Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Rabobank, a multinational banking and financial services company based in the Netherlands, is committed to growing a better world together. As part of this mission, Rabobank has embraced conversational banking—prioritizing friendly and efficient customer service on demand, in alignment with the company's principles of cooperation and putting people first.
In this case study, you learn how to:
- Use Copilot Studio to assist bank customers
- Continuously improve intent recognition
- Anonymize customer conversations for testing
- Use generative AI features and stay compliant
- Integrate Azure AI Speech service with Copilot Studio
Business challenges
Rabobank started to explore chatbot functionality for customer self-service to improve efficiency and lower operational costs. With rising customer expectations and increased inquiries, the bank needed a chatbot to answer common customer questions.
Initially, Rabobank set up text- and voice-enabled chatbot functionality on another platform, partly on-premises, and relied on vendors for implementation and maintenance.
However, this solution presented several challenges:
Inefficiency: Chat and voice systems had to be updated with new conversations and logic separately. Even when the systems used the same information and models, they required separate updates.
Slow to market: The platform required specialized developer support, which slowed innovation and time to market.
Integration complexity: The chatbot was hard to integrate with external systems and APIs, a requirement to obtain the right output for agent conversations and make agents actionable, including to support end-to-end processes.
We needed a flexible platform that could integrate with external APIs, transforming our chatbot into a true financial assistant. We wanted one conversational platform to manage all chatbots and to optimize it ourselves.
— Chris den Arend, Solution Architect, Rabobank
Solution
Rabobank turned to Microsoft Copilot Studio. They used Copilot Studio to create three Copilot Studio agents for customer self-service, one voice-enabled agent and two text-based agents. The text-based agents focus on business banking and supporting retail customers.
Customers either call the bank or start a chat. During a call, the agent asks why they're calling, performs intent recognition, and routes the caller to the correct live agent.
For text-based conversations, an intent recognition process identifies and routes queries to Copilot Studio topics, which are designed to solve complete processes like blocking a credit card.
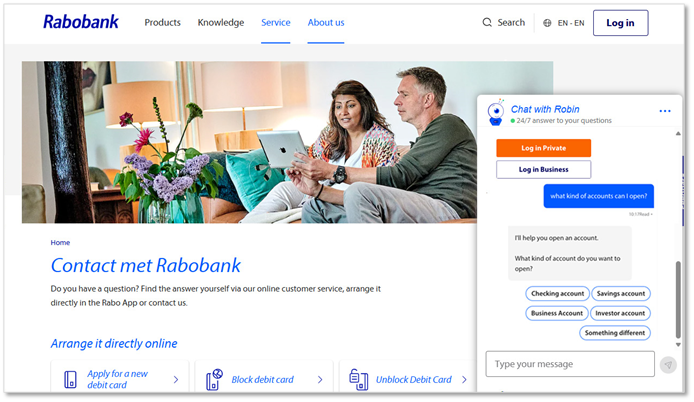
The following image shows the text-based agent embedded on Rabobank's website.
Implementation approach
Rabobank migrated from its previous platform to Copilot Studio. The implementation included migration of topics. Setting up the Copilot Studio agents was a straightforward process, with the text-based agents created and deployed within just three months.
To provide escalation to human live agents, Rabobank chose Genesys Cloud. With no native integration between Genesys Cloud and Copilot Studio, the team built custom middleware to bridge the gap.
Specific processes were integrated with APIs, mainly using Power Automate and HTTP calls. For customer inquiries that can't be solved, fallback topics are invoked, which rely on generative AI.
Challenges faced during implementation included improving intent recognition, managing communication between Genesys Cloud and Copilot Studio, and overcoming barriers related to using generative AI features.
Intent recognition
Rabobank finds intent recognition essential for creating successful agents. If the voice-enabled agent doesn't understand the intent, it might route the call to the wrong advisor. Similarly, a text-based agent that doesn't understand the customer's intent isn't able to help that customer.
Rabobank plans to work on improving intent recognition and put a process in place to find areas for improvement and methods to properly test the changes.
The intent recognition process includes:
- Genesys Cloud and Pega Business Rules
- An external intent catalog, based on TIBCO EBX
- Copilot Studio topics and specified trigger phrases
- Escalation to the appropriate live agent's queue for the voice-enabled chatbot
All calls and text inquiries start in Genesys Cloud. The voice-enabled agent focuses on intent recognition to route calls to the correct team, whereas the text-based agent solves more end-to-end processes.
