Notitie
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen u aan te melden of de directory te wijzigen.
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen de mappen te wijzigen.
Note
Dit is niet de nieuwste versie van dit artikel. Zie de .NET 9-versie van dit artikel voor de huidige release.
Warning
Deze versie van ASP.NET Core wordt niet meer ondersteund. Zie het .NET- en .NET Core-ondersteuningsbeleid voor meer informatie. Zie de .NET 9-versie van dit artikel voor de huidige release.
Important
Deze informatie heeft betrekking op een pre-releaseproduct dat aanzienlijk kan worden gewijzigd voordat het commercieel wordt uitgebracht. Microsoft geeft geen garanties, uitdrukkelijk of impliciet, met betrekking tot de informatie die hier wordt verstrekt.
Zie de .NET 9-versie van dit artikel voor de huidige release.
Door Rick Anderson en Kirk Larkin
ASP.NET Core configureert app-gedrag op basis van de runtime-omgeving met behulp van een omgevingsvariabele.
Zie BlazorASP.NET Core-omgevingen Blazorvoor richtlijnen voor omgevingen die worden toegevoegd aan of vervangen door de richtlijnen in dit artikel.
Environments
Om de runtime-omgeving te bepalen, leest ASP.NET Core de volgende omgevingsvariabelen uit:
- DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT
-
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTwanneer de WebApplication.CreateBuilder methode wordt aangeroepen. De standaard-ASP.NET Core-web-app-sjablonen worden aangeroepenWebApplication.CreateBuilder. DeASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTwaarde overschrijftDOTNET_ENVIRONMENT.
Om de runtime-omgeving te bepalen, leest ASP.NET Core de volgende omgevingsvariabelen uit:
- DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT
-
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTwanneer de WebApplication.CreateBuilder methode wordt aangeroepen. De standaard-ASP.NET Core-web-app-sjablonen worden aangeroepenWebApplication.CreateBuilder. DeDOTNET_ENVIRONMENTwaarde overschrijftASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTwanneerWebApplicationBuilderdeze wordt gebruikt. Voor andere hosts, zoalsConfigureWebHostDefaultsenWebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder,ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTheeft een hogere prioriteit.
IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName kan worden ingesteld op elke waarde, maar de volgende waarden worden geleverd door het framework:
-
Development: het launchSettings.json bestand wordt ingesteld
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTDevelopmentop de lokale computer. - Staging
-
Production: De standaardinstelling als
DOTNET_ENVIRONMENTenASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTniet zijn ingesteld.
De volgende code:
- Is vergelijkbaar met de code die is gegenereerd door de ASP.NET Core-sjablonen.
- Hiermee schakelt u de uitzonderingspagina voor ontwikkelaars in wanneer
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTdeze is ingesteld opDevelopment. Dit wordt automatisch gedaan door de WebApplication.CreateBuilder methode. - Roept aan UseExceptionHandler wanneer de waarde
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTvan iets anders is danDevelopment. - Biedt een IWebHostEnvironment exemplaar in de Environment eigenschap van
WebApplication.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
De Environment Tag Helper gebruikt de waarde van IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName om markeringen op te nemen of uit te sluiten in het element:
<environment include="Development">
<div>Environment is Development</div>
</environment>
<environment exclude="Development">
<div>Environment is NOT Development</div>
</environment>
<environment include="Staging,Development,Staging_2">
<div>Environment is: Staging, Development or Staging_2</div>
</environment>
De pagina Info uit de voorbeeldcode bevat de voorgaande markeringen en geeft de waarde weer van IWebHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName.
In Windows en macOS zijn omgevingsvariabelen en -waarden niet hoofdlettergevoelig. Linux-omgevingsvariabelen en -waarden zijn standaard hoofdlettergevoelig.
Create EnvironmentsSample
De voorbeeldcode die in dit artikel wordt gebruikt, is gebaseerd op een Razor Pages-project met de naam EnvironmentsSample.
Met de volgende .NET CLI-opdrachten maakt u een web-app met de naam EnvironmentsSample en voert u deze uit:
dotnet new webapp -o EnvironmentsSample
cd EnvironmentsSample
dotnet run --verbosity normal
Wanneer de app wordt uitgevoerd, wordt uitvoer weergegeven die er ongeveer als volgt uitziet:
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: https://localhost:7152
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: http://localhost:5105
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Application started. Press Ctrl+C to shut down.
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Hosting environment: Development
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Content root path: C:\Path\To\EnvironmentsSample
Omgeving instellen op de opdrachtregel
Gebruik de --environment vlag om de omgeving in te stellen. For example:
dotnet run --environment Production
Met de voorgaande opdracht wordt de omgeving ingesteld Production en wordt uitvoer weergegeven die vergelijkbaar is met het volgende in het opdrachtvenster:
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: https://localhost:7262
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: http://localhost:5005
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Application started. Press Ctrl+C to shut down.
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Hosting environment: Production
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Content root path: C:\Path\To\EnvironmentsSample
Ontwikkeling en launchSettings.json
De ontwikkelomgeving kan functies inschakelen die niet in productie mogen worden weergegeven. Met de ASP.NET Core-projectsjablonen kunt u bijvoorbeeld de ontwikkelaars-uitzonderingspagina in de ontwikkelomgeving inschakelen. Vanwege de prestatiekosten vindt bereikvalidatie en afhankelijkheidsvalidatie alleen plaats in ontwikkeling.
