Create a cloud flow by using an instant, automated, or scheduled trigger
This learning unit guides you through the different types of triggers available in Power Automate. You learn how to create instant flows, set up automated flows that respond to external events, and design scheduled flows for recurring tasks.
Understanding triggers in Power Automate
In Power Automate, a trigger is the event that initiates a cloud flow. Think of it as the starting point or signal that tells your flow to begin executing its actions. Power Automate provides three main types of triggers, each tailored to different use cases:
Instant Triggers: These triggers are manually activated by the user. For instance, you might use an instant trigger to send a quick reminder email with just a button click.
Automated Triggers: These triggers are event-driven and activate automatically when something specific happens. For example, you could set up an automated trigger to notify you whenever you receive an email from a particular sender.
Scheduled Triggers: These run flows at regular intervals based on a predefined schedule. A common use case might be generating a weekly report every Monday morning.
Choosing the right type of trigger depends on the nature of the task you want to automate. For example, if you need to monitor social media activity, an automated trigger could notify you whenever someone tweets using a specific hashtag.
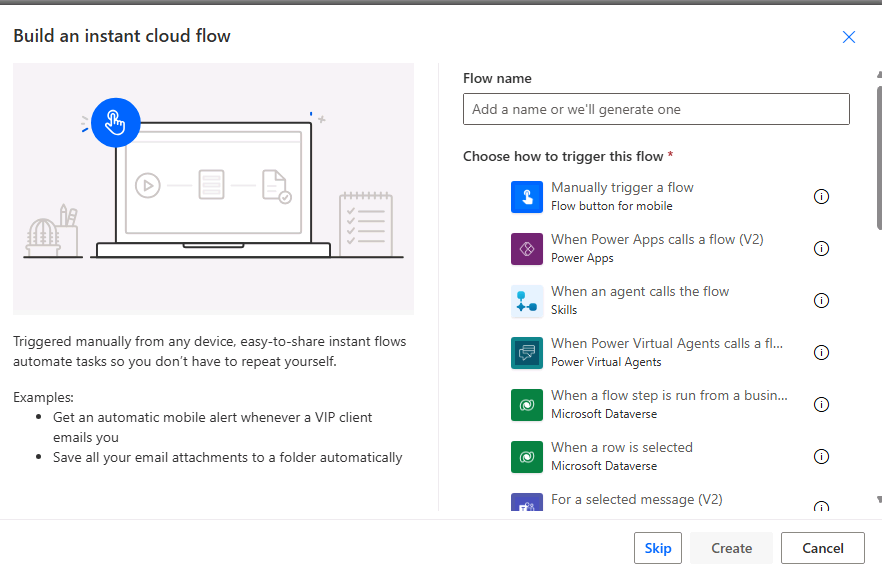
Creating an instant flow: An instant flow is designed to execute tasks immediately upon a manual trigger, making it ideal for scenarios where users need on-demand automation. For example, you could associate an instant flow with a device such as a flick button. When the button is pushed, it launches the flow.
To create an instant flow, start by selecting the "Instant cloud flow" option in Power Automate. You need to select how to trigger the flow: "Manually trigger a flow," or "When Power Apps calls a flow," which allows users to initiate the process with a button click. For example, you could create an instant flow that sends a prewritten email to a team when a project milestone is achieved. Once the trigger is set, define the subsequent actions, such as sending notifications, updating records, or generating reports. This type of flow is perfect for tasks requiring user intervention to start the process.