For the two text-based agents, there are 300 to 400 topics, and the intent recognition process is similar to the voice-enabled agent. The chat first goes to Genesys Cloud, then to the Copilot Studio agent. Based on intent, the customer's question is redirected to a path in the agent designed to solve entire end-to-end processes, such as blocking a credit card.
Genesys Cloud and Copilot Studio integration
Genesys Cloud and Copilot Studio lack native interoperability, so Rabobank uses custom-built middleware to manage communication. For text-based agents, a Java application manages translation between the systems. For voice-enabled agents, AudioCodes handles translation, while Azure Speech to Text and Text to Speech process the interaction.
Rabobank plans to strengthen its voice branding by making their voice-enabled bot sound more natural. They're exploring the possibility of using a voice that is a good fit for their brand. The process involves inviting the chosen individual into a studio to create a synthetic voice, which will then be integrated into Azure AI Speech services.
Generative AI features
To meet regulatory requirements, Rabobank hasn't yet adopted the built-in generative AI features of Copilot Studio. Instead, they continue to use classic orchestration and have developed an alternative approach for using generative AI.
Their decision is driven by three key factors:
Platform compliance: Enabling generative AI features while maintaining compliance proved complex, requiring involvement from dedicated security personnel whenever new features were introduced.
Scalability: They faced challenges in efficiently integrating rabobank.nl as a knowledge source, given its 8,000+ URLs. Using Bing Search Service isn't viable because it stores data outside their region.
Quality control: Ensuring reliable output before production, including model evaluation, was difficult, making it challenging to maintain a high level of quality.
Rabobank uses generative AI in their fallback topics when the agent can't answer a question. However, the setup resides outside Copilot Studio.
They currently use Azure AI Foundry to deploy AI models, within their own Azure subscription to ensure compliance, which is important to Rabobank. To use generative AI in SaaS (Software as a Service) products, certain approvals are required. Deploying models in their own Azure subscription is a more efficient way to use generative AI.
An Azure Function is called from the agent's fallback topic, through an HTTP call, including the conversation ID and bot ID. It performs the following functions:
- Retrieves the transcript.
- Sends the transcript to Azure OpenAI to get the user inquiry from the transcript.
- Sends the user inquiry and their own data to Azure OpenAI.
- Gets a response back and the agent responds to the user.
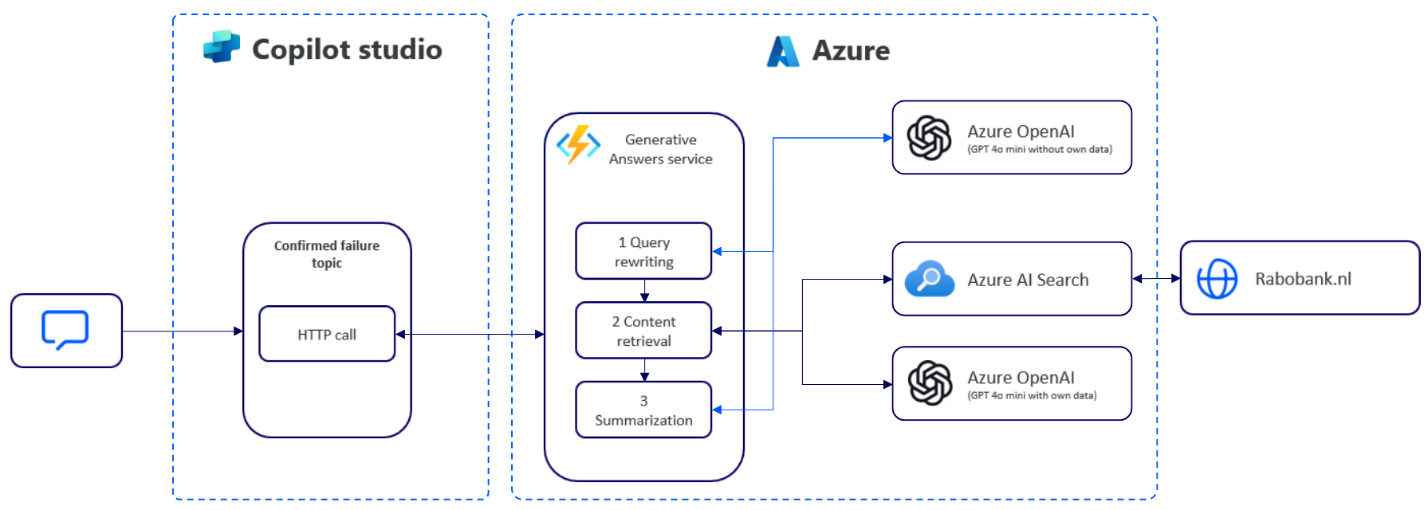
This setup includes Azure AI Search for indexing content from Rabobank's website. The following image illustrates the process.