De omgeving voor het ontwikkelen van lokale machines kan worden ingesteld in de eigenschappen\launchSettings.jsin het bestand van het project. Omgevingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in launchSettings.json onderdrukkingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in de systeemomgeving.
Het bestand launchSettings.json:
- Wordt alleen gebruikt op de lokale ontwikkelcomputer.
- Is niet geïmplementeerd.
- Bevat profielinstellingen.
In de volgende JSON ziet u het bestand voor een ASP.NET Core-webproject met de launchSettings.json naam EnvironmentsSample dat is gemaakt met Visual Studio of dotnet new:
{
"iisSettings": {
"windowsAuthentication": false,
"anonymousAuthentication": true,
"iisExpress": {
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:59481",
"sslPort": 44308
}
},
"profiles": {
"EnvironmentsSample": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:7152;http://localhost:5105",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
}
}
De voorgaande JSON bevat twee profielen:
EnvironmentsSample: De profielnaam is de projectnaam. Als het eerste profiel dat wordt vermeld, wordt dit profiel standaard gebruikt. De"commandName"sleutel heeft de waarde"Project", dus de Kestrel webserver wordt gestart.IIS Express: De"commandName"sleutel heeft de waarde"IISExpress", dus IISExpress is de webserver.
U kunt het startprofiel instellen op het project of een ander profiel dat is opgenomen in launchSettings.json. Als u bijvoorbeeld in de onderstaande afbeelding de projectnaam selecteert, wordt de Kestrel webserver gestart.
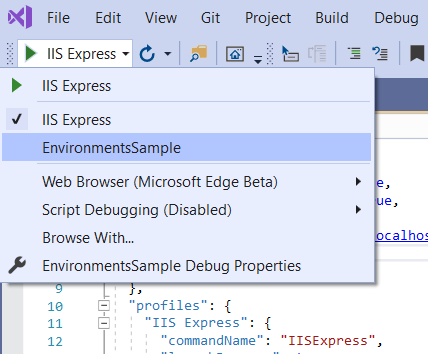
De waarde van commandName kan de webserver opgeven die moet worden gestart.
commandName kan een van de volgende zijn:
-
IISExpress: start IIS Express. -
IIS: Er is geen webserver gestart. IIS is naar verwachting beschikbaar. -
Project: Lanceringen Kestrel.
De projecteigenschappen van Visual Studio 2022 Foutopsporing/algemeen tabblad biedt een koppeling voor het openen van startprofielen voor foutopsporing . Met deze koppeling opent u een dialoogvenster Profielen starten waarmee u de instellingen van de omgevingsvariabele in het launchSettings.json bestand kunt bewerken. U kunt het dialoogvenster Profielen starten ook openen in het menu Foutopsporing door projectnaam> Eigenschappen voor foutopsporing te< selecteren. Wijzigingen die zijn aangebracht in projectprofielen, worden mogelijk pas van kracht nadat de webserver opnieuw is opgestart.
Kestrel moet opnieuw worden gestart voordat wijzigingen in de omgeving kunnen worden gedetecteerd.
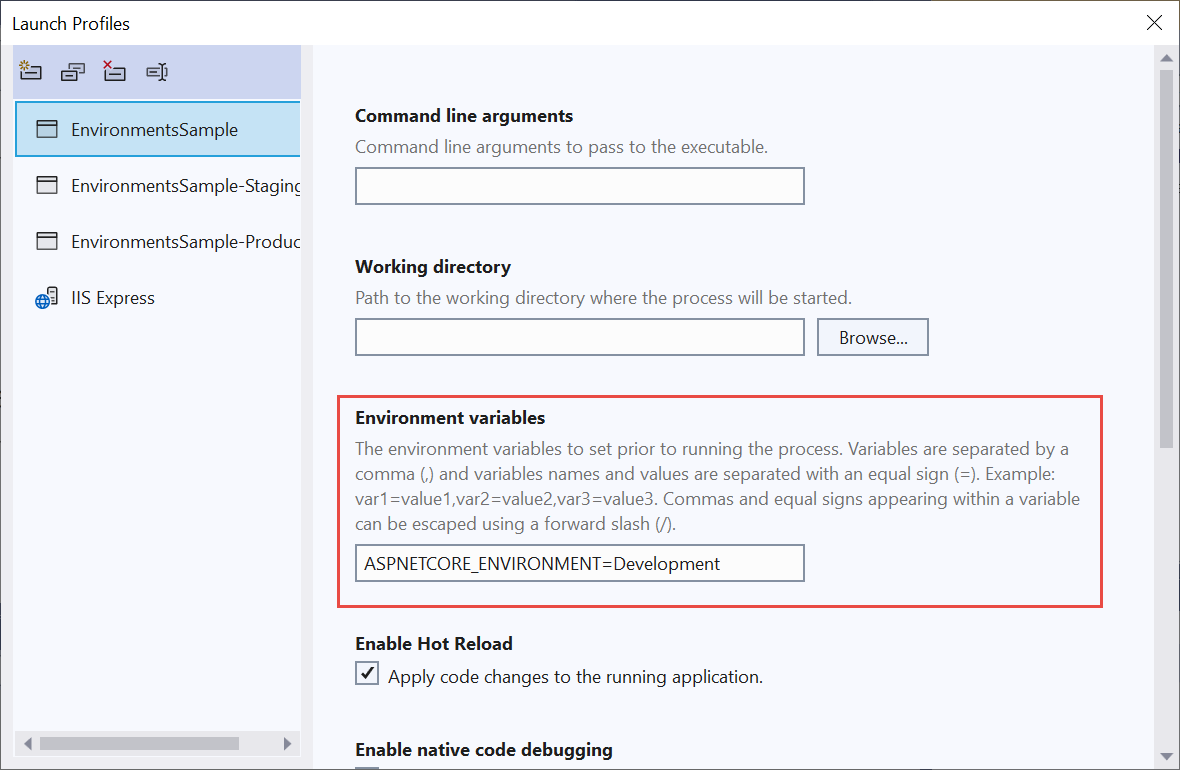
Het volgende launchSettings.json bestand bevat meerdere profielen:
{
"iisSettings": {
"windowsAuthentication": false,
"anonymousAuthentication": true,
"iisExpress": {
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:59481",
"sslPort": 44308
}
},
"profiles": {
"EnvironmentsSample": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:7152;http://localhost:5105",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"EnvironmentsSample-Staging": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:7152;http://localhost:5105",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Staging",
"ASPNETCORE_DETAILEDERRORS": "1",
"ASPNETCORE_SHUTDOWNTIMEOUTSECONDS": "3"
}
},
"EnvironmentsSample-Production": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:7152;http://localhost:5105",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Production"
}
},
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
}
}
Profielen kunnen worden geselecteerd:
Vanuit de Visual Studio-gebruikersinterface.
