Exercise - Create an ASP.NET Core web app project from a template
In this exercise, you will:
- Create an ASP.NET Core web app project from a template.
- Examine the structure of the created project.
Create an ASP.NET Core web app using a template
In Visual Studio Code, create a new project:
Select the Explorer view:
Select the Create .NET Project button. Alternatively, you can bring up the Command Palette using Ctrl+Shift+P, and then type "
.NET" to find and select the .NET: New Project command.
Select the ASP.NET Core Empty project template from the list.
In the Project Location dialog, create a folder named
MyWebAppto contain the project.In the Command Palette, name the project
MyWebApp, including matching the capitalization. Using this exact project name is important to ensure that the namespaces for code in this instruction match yours.Select Create project from the Command Palette.
Examine the structure of the project
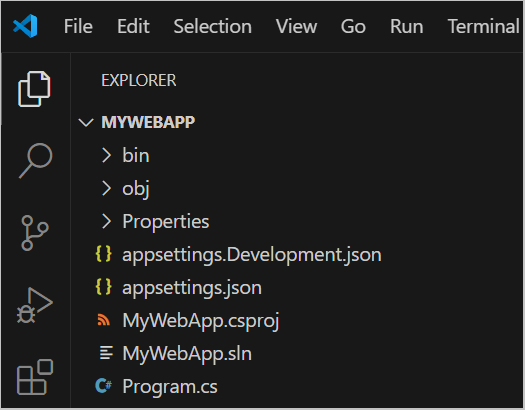
The MyWebApp project folder contents are displayed in the Visual Studio Code Explorer:
From a terminal or the command line, create a new project:
Change to the directory (
cd) that's going to contain the project.Create an ASP.NET Core web app in a directory named MyWebApp by running the .NET CLI command
dotnet new:dotnet new web -o MyWebAppA new ASP.NET Core empty web project is created in a directory named MyWebApp.
The following outlines the command syntax:
dotnet new: A .NET CLI command for creating various .NET development artifacts based on templates such as projects, solutions, libraries, configuration, and other specialized files.web: A project template used to create an ASP.NET Core empty web project, containing no example content.webis one of the many built-in project templates available in the .NET SDK.-o: The output option specifies the directory where the new project is created:- If the directory doesn't exist, the .NET CLI creates it.
- The directory where the project is created serves as the default project name, namespace, and assembly name (the name of the compiled output).
- If the output option
-o <directory>isn't used, then the current directory is used.
Open the MyWebApp project folder.
Examine the structure of the project
The MyWebApp project folder contents are displayed in the Visual Studio Code Explorer:

The following sections contain an overview of the main project folders and files of the empty ASP.NET Core project:
The MyWebApp.csproj project file
The .csproj project file is used to:
- Configure how to build the project
- Specify which version of .NET to target
- Manage project dependencies
The .sln solution file
When an ASP.NET Core project is created or opened in Visual Studio Code (with the C# Dev Kit extension), it creates a [project name].sln solution file. The [project name].sln solution file contains information for one or more related projects, including build information, settings, and any miscellaneous files that aren’t associated with just one particular project.
The obj folder
The obj folder contains intermediate files that are used by the build system, including compiled object files generated from the source files. The final build output is placed in a bin folder created during the build process.
The Properties/launchSettings.json file
The Properties/launchSettings.json file contains configuration data for how the app is launched during development. These settings include the applicationUrl property, which specifies the root URL the app uses, such as https://localhost:{port}, where {port} is a random local port number assigned when the project is created.
The launchSettings.json file contains the following configuration:
{
"$schema": "https://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.json",
"profiles": {
"http": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5218",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"https": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:7140;http://localhost:5218",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
}
}
The Program.cs file
The Program.cs file serves as the entry point for an ASP.NET Core app and has several key purposes, which include:
- Host configuration: Configures the host, including setting up the web server.
- Service registration: Adds services to the app’s functionality, such as database contexts, logging, and specialized services for specific frameworks.
- Middleware pipeline configuration: Defines the app’s request handling pipeline as a series of middleware instances.
- Environment configuration: Sets up environment-specific settings for development, staging, and production.
In the new empty ASP.NET Core project you created, the Program.cs file contains the following minimal code:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.Run();
The following lines of code in this file create a WebApplicationBuilder with preconfigured defaults, and builds the app:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var app = builder.Build();
The app.MapGet() method directly defines an endpoint that handles HTTP GET requests:
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.MapGet("/"): Defines a route for the HTTP GET request. The / indicates this route responds to the requests made to the root URL of the app. For example, http://localhost:{port}/, where {port} is a randomly assigned port number assigned in the Properties/launchSettings.json file at project creation.
() => "Hello World!": A lambda expression that serves as the request handler. When a GET request is made to the root URL, this lambda expression is executed, and it returns the string "Hello World!"