Rabobank uses an alternative approach to get the correct data from their website for the agent. They scrape their website daily using a custom Python-based solution that includes four steps:
- Create new Azure AI Search index.
- Get and filter website data so old irrelevant pages aren't used.
- Clean the data with OpenAI, model: text-embedding-ada-002.
- Add data to Azure AI Search.
The Copilot Studio agent uses Azure AI Search for retrieving their filtered website information, which provides more accurate retrieval of information while staying compliant. The following image illustrates the approach.
Test strategy
Rabobank uses Power BI to analyze transcripts and identify areas for optimization. When they update or merge trigger phrases, they validate the changes before moving to production. For validation, they use real conversations. The process involves taking a list of customer inputs (questions), anonymizing them, and testing the changes with those conversations to check if intent recognition improves.
Testing is conducted in multiple ways, including using a self-built tool designed to verify the accuracy of virtual agents. The tool accepts large sets of trigger phrases and checks if the correct topics are triggered and the desired responses are generated.
Technologies used
This solution uses the following technologies:
- Power Platform:
- Microsoft Copilot Studio as the agent platform
- Power Automate to connect to external APIs through HTTP calls
- Power BI to track conversation success
- Azure services:
- Azure AI Search for more accurate information retrieval from Rabobank's website
- Azure AI Foundry as a compliant generative AI enabler that uses specific AI models
- Azure AI Speech service for the voice-enabled agent
Architecture
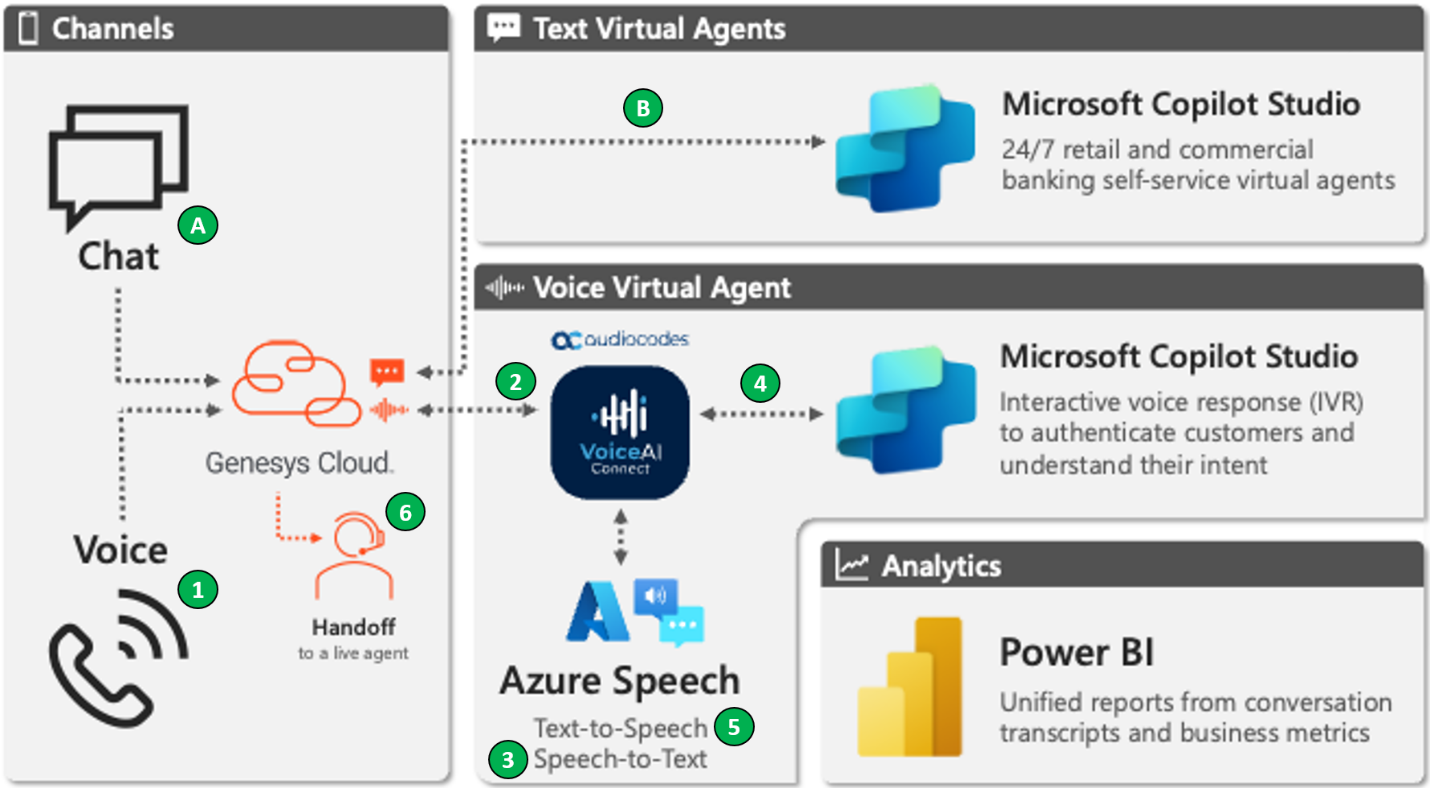
Rabobank's conversational AI architecture integrates several Microsoft technologies to streamline customer interactions across chat and voice channels. Genesys Cloud lets initial chat contacts escalate to live agents, while voice interactions use Azure Speech for text-to-speech and speech-to-text features.
Microsoft Copilot Studio manages both text and voice virtual agents, offering 24/7 self-service and interactive voice response (IVR) features for authentication and intent recognition. Power BI provides unified analytics, tracking conversation transcripts and business metrics to help deliver efficient, high-quality customer service.
For voice-enabled interactions:
- A customer calls and the call lands in Genesys Cloud.
- The conversation redirects to the Copilot Studio agent. AudioCodes manages translations.
- Azure Speech-to-Text translates the message.
