Exercise - Refactor your Bicep file to use modules
In this exercise, you'll update the Bicep file you previously created so it uses a module for the Azure App Service resources. Modules help to keep the intention of the main file clearer. You can reuse the App Service module in other Bicep files if you choose to.
During the process, you'll:
- Add a new module and move the App Service resources into it.
- Reference the module from the main Bicep file.
- Add an output for the App Service app's host name, and emit it from the module and Bicep file deployments.
- Test the deployment to ensure that the Bicep file is valid.
Add a new module file
In Visual Studio Code, create a new folder called modules in the same folder where you created your main.bicep file. In the modules folder, create a file called appService.bicep. Save the file.
Add the following content into the appService.bicep file:
param location string param appServiceAppName string @allowed([ 'nonprod' 'prod' ]) param environmentType string var appServicePlanName = 'toy-product-launch-plan' var appServicePlanSkuName = (environmentType == 'prod') ? 'P2v3' : 'F1' resource appServicePlan 'Microsoft.Web/serverfarms@2024-04-01' = { name: appServicePlanName location: location sku: { name: appServicePlanSkuName } } resource appServiceApp 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2024-04-01' = { name: appServiceAppName location: location properties: { serverFarmId: appServicePlan.id httpsOnly: true } }Notice that you've copied the parameters and variables from your main.bicep Bicep file since the appService.bicep Bicep file needs to be self-contained.
Save the changes to the file. Notice that Visual Studio Code doesn't show you any red squiggles to indicate warnings about missing variables, missing parameters, or invalid resources.
Add a reference to the module from the parent Bicep file
Now that you've a complete module to deploy the App Service resources, you can refer to the module within the parent Bicep file. Because the module deploys the App Service resources, you can delete the associated resources and variables from the parent file.
In the main.bicep file, delete the App Service resources and the
appServicePlanNameandappServicePlanSkuNamevariable definitions. Don't delete the App Service parameters, because you still need them. Also, don't delete the storage account parameters, variable, or resources.At the bottom of the main.bicep file, add the following Bicep code:
module appService 'modules/appService.bicep' = { name: 'appService' params: { location: location appServiceAppName: appServiceAppName environmentType: environmentType } }Notice that you're specifying the parameters for your module by referencing the parameters in the parent Bicep file.
Save the changes to the file.
Add the host name as an output
Add the following Bicep code at the bottom of the appService.bicep file:
output appServiceAppHostName string = appServiceApp.properties.defaultHostNameThis code declares that an output for this module, which will be named
appServiceAppHostName, will be of typestring. The output will take its value from thedefaultHostNameproperty of the App Service app.Save the changes to the file.
This output is declared within a Bicep file we'll use as a module, so it's going to be available only to the parent Bicep file. You also need to return the output to the person who deployed the file.
Open the main.bicep file and add the following code at the bottom of the file:
output appServiceAppHostName string = appService.outputs.appServiceAppHostNameNotice that this output is declared in a similar way to the output in the module. But this time, you're referencing the module's output instead of a resource property.
Save the changes to the file.
Verify your Bicep files
After you've completed all of the preceding changes, your main.bicep file should look like this example:
param location string = 'eastus'
param storageAccountName string = 'toylaunch${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}'
param appServiceAppName string = 'toylaunch${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}'
@allowed([
'nonprod'
'prod'
])
param environmentType string
var storageAccountSkuName = (environmentType == 'prod') ? 'Standard_GRS' : 'Standard_LRS'
resource storageAccount 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2023-05-01' = {
name: storageAccountName
location: location
sku: {
name: storageAccountSkuName
}
kind: 'StorageV2'
properties: {
accessTier: 'Hot'
}
}
module appService 'modules/appService.bicep' = {
name: 'appService'
params: {
location: location
appServiceAppName: appServiceAppName
environmentType: environmentType
}
}
output appServiceAppHostName string = appService.outputs.appServiceAppHostName
Your appService.bicep file should look like this example:
param location string
param appServiceAppName string
@allowed([
'nonprod'
'prod'
])
param environmentType string
var appServicePlanName = 'toy-product-launch-plan'
var appServicePlanSkuName = (environmentType == 'prod') ? 'P2v3' : 'F1'
resource appServicePlan 'Microsoft.Web/serverfarms@2024-04-01' = {
name: appServicePlanName
location: location
sku: {
name: appServicePlanSkuName
}
}
resource appServiceApp 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2024-04-01' = {
name: appServiceAppName
location: location
properties: {
serverFarmId: appServicePlan.id
httpsOnly: true
}
}
output appServiceAppHostName string = appServiceApp.properties.defaultHostName
If either Bicep file doesn't match, copy the example or adjust your file to match the example.
