.
*/
private static string accessToken = "[MICROSOFT_ENTRA_TOKEN]";
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(HttpRequestMessage req, TraceWriter log)
{
try
{
log.Info("Service Hook Received.");
// Get request body
dynamic data = await req.Content.ReadAsAsync<object>();
log.Info("Data Received: " + data.ToString());
// Get the pull request object from the service hooks payload
dynamic jObject = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(data.ToString());
// Get the pull request id
int pullRequestId;
if (!Int32.TryParse(jObject.resource.pullRequestId.ToString(), out pullRequestId))
{
log.Info("Failed to parse the pull request id from the service hooks payload.");
};
// Get the pull request title
string pullRequestTitle = jObject.resource.title;
log.Info("Service Hook Received for PR: " + pullRequestId + " " + pullRequestTitle);
PostStatusOnPullRequest(pullRequestId, ComputeStatus(pullRequestTitle));
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
log.Info(ex.ToString());
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError);
}
}
private static void PostStatusOnPullRequest(int pullRequestId, string status)
{
string Url = string.Format(
@"https://dev.azure.com/{0}/{1}/_apis/git/repositories/{2}/pullrequests/{3}/statuses?api-version=4.1",
organizationName,
projectName,
repositoryName,
pullRequestId);
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", accessToken);
var method = new HttpMethod("POST");
var request = new HttpRequestMessage(method, Url)
{
Content = new StringContent(status, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json")
};
using (HttpResponseMessage response = client.SendAsync(request).Result)
{
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
}
}
private static string ComputeStatus(string pullRequestTitle)
{
string state = "succeeded";
string description = "Ready for review";
if (pullRequestTitle.ToLower().Contains("wip"))
{
state = "pending";
description = "Work in progress";
}
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(
new
{
State = state,
Description = description,
TargetUrl = "https://visualstudio.microsoft.com",
Context = new
{
Name = "PullRequest-WIT-App",
Genre = "pr-azure-function-ci"
}
});
}
创建新的 PR 并测试状态服务器
现在服务器正在运行并侦听服务挂钩通知,请创建一个拉取请求来测试它。
在文件视图中启动。 编辑存储库中的 readme.md 文件(如果没有 readme.md,则编辑任何其他文件)。
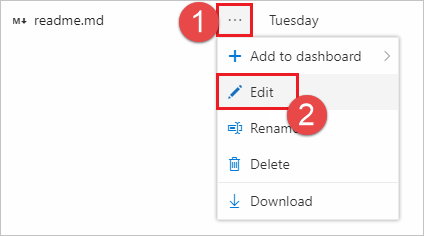
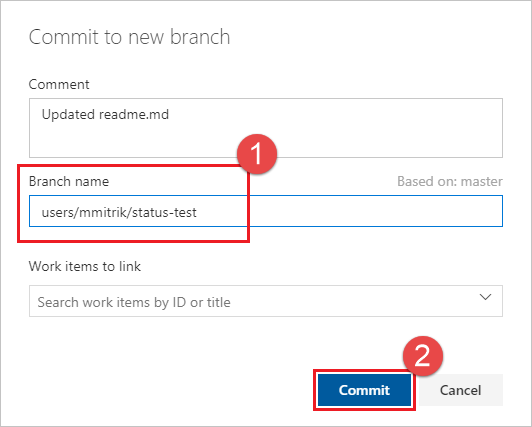
进行编辑并将更改提交到存储库。

请务必将更改提交到新分支,以便在下一步中创建 PR。
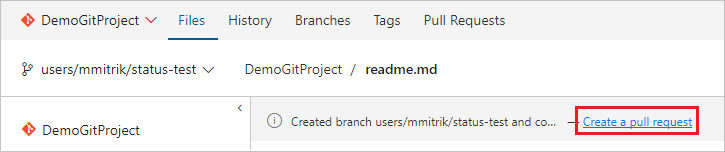
选择“创建拉取请求”链接。
在标题中添加 WIP 以测试应用的功能。 选择 创建 以创建 PR。
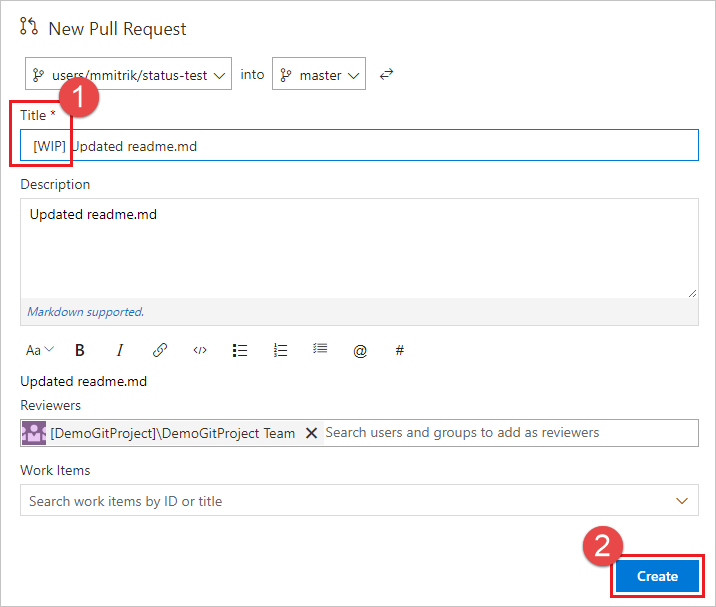
创建 PR 后,状态部分会显示,其中的 工作正在进行 条目链接到载荷中指定的 URL。
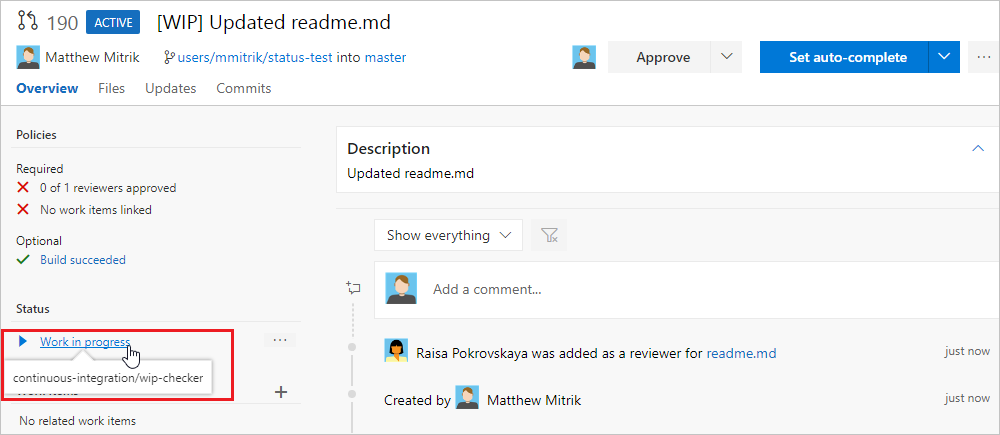
更新 PR 标题并删除 WIP 文本,注意状态将从“正在进行”更改为“可供评审”。