- The Copilot Studio agent authenticates the customer and manages intent recognition. The conversation is labeled by intent.
- The text output from the agent is converted into speech using Azure Text-to-Speech before it's delivered to the customer.
- In Genesys Cloud, Pega Business Rules use parameters (like business area and intent in the external intent catalog) to determine to which live agent queue to redirect the conversation.
For text-enabled interactions, the process is similar. A customer starts a chat and it lands in Genesys Cloud (A). The chat redirects to the Copilot Studio agent, which uses topics for intent recognition and management of end-to-end processes (B). Fallback topics use generative AI to better answer customer inquiries (not shown).
Key takeaways
Rabobank's transition to Microsoft Copilot Studio demonstrates how you can use Copilot Studio and other Microsoft technologies to set up agents for chat and voice scenarios. Here are some key takeaways for IT professionals who are considering implementing a similar solution:
- Set up a process to improve your agents' intent recognition.
- Establish a robust test strategy. Use anonymized user queries.
- Consider different approaches when seeking approvals to use generative AI in SaaS products.
With the migration to Copilot Studio, Rabobank has improved customer experience through faster response times and more accurate answers:
- 20,000 daily calls and 7,000 daily chats
- 62 percent self-service rate for chats (that is, not escalated to live agents)
In addition, Rabobank can now manage and update its virtual agents without external help.
We wanted a complete solution with the control, openness, and flexibility to tune it to our detailed needs and differentiate ourselves from virtual assistants in the market, and we found that.
— Chris den Arend, Solution Architect, Rabobank
Looking ahead
Rabobank plans to transition to built-in features for generative AI, while examining how to remain compliant. This includes:
- Testing generative orchestration and verifying that it improves recognition.
- Using generative answers for questions that use Rabobank's knowledge bases.
- Connecting generative actions with the bank's systems and APIs.
- Exploring future options in Copilot Studio, such as bringing in their own model.
Other improvement areas include adding:
- Azure AI Search as a knowledge source in the agent instead of Azure Function.
- More knowledge sources.
- A custom voice for the voice-enabled chatbot.
- Real-time monitoring of all conversations.
- Functionality to make the chatbot easier to reach on the website.
- First-party voice and IVR capabilities to remove the dependency on AudioCodes.