Lessen cognitive load
Cognitive load is the mental effort exerted to complete a task. Cognitive Load Theory is comprised of three components: intrinsic load, extraneous load, and germane load. With only finite space in the working memory, managing the cognitive load of a task helps a learner transfer information from their working memory into their long-term memory.
Learners undergo a process to acquire and utilize new knowledge. First, learners input information. They briefly move it to the sensory memory (hearing, seeing) and then into working memory. Working memory has limited capacity and is considered the gatekeeper to long-term memory. Working memory is affected by multiple factors, including emotion, attention, motivation, and interest. If information remains in the working memory long enough, it's transferred to the long-term memory. Knowledge is then available for retrieval from the long-term memory.
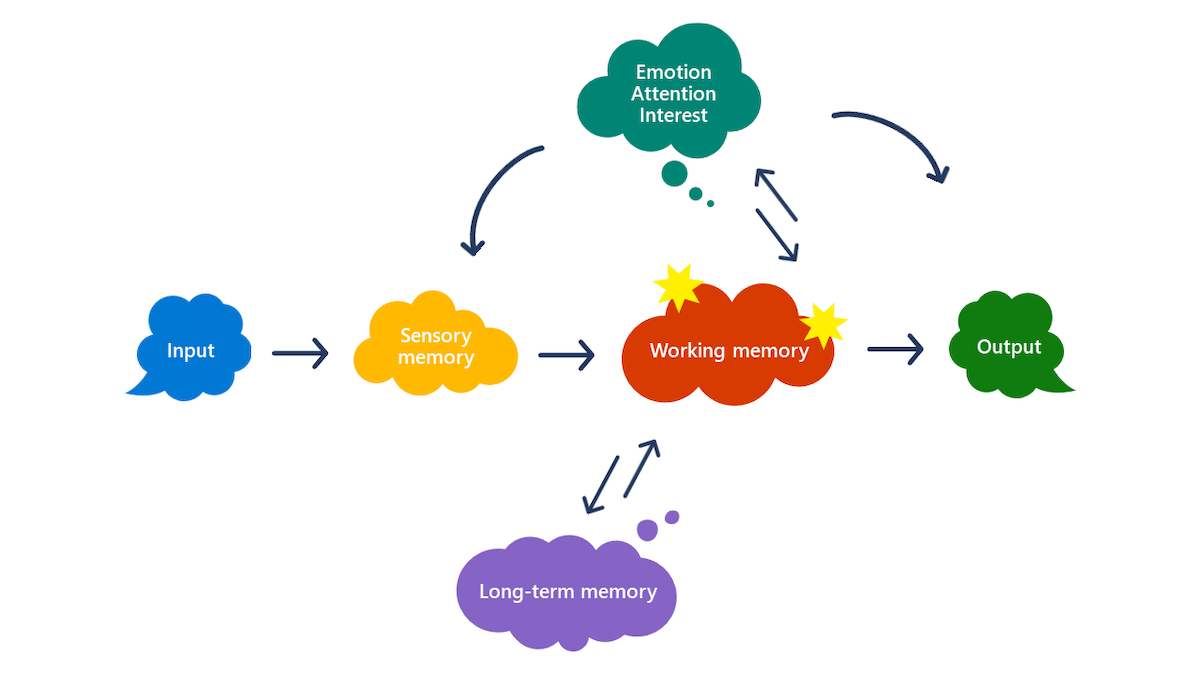
Graphic showing arrows pointing to and from bubbles with words in them. Starting on the left the word input points to sensory memory, which points to working memory, which points to output on the far right. Working memory has arrows pointing up to and from emotion attention interest at the top, which also has arrows pointing down/left to sensory memory and down right to output. Working memory also has arrows pointing down to and from long-term memory.
Intrinsic load is the core content or elements of a learning task-the things the learner needs to know. If these elements are changed, then the learning outcomes of the task are changed. The complexity of the task also determines how high the intrinsic load of the task is. Extraneous load is elements in the learning task that aren't related to the learning task and can be a distraction. Mental effort is moved away from the intrinsic load to the extraneous load and impacts learning.
Consider how to utilize Microsoft tools to reduce cognitive load:
OneNote: Learners have a clearly organized and defined set of materials in OneNote. Everything needed is in one place, decreasing the extraneous load and split attention of having to find and coordinate materials in multiple locations. Students have multiple means of engaging in tasks using additional tools including digital inking, dictation, audio and video recording, and drag and drop to name a few.
Focus Mode: Reduce distractions from extraneous notifications with Focus Mode. For learners who struggle with maintaining focus, Focus Mode promotes dedicated attention to the required task.
Speech to Text: Writings tasks are complex and involve the intersection of critical thinking skills. Utilize Speech to Text to reduce the cognitive load or simply to aid students who are more comfortable applying their oral language skills with the generation of ideas.
For learners with differing needs consider how to reduce barriers to learning, like cognitive load. Utilize Microsoft applications to streamline access to content and demonstration of learning. Bring learners’ attention back to the content and learning.