Gebruik de
dotnet runCLI-opdracht met de--launch-profileoptie die is ingesteld op de naam van het profiel. Deze benadering ondersteunt Kestrel alleen profielen.dotnet run --launch-profile "EnvironmentsSample"
Warning
launchSettings.json mag geen geheimen opslaan. Het hulpprogramma Secret Manager kan worden gebruikt om geheimen op te slaan voor lokale ontwikkeling.
Wanneer u Visual Studio Code gebruikt, kunnen omgevingsvariabelen worden ingesteld in het .vscode/launch.json bestand. In het volgende voorbeeld worden verschillende omgevingsvariabelen ingesteld voor hostconfiguratiewaarden:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": ".NET Core Launch (web)",
"type": "coreclr",
// Configuration ommitted for brevity.
"env": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development",
"ASPNETCORE_URLS": "https://localhost:5001",
"ASPNETCORE_DETAILEDERRORS": "1",
"ASPNETCORE_SHUTDOWNTIMEOUTSECONDS": "3"
},
// Configuration ommitted for brevity.
Het .vscode/launch.json bestand wordt alleen gebruikt door Visual Studio Code.
Production
De productieomgeving moet worden geconfigureerd om de robuustheid van beveiliging, prestaties en toepassingen te maximaliseren. Enkele algemene instellingen die verschillen van ontwikkeling zijn onder andere:
- Caching.
- Resources aan de clientzijde worden gebundeld, geminimificeerd en mogelijk geleverd vanuit een CDN.
- Diagnostische foutpagina's uitgeschakeld.
- Beschrijvende foutpagina's ingeschakeld.
- Productielogboekregistratie en -bewaking ingeschakeld. Gebruik bijvoorbeeld Application Insights.
De omgeving instellen door een omgevingsvariabele in te stellen
Het is vaak handig om een specifieke omgeving in te stellen voor testen met een omgevingsvariabele of platforminstelling. Als de omgeving niet is ingesteld, wordt deze standaard Productioningesteld, waardoor de meeste foutopsporingsfuncties worden uitgeschakeld. De methode voor het instellen van de omgeving is afhankelijk van het besturingssysteem.
Wanneer de host is gebouwd, bepaalt de laatste omgevingsinstelling die door de app wordt gelezen de omgeving van de app. De omgeving van de app kan niet worden gewijzigd terwijl de app wordt uitgevoerd.
Op de pagina Info uit de voorbeeldcode wordt de waarde van IWebHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName.
Azure App Service
Production is de standaardwaarde als DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT en ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT niet zijn ingesteld. Apps die in Azure zijn geïmplementeerd, zijn Production standaard.
De omgeving instellen in een Azure App Service-app met behulp van de portal:
- Selecteer de app op de pagina App Services .
- Selecteer omgevingsvariabelen in de groep Instellingen.
- Selecteer + Toevoegen op het tabblad App-instellingen.
- Geef
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTin het venster Toepassingsinstelling toevoegen/bewerken de naam op. Geef voor Waarde de omgeving op (bijvoorbeeldStaging). - Schakel het selectievakje Implementatiesite-instelling in als u wilt dat de omgevingsinstelling bij de huidige site blijft wanneer implementatiesites worden gewisseld. Zie Faseringsomgevingen instellen in Azure App Service in de Azure-documentatie voor meer informatie.
- Selecteer OK om het dialoogvenster Toepassingsinstelling toevoegen/bewerken te sluiten.
- Selecteer Opslaan boven aan de pagina Configuratie .
Azure App Service start de app automatisch opnieuw op nadat een app-instelling is toegevoegd, gewijzigd of verwijderd in Azure Portal.
Windows - Omgevingsvariabele instellen voor een proces
Omgevingswaarden in launchSettings.json onderdrukkingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in de systeemomgeving.
