Configure tables
You're ready to enhance its design when your model contains the required tables and columns and the relationships are configured. You enhance the model by setting properties of model objects, like tables and columns. You can also create new model objects, like hierarchies, measures, and parameters.
Configure table properties
Power BI Desktop provides you with choice when creating model objects and setting their properties. You can use the ribbon, the Data pane, or the model diagram and its associated Properties pane. Typically, it's easier to work in Model view and use the Properties pane because it supports multi-select and bulk property updates.
Every model table has a Name property, which allows you to rename it. Its name is always inherited from the Power Query query name. So, if you rename a table in Power BI Desktop, the Power Query name is updated. Model table names must be unique in the model, and you should strive to set user-friendly names.
A model table also has a Description property, which is optional. It allows you to set a detailed definition of the table that appears when report authors hover their cursor over the table in the Data pane.
The Synonyms property allows you to set one or more alternative names for the table, so that Q&A or Copilot can better understand and resolve requests made to automatically generate visuals or DAX formulas.
A model table can be hidden, in which case it's not listed in the Data pane (unless the report author expressly wants hidden objects to be shown). You should hide model objects that shouldn't be used directly by report authors. For example, you should hide a bridging table used to support a many-to-many relationship between dimension tables, like the SalespersonRegion table described in the previous unit.
Mark date tables
By default, Power BI includes an Auto date/time feature to support time intelligence. When enabled, it creates hidden date tables for each column that has a date or date/time data type.
While this option might be useful for novice data modelers or experimentation, it's better to disable it. You can use an existing source data table or create a calculated table with DAX. Each date table in your model should contain a column of dates and be marked as a date table. That way, DAX time intelligence functions return appropriate results.
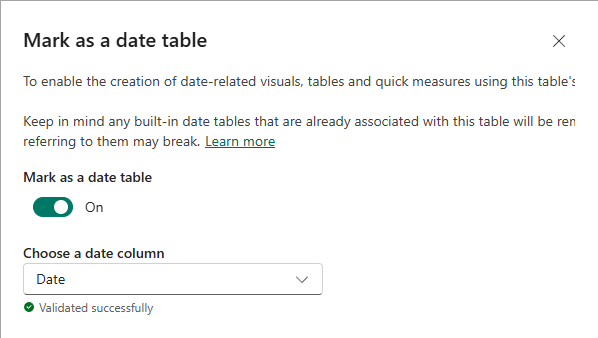
Marking a date table involves selecting the column that contains date values.
Power BI Desktop performs validations to ensure that the date column you select contain unique values, no BLANKs, and comprises contiguous values from beginning to end.