Deploy the updated Bicep file
Run the following Azure CLI command in the terminal.
az deployment group create \
--name main \
--template-file main.bicep \
--parameters environmentType=nonprod
Run the following Azure PowerShell command in the terminal.
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment `
-Name main `
-TemplateFile main.bicep `
-environmentType nonprod
Check your deployment
In your browser, go back to the Azure portal. Go to your resource group; there are now two successful deployments.
Select the 2 Succeeded link. Notice that you have a deployment called main in the list, and a new deployment called appService.
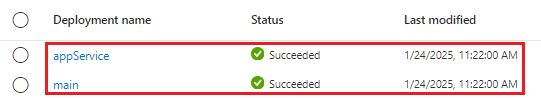
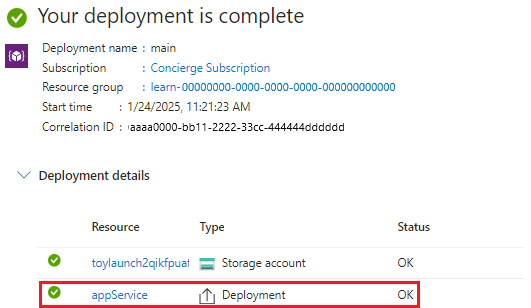
Select the deployment called main, then select Deployment details to expand the list of deployed resources.
Notice that our module deployment appears in the list.
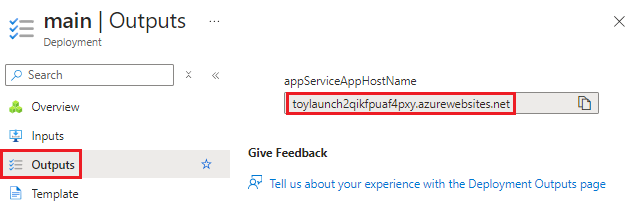
Select the Outputs tab. Notice that there's an output called appServiceAppHostName with the host name of your App Service app. Copy the host name to your clipboard.
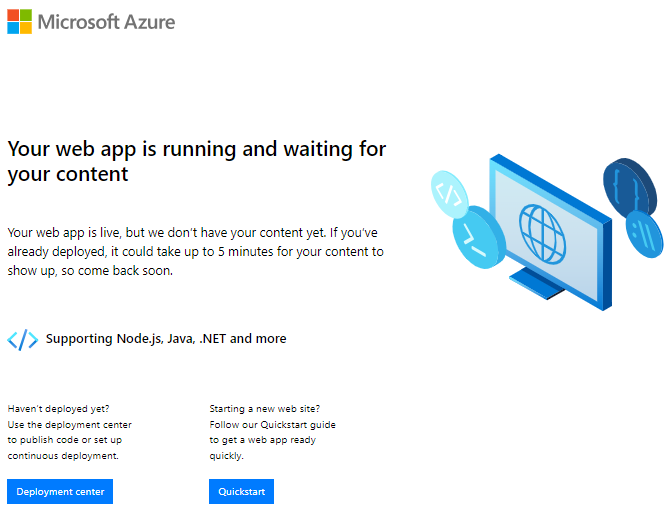
Open a new browser tab and paste the host name that you copied. You should see the default App Service welcome page.
Congratulations! You've successfully deployed the foundations for a great app.