Als u de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT voor de huidige sessie wilt instellen wanneer de app wordt gestart met dotnet-uitvoering, gebruikt u de volgende opdrachten bij een opdrachtprompt of in PowerShell:
set ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging
dotnet run --no-launch-profile
$Env:ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT = "Staging"
dotnet run --no-launch-profile
Windows - Omgevingsvariabele globaal instellen
De voorgaande opdrachten zijn alleen ingesteld ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT voor processen die vanuit dat opdrachtvenster worden gestart.
Als u de waarde globaal in Windows wilt instellen, gebruikt u een van de volgende methoden:
Open degeavanceerde systeeminstellingen van het Configuratiescherm>> en voeg de waarde toe of bewerk deze
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT: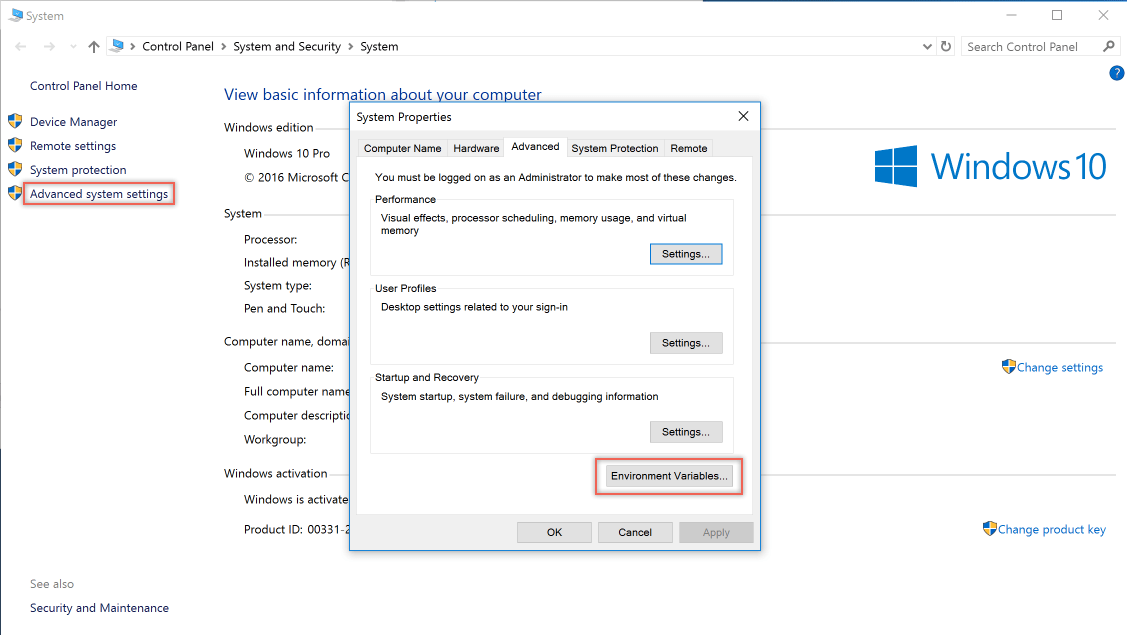
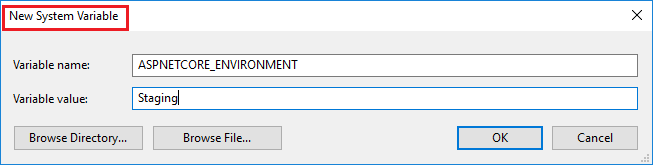
Open een beheeropdrachtprompt en gebruik de
setxopdracht of open een PowerShell-opdrachtprompt met beheerdersrechten en gebruik[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable:-
setx ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT Staging /MDe
/Mswitch stelt de omgevingsvariabele in op systeemniveau. Als de/Mswitch niet wordt gebruikt, wordt de omgevingsvariabele ingesteld voor het gebruikersaccount. -
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT", "Staging", "Machine")Met
Machinede optie wordt de omgevingsvariabele ingesteld op systeemniveau. Als de optiewaarde wordt gewijzigdUserin , wordt de omgevingsvariabele ingesteld voor het gebruikersaccount.
-
Wanneer de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele globaal is ingesteld, wordt deze van kracht in dotnet run een opdrachtvenster dat wordt geopend nadat de waarde is ingesteld. Omgevingswaarden in launchSettings.json onderdrukkingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in de systeemomgeving.
Windows : web.config gebruiken
Als u de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele wilt web.configinstellen, raadpleegt u de sectie Omgevingsvariabelen instellen van web.config bestand.
Windows - IIS-implementaties
Neem de <EnvironmentName> eigenschap op in het publicatieprofiel (.pubxml) of projectbestand. Met deze methode wordt de omgeving ingesteld in web.config wanneer het project wordt gepubliceerd:
<PropertyGroup>
<EnvironmentName>Development</EnvironmentName>
</PropertyGroup>
Als u de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele wilt instellen voor een app die wordt uitgevoerd in een geïsoleerde groep van toepassingen (ondersteund op IIS 10.0 of hoger), raadpleegt u de sectieAppCmd.exe opdracht van omgevingsvariabelen <environmentVariables>. Wanneer de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele is ingesteld voor een app-pool, overschrijft de waarde ervan een instelling op systeemniveau.
