Choose appropriate data types
SQL Server offers a wide variety of data types, and your choice can significantly impact performance. While SQL Server can automatically convert some data types (known as 'implicit conversion'), this process can be costly and negatively affect query plans. The alternative is explicit conversion, where you use the CAST or CONVERT function in your code to force a data type conversion.
Also, choosing data types that are larger than necessary can lead to wasted space and require more pages to be read. It's crucial to select the appropriate data types for your data, as this will reduce the total storage required for the database and improve query performance.
Note
In some cases, conversions aren't possible at all. For example, a date can't be converted to a bit. Conversions can negatively impact query performance by causing index scans where seeks would have been possible, and extra CPU overhead from the conversion itself.
The following image indicates in which cases SQL Server can do an implicit conversion and in which cases you must explicitly convert data types in your code.
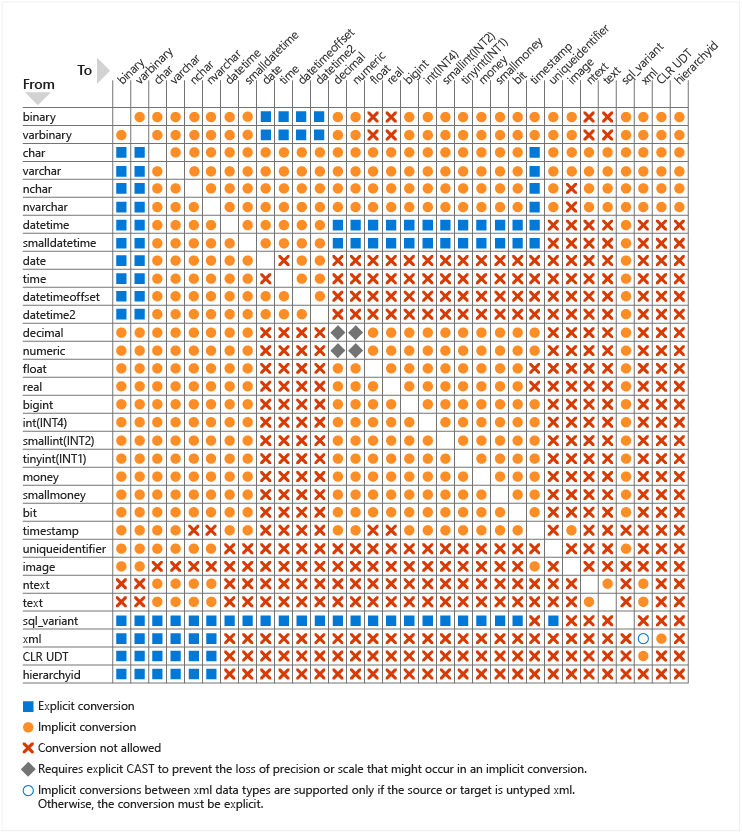
SQL Server provides various system-supplied data types that can be used in your tables and queries. Also, SQL Server allows the creation of user-defined data types using either T-SQL or the .NET framework.