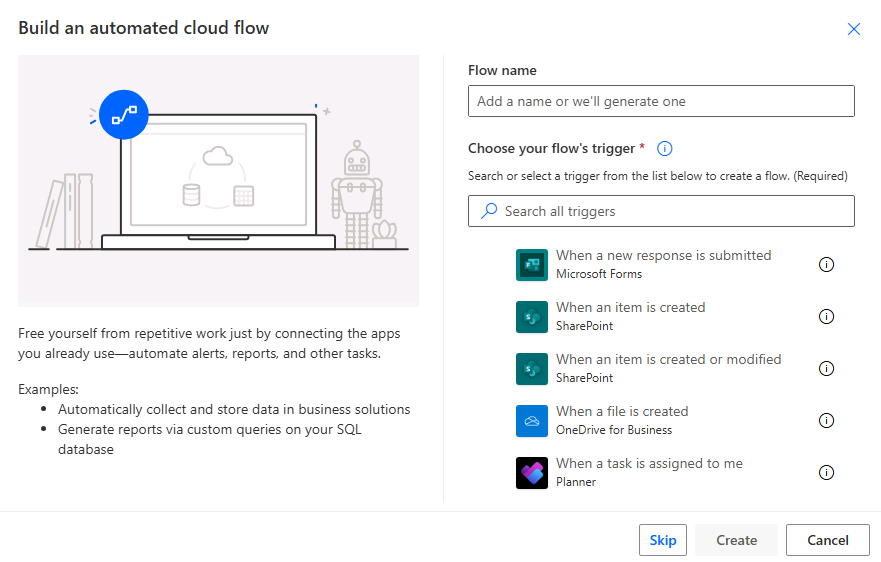
Creating an automated flow: Specific events or conditions trigger automated flows, making them ideal for streamlining repetitive tasks. To create an automated flow, select the "Automated cloud flow" option and choose a trigger based on the event you want to monitor. For instance, you might use the "When a new email arrives" trigger to automatically save email attachments to a designated folder. After selecting the trigger, define the actions that should follow, such as creating a task, updating a database, or sending a notification. Automated flows are useful for improving efficiency by eliminating the need for manual intervention in routine processes.
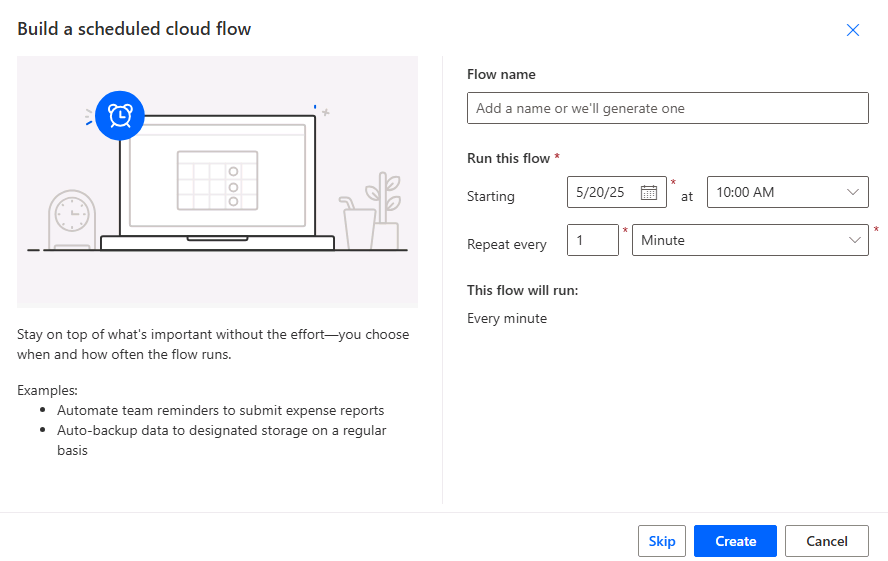
Creating a Scheduled Flow: Scheduled flows run at predefined intervals, making them perfect for recurring tasks like data backups or report generation. To create a scheduled flow, select the "Scheduled cloud flow" option and specify the frequency and timing for the flow to run, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. For example, you could set up a scheduled flow to generate and email a sales performance report every Monday morning. Once the schedule is configured, add the necessary actions, such as querying data, compiling reports, or sending reminders. Scheduled flows ensure consistency and reliability for time-sensitive tasks without requiring manual oversight.
By understanding the different types of triggers, you're better equipped to design flows that align with your specific needs, whether it's responding to real-time events, running tasks on demand, or scheduling recurring processes.