Wanneer u een app host in IIS en de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele toevoegt of wijzigt, gebruikt u een van de volgende methoden om de nieuwe waarde te laten ophalen door apps:
- Voer
net stop was /yde opdracht uit gevolgd doornet start w3svceen opdrachtprompt. - Start de server opnieuw op.
macOS
Het instellen van de huidige omgeving voor macOS kan inline worden uitgevoerd bij het uitvoeren van de app:
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging dotnet run
U kunt ook de omgeving instellen voordat export u de app uitvoert:
export ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging
Omgevingsvariabelen op machineniveau worden ingesteld in het .bashrc - of .bash_profile-bestand . Bewerk het bestand met een teksteditor. Voeg de volgende instructie toe:
export ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging
Linux
Voor Linux-distributies gebruikt u de export opdracht bij een opdrachtprompt voor instellingen voor sessievariabele en het bash_profile-bestand voor omgevingsinstellingen op computerniveau.
De omgeving instellen in code
Als u de omgeving in code wilt instellen, gebruikt WebApplicationOptions.EnvironmentName u deze bij het maken WebApplicationBuilder, zoals wordt weergegeven in het volgende voorbeeld:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(new WebApplicationOptions
{
EnvironmentName = Environments.Staging
});
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
Configuratie per omgeving
Zie Configuratie in ASP.NET Core als u de configuratie per omgeving wilt laden.
Services en middleware per omgeving configureren
Gebruik WebApplicationBuilder.Environment of WebApplication.Environment om services of middleware voorwaardelijk toe te voegen, afhankelijk van de huidige omgeving. De projectsjabloon bevat een voorbeeld van code waarmee alleen middleware wordt toegevoegd wanneer de huidige omgeving geen ontwikkeling is:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
De gemarkeerde code controleert de huidige omgeving tijdens het bouwen van de aanvraagpijplijn. Als u de huidige omgeving wilt controleren tijdens het configureren van services, gebruikt builder.Environment u in plaats van app.Environment.
Additional resources
Door Rick Anderson en Kirk Larkin
ASP.NET Core configureert app-gedrag op basis van de runtime-omgeving met behulp van een omgevingsvariabele.
Environments
Om de runtime-omgeving te bepalen, leest ASP.NET Core de volgende omgevingsvariabelen uit:
- DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT
-
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTwanneer ConfigureWebHostDefaults wordt aangeroepen. De standaard-ASP.NET Core-web-app-sjablonen worden aangeroepenConfigureWebHostDefaults. DeASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTwaarde overschrijftDOTNET_ENVIRONMENT.
IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName kan worden ingesteld op elke waarde, maar de volgende waarden worden geleverd door het framework:
-
Development : het launchSettings.json bestand wordt ingesteld
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTDevelopmentop de lokale computer. - Staging
-
Production : De standaardinstelling als
DOTNET_ENVIRONMENTenASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTniet zijn ingesteld.
De volgende code:
- Oproepen UseDeveloperExceptionPage wanneer
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTis ingesteld opDevelopment. - Aanroepen UseExceptionHandler wanneer de waarde
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTis ingesteld opStaging,ProductionofStaging_2. - Injecteert IWebHostEnvironment in
Startup.Configure. Deze benadering is handig wanneer de app alleen moet worden aangepastStartup.Configurevoor een paar omgevingen met minimale codeverschillen per omgeving. - Is vergelijkbaar met de code die is gegenereerd door de ASP.NET Core-sjablonen.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
if (env.IsProduction() || env.IsStaging() || env.IsEnvironment("Staging_2"))
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
De Environment Tag Helper gebruikt de waarde van IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName om markeringen op te nemen of uit te sluiten in het element:
<environment include="Development">
<div>The effective tag is: <environment include="Development"></div>
</environment>
<environment exclude="Development">
<div>The effective tag is: <environment exclude="Development"></div>
</environment>
<environment include="Staging,Development,Staging_2">
<div>
The effective tag is:
<environment include="Staging,Development,Staging_2">
</div>
</environment>
De pagina Info uit de voorbeeldcode bevat de voorgaande markeringen en geeft de waarde weer van IWebHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName.
In Windows en macOS zijn omgevingsvariabelen en -waarden niet hoofdlettergevoelig. Linux-omgevingsvariabelen en -waarden zijn standaard hoofdlettergevoelig .
Create EnvironmentsSample
De voorbeeldcode die in dit document wordt gebruikt, is gebaseerd op een Razor Pages-project met de naam EnvironmentsSample.
Met de volgende code wordt een web-app met de naam EnvironmentsSample gemaakt en uitgevoerd:
dotnet new webapp -o EnvironmentsSample
cd EnvironmentsSample
dotnet run --verbosity normal
Wanneer de app wordt uitgevoerd, wordt een aantal van de volgende uitvoer weergegeven:
Using launch settings from c:\tmp\EnvironmentsSample\Properties\launchSettings.json
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Now listening on: https://localhost:5001
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Application started. Press Ctrl+C to shut down.
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Hosting environment: Development
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Content root path: c:\tmp\EnvironmentsSample
Ontwikkeling en launchSettings.json
De ontwikkelomgeving kan functies inschakelen die niet in productie mogen worden weergegeven. Met de ASP.NET Core-sjablonen kunt u bijvoorbeeld de uitzonderingspagina voor ontwikkelaars inschakelen in de ontwikkelomgeving.
De omgeving voor het ontwikkelen van lokale machines kan worden ingesteld in de eigenschappen\launchSettings.jsin het bestand van het project. Omgevingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in launchSettings.json onderdrukkingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in de systeemomgeving.
Het bestand launchSettings.json:
- Wordt alleen gebruikt op de lokale ontwikkelcomputer.
- Is niet geïmplementeerd.
- bevat profielinstellingen.
In de volgende JSON ziet u het bestand voor een ASP.NET Core-webproject met de launchSettings.json naam EnvironmentsSample dat is gemaakt met Visual Studio of dotnet new:
{
"iisSettings": {
"windowsAuthentication": false,
"anonymousAuthentication": true,
"iisExpress": {
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:64645",
"sslPort": 44366
}
},
"profiles": {
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"EnvironmentsSample": {
"commandName": "Project",
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:5001;http://localhost:5000",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
}
}
De voorgaande markering bevat twee profielen:
IIS Express: Het standaardprofiel dat wordt gebruikt bij het starten van de app vanuit Visual Studio. De"commandName"sleutel heeft de waarde"IISExpress", dus IISExpress is de webserver. U kunt het startprofiel instellen op het project of een ander profiel dat is opgenomen. Als u bijvoorbeeld in de onderstaande afbeelding de projectnaam selecteert, wordt de Kestrel webserver gestart.
EnvironmentsSample: De profielnaam is de projectnaam. Dit profiel wordt standaard gebruikt bij het starten van de app metdotnet run. De"commandName"sleutel heeft de waarde"Project", dus de Kestrel webserver wordt gestart.
De waarde van commandName kan de webserver opgeven die moet worden gestart.
commandName kan een van de volgende zijn:
-
IISExpress: start IIS Express. -
IIS: Er is geen webserver gestart. IIS is naar verwachting beschikbaar. -
Project: Lanceringen Kestrel.
Het tabblad Foutopsporing van visual Studio-projecteigenschappen biedt een GUI om het launchSettings.json bestand te bewerken. Wijzigingen die zijn aangebracht in projectprofielen, worden mogelijk pas van kracht nadat de webserver opnieuw is opgestart.
Kestrel moet opnieuw worden gestart voordat wijzigingen in de omgeving kunnen worden gedetecteerd.
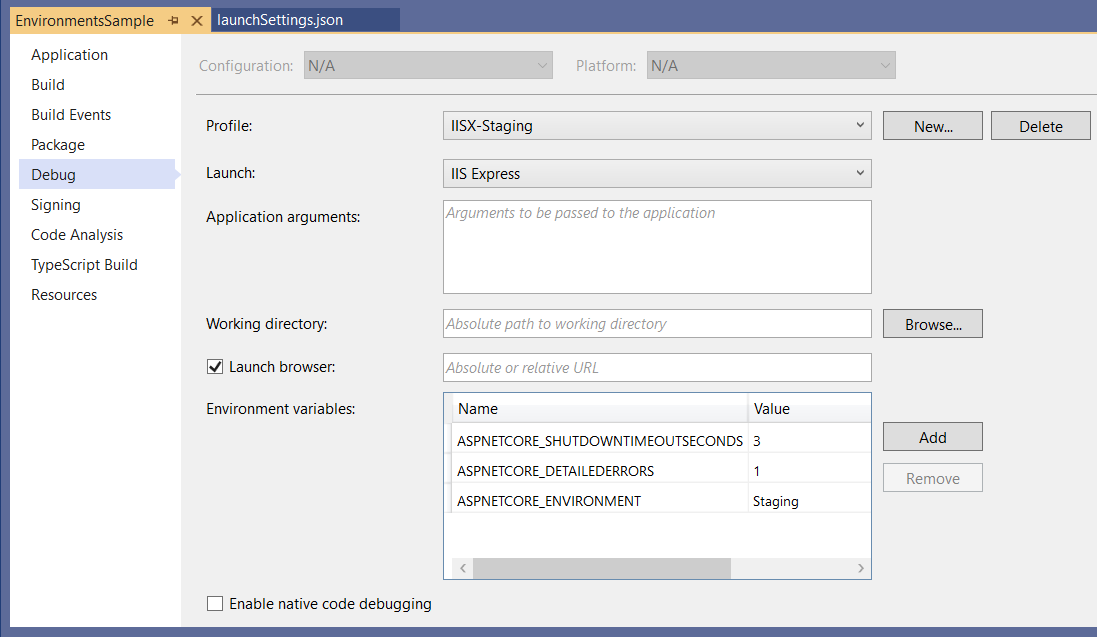
Het volgende launchSettings.json bestand bevat meerdere profielen:
{
"iisSettings": {
"windowsAuthentication": false,
"anonymousAuthentication": true,
"iisExpress": {
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:64645",
"sslPort": 44366
}
},
"profiles": {
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"IISX-Production": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Production"
}
},
"IISX-Staging": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Staging",
"ASPNETCORE_DETAILEDERRORS": "1",
"ASPNETCORE_SHUTDOWNTIMEOUTSECONDS": "3"
}
},
"EnvironmentsSample": {
"commandName": "Project",
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:5001;http://localhost:5000",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"KestrelStaging": {
"commandName": "Project",
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:5001;http://localhost:5000",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Staging"
}
}
}
}
Profielen kunnen worden geselecteerd:
Vanuit de Visual Studio-gebruikersinterface.
Gebruik de
dotnet runopdracht in een opdrachtshell met de--launch-profileoptie ingesteld op de naam van het profiel. Deze benadering ondersteunt Kestrel alleen profielen.dotnet run --launch-profile "SampleApp"
Warning
launchSettings.json mag geen geheimen opslaan. Het hulpprogramma Secret Manager kan worden gebruikt om geheimen op te slaan voor lokale ontwikkeling.
Wanneer u Visual Studio Code gebruikt, kunnen omgevingsvariabelen worden ingesteld in het .vscode/launch.json bestand. In het volgende voorbeeld worden verschillende omgevingsvariabelen voor hostconfiguratiewaarden ingesteld:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": ".NET Core Launch (web)",
"type": "coreclr",
// Configuration ommitted for brevity.
"env": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development",
"ASPNETCORE_URLS": "https://localhost:5001",
"ASPNETCORE_DETAILEDERRORS": "1",
"ASPNETCORE_SHUTDOWNTIMEOUTSECONDS": "3"
},
// Configuration ommitted for brevity.
Het .vscode/launch.json bestand wordt alleen gebruikt door Visual Studio Code.
Production
De productieomgeving moet worden geconfigureerd om de robuustheid van beveiliging, prestaties en toepassingen te maximaliseren. Enkele algemene instellingen die verschillen van ontwikkeling zijn onder andere:
- Caching.
- Resources aan de clientzijde worden gebundeld, geminimificeerd en mogelijk geleverd vanuit een CDN.
- Diagnostische foutpagina's uitgeschakeld.
- Beschrijvende foutpagina's ingeschakeld.
- Productielogboekregistratie en -bewaking ingeschakeld. Gebruik bijvoorbeeld Application Insights.
De omgeving instellen
Het is vaak handig om een specifieke omgeving in te stellen voor testen met een omgevingsvariabele of platforminstelling. Als de omgeving niet is ingesteld, wordt deze standaard Productioningesteld, waardoor de meeste foutopsporingsfuncties worden uitgeschakeld. De methode voor het instellen van de omgeving is afhankelijk van het besturingssysteem.
Wanneer de host is gebouwd, bepaalt de laatste omgevingsinstelling die door de app wordt gelezen de omgeving van de app. De omgeving van de app kan niet worden gewijzigd terwijl de app wordt uitgevoerd.
Op de pagina Info uit de voorbeeldcode wordt de waarde van IWebHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName.
Azure App Service
Production is de standaardwaarde als DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT en ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT niet zijn ingesteld. Apps die in Azure zijn geïmplementeerd, zijn Production standaard.
Voer de volgende stappen uit om de omgeving in Azure App Service in te stellen:
- Selecteer de app op de blade App Services .
- Selecteer in de groep Instellingen de blade Configuratie .
- Selecteer op het tabblad Toepassingsinstellingen de optie Nieuwe toepassingsinstelling.
- Geef
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENTin het venster Toepassingsinstelling toevoegen/bewerken de naam op. Geef voor Waarde de omgeving op (bijvoorbeeldStaging). - Schakel het selectievakje Implementatiesite-instelling in als u wilt dat de omgevingsinstelling bij de huidige site blijft wanneer implementatiesites worden gewisseld. Zie Faseringsomgevingen instellen in Azure App Service in de Azure-documentatie voor meer informatie.
- Selecteer OK om het venster Toepassingsinstelling toevoegen/bewerken te sluiten.
- Selecteer Opslaan boven aan de blade Configuratie .
Azure App Service start de app automatisch opnieuw op nadat een app-instelling is toegevoegd, gewijzigd of verwijderd in Azure Portal.
Windows
Omgevingswaarden in launchSettings.json onderdrukkingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in de systeemomgeving.
Als u de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT voor de huidige sessie wilt instellen wanneer de app wordt gestart met dotnet-uitvoering, worden de volgende opdrachten gebruikt:
Command prompt
set ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging
dotnet run --no-launch-profile
PowerShell
$Env:ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT = "Staging"
dotnet run --no-launch-profile
Met de voorgaande opdracht wordt alleen ingesteld ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT voor processen die vanuit dat opdrachtvenster worden gestart.
Als u de waarde globaal in Windows wilt instellen, gebruikt u een van de volgende methoden:
Open degeavanceerde systeeminstellingen van het Configuratiescherm>> en voeg de waarde toe of bewerk deze
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT:

Open een beheeropdrachtprompt en gebruik de
setxopdracht of open een PowerShell-opdrachtprompt met beheerdersrechten en gebruik[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable:Command prompt
setx ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT Staging /MDe
/Mswitch geeft aan dat de omgevingsvariabele moet worden ingesteld op systeemniveau. Als de/Mswitch niet wordt gebruikt, wordt de omgevingsvariabele ingesteld voor het gebruikersaccount.PowerShell
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT", "Staging", "Machine")De
Machineoptiewaarde geeft aan dat de omgevingsvariabele moet worden ingesteld op systeemniveau. Als de optiewaarde wordt gewijzigdUserin , wordt de omgevingsvariabele ingesteld voor het gebruikersaccount.
Wanneer de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele globaal is ingesteld, wordt deze van kracht in dotnet run een opdrachtvenster dat wordt geopend nadat de waarde is ingesteld. Omgevingswaarden in launchSettings.json onderdrukkingswaarden die zijn ingesteld in de systeemomgeving.
web.config
Als u de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele wilt web.configinstellen, raadpleegt u de sectie Omgevingsvariabelen instellen van web.config bestand.
Projectbestand of publicatieprofiel
Voor Windows IIS-implementaties: Neem de <EnvironmentName> eigenschap op in het publicatieprofiel (.pubxml) of projectbestand. Met deze methode wordt de omgeving ingesteld in web.config wanneer het project wordt gepubliceerd:
<PropertyGroup>
<EnvironmentName>Development</EnvironmentName>
</PropertyGroup>
Per IIS-groep van toepassingen
Als u de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele wilt instellen voor een app die wordt uitgevoerd in een geïsoleerde groep van toepassingen (ondersteund op IIS 10.0 of hoger), raadpleegt u de sectieAppCmd.exe opdracht van het onderwerp Omgevingsvariabelen <omgevingVariables> . Wanneer de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele is ingesteld voor een app-pool, overschrijft de waarde ervan een instelling op systeemniveau.
Wanneer u een app host in IIS en de ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT omgevingsvariabele toevoegt of wijzigt, gebruikt u een van de volgende methoden om de nieuwe waarde te laten ophalen door apps:
- Voer
net stop was /yde opdracht uit gevolgd doornet start w3svceen opdrachtprompt. - Start de server opnieuw op.
macOS
Het instellen van de huidige omgeving voor macOS kan inline worden uitgevoerd bij het uitvoeren van de app:
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging dotnet run
U kunt ook de omgeving instellen voordat export u de app uitvoert:
export ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging
Omgevingsvariabelen op machineniveau worden ingesteld in het .bashrc - of .bash_profile-bestand . Bewerk het bestand met een teksteditor. Voeg de volgende instructie toe:
export ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Staging
Linux
Voor Linux-distributies gebruikt u de export opdracht bij een opdrachtprompt voor instellingen voor variabelen op basis van een sessie en bash_profile bestand voor omgevingsinstellingen op computerniveau.
De omgeving instellen in code
Roep aan UseEnvironment bij het bouwen van de host. Zie .NET Generic Host in ASP.NET Core.
Configuratie per omgeving
Zie Configuratie in ASP.NET Core als u de configuratie per omgeving wilt laden.
Opstartklasse en -methoden op basis van omgeving
IWebHostEnvironment injecteren in de opstartklasse
Injecteer IWebHostEnvironment in de Startup constructor. Deze benadering is handig wanneer de app slechts een paar omgevingen moet configureren Startup met minimale codeverschillen per omgeving.
In het volgende voorbeeld:
- De omgeving wordt in het
_envveld gehouden. -
_envwordt gebruikt inConfigureServicesenConfigureom opstartconfiguratie toe te passen op basis van de omgeving van de app.
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
Configuration = configuration;
_env = env;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
private readonly IWebHostEnvironment _env;
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
if (_env.IsDevelopment())
{
Console.WriteLine(_env.EnvironmentName);
}
else if (_env.IsStaging())
{
Console.WriteLine(_env.EnvironmentName);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Not dev or staging");
}
services.AddRazorPages();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
if (_env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
}
Opstartklasseconventies
Wanneer een ASP.NET Core-app wordt gestart, start de opstartklasse de app op. De app kan meerdere Startup klassen definiëren voor verschillende omgevingen. De juiste Startup klasse wordt geselecteerd tijdens runtime. De klasse waarvan het achtervoegsel de naam overeenkomt met de huidige omgeving, krijgt prioriteit. Als er geen overeenkomende Startup{EnvironmentName} klasse wordt gevonden, wordt de Startup klasse gebruikt. Deze aanpak is handig wanneer de app het opstarten voor verschillende omgevingen moet configureren met veel codeverschillen per omgeving. Typische apps hebben deze benadering niet nodig.
Als u omgevingsklassen Startup wilt implementeren, maakt u een Startup{EnvironmentName} klassen en een terugvalklasse Startup :
public class StartupDevelopment
{
public StartupDevelopment(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
Console.WriteLine(MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod().DeclaringType.Name);
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
}
public class StartupProduction
{
public StartupProduction(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
Console.WriteLine(MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod().DeclaringType.Name);
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
}
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
Console.WriteLine(MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod().DeclaringType.Name);
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
}
Gebruik de UseStartup(IWebHostBuilder, String) overbelasting die een assemblynaam accepteert:
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args)
{
var assemblyName = typeof(Startup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.FullName;
return Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup(assemblyName);
});
}
}
Conventies voor opstartmethoden
Configure and ConfigureServices support environment-specific versions of the form Configure<EnvironmentName> and Configure<EnvironmentName>Services. Als een overeenkomende Configure<EnvironmentName>Services of Configure<EnvironmentName> methode niet wordt gevonden, wordt de ConfigureServices of Configure methode respectievelijk gebruikt. Deze benadering is handig wanneer de app het opstarten voor verschillende omgevingen moet configureren met veel codeverschillen per omgeving:
public class Startup
{
private void StartupConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
}
public void ConfigureDevelopmentServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
MyTrace.TraceMessage();
StartupConfigureServices(services);
}
public void ConfigureStagingServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
MyTrace.TraceMessage();
StartupConfigureServices(services);
}
public void ConfigureProductionServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
MyTrace.TraceMessage();
StartupConfigureServices(services);
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
MyTrace.TraceMessage();
StartupConfigureServices(services);
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
MyTrace.TraceMessage();
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
public void ConfigureStaging(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
MyTrace.TraceMessage();
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
}
public static class MyTrace
{
public static void TraceMessage([CallerMemberName] string memberName = "")
{
Console.WriteLine($"Method: {memberName}");
}
}
