Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Protecting sensitive data is critical when automating processes with Power Automate. This article explains best practices and actionable steps to secure your data: setting up credentials, managing sensitive variables, controlling access to desktop flows and related components, enforcing data loss prevention (DLP) policies, and capturing audit logs. Follow these guidelines to comply with security standards and safeguard your automation workflows.
Set up Power Automate credentials
Create, edit, and share Power Automate credentials using Azure Key Vault or CyberArk. Use them in desktop flow connections, desktop flows, or network connections.
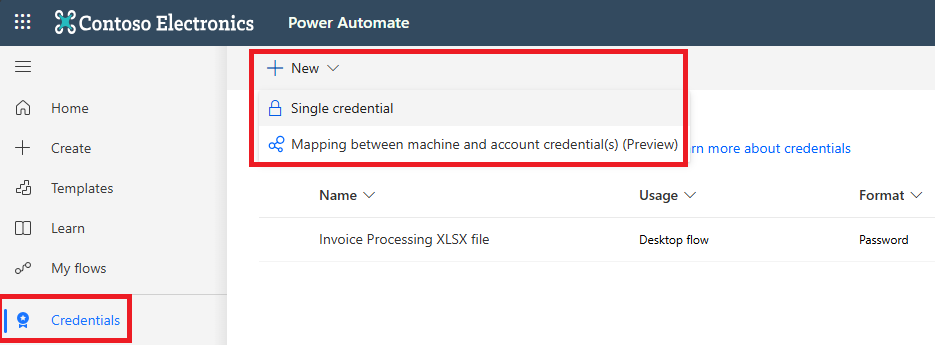
Desktop flow connection: Use credentials in desktop flow connections to sign in to the machine during runtime (attended and unattended runs). Learn more about managing desktop flow connections.
- Create a mapping between machines and user account credentials to sign in to each machine or Windows session with dedicated credentials. Learn more about machine mapping.
- Meet multifactor authentication (MFA) requirements by using certificate-based authentication.
Desktop flow: Use credentials in desktop flow actions to sign in to applications and files. This way, you can enter passwords or sensitive values without keeping sensitive information in the script. For example, SAP credential, SharePoint credential, or Excel password. Learn more about Power Automate secret variables actions.
Network: Use credentials when creating Microsoft Entra hybrid join network connection to connect hosted machine groups to the Active Directory (AD) domain. Learn more about using a custom virtual network for your hosted machine groups.
Tip
- In desktop flows, use the Get credential action to retrieve sensitive values instead of passing them as input variables. This practice ensures credential variables are marked as sensitive by default and aren't stored in the flow run logs.
- Another way to retrieve application or file credentials is through environment variables, using the Dataverse connector's action Perform an unbound action in selected environment in desktop flows. Make sure to mark the output of that action as sensitive. Learn more about using environment variables for Azure Key Vault secrets.
Use sensitive variables
The values of sensitive variables are masked during debugging in the flow designer, and they aren't stored in flow run logs.
Mark as sensitive all variables that store and use sensitive data, including input, output, and flow variables.
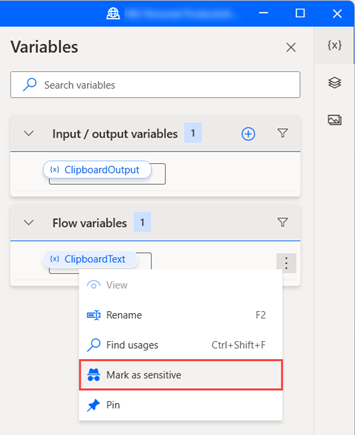
Don't store sensitive values in non-sensitive variables, as sensitivity isn't inheritable (except for credential variable types). For example, don't use a sensitive password variable in a non-sensitive connection string.
Instead of passing sensitive values to the desktop flow as input variables, use the Get credential action. This practice ensures that credential variables are marked as sensitive by default and aren't stored in flow run logs.
Learn more about sensitive variables and using passwords in desktop flows.
Manage access to desktop flows
Any user with access to a desktop flow can have owner, co-owner, or user access.
- To enable other makers to manage your flow and collaborate on it, share it with them with Co-owner access.
- To enable other users to trigger your flow without providing additional access, share it with them with User access.
Note
- Desktop flows are stored in the Process Dataverse table along with other types of flows.
- Users with a Dataverse security role that grants them Read access to all records in the Process table automatically become co-owners of all desktop flows in the environment.
Learn more about managing desktop flows access and managing security for Power Automate.
Manage access to the desktop flow's related components
While sharing a desktop flow that references other Power Platform components, ensure that end users have appropriate access to the connectors as well.
Access is managed either through the dedicated page of each component in the Power Automate Portal or through a Dataverse security role that grants access to the records in the component's table.
The following table lists the most common components that may be referenced by a desktop flow, how to reference them through the flow, the location of their access management settings, and their respective Dataverse tables.
| Component | How to reference component in designer | Access management settings | Dataverse table |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Child) Desktop flows | Use the Run desktop flow action | Share desktop flows | Process |
| Work queues | Use an action from Work queues group of actions | Share a work queue | Work Queue, Work Queue Item |
| Credentials | Use the Get credential action | Share a credential | Credential |
| UI elements collections | Open Assets Library and add the collection | Share a UI elements collection | Desktop Flow Module |
| Custom actions | Open Assets Library and add the custom action | Share custom actions | Desktop Flow Module |
| Connection references | Add a cloud connector action and manage through Connection references | Access is managed through desktop flow sharing. Learn how to share desktop flows that contain connector actions. | Connection Reference |
Tip
Review the list of additional automation-related tables frequently used for reporting and observability.
Enable data loss prevention (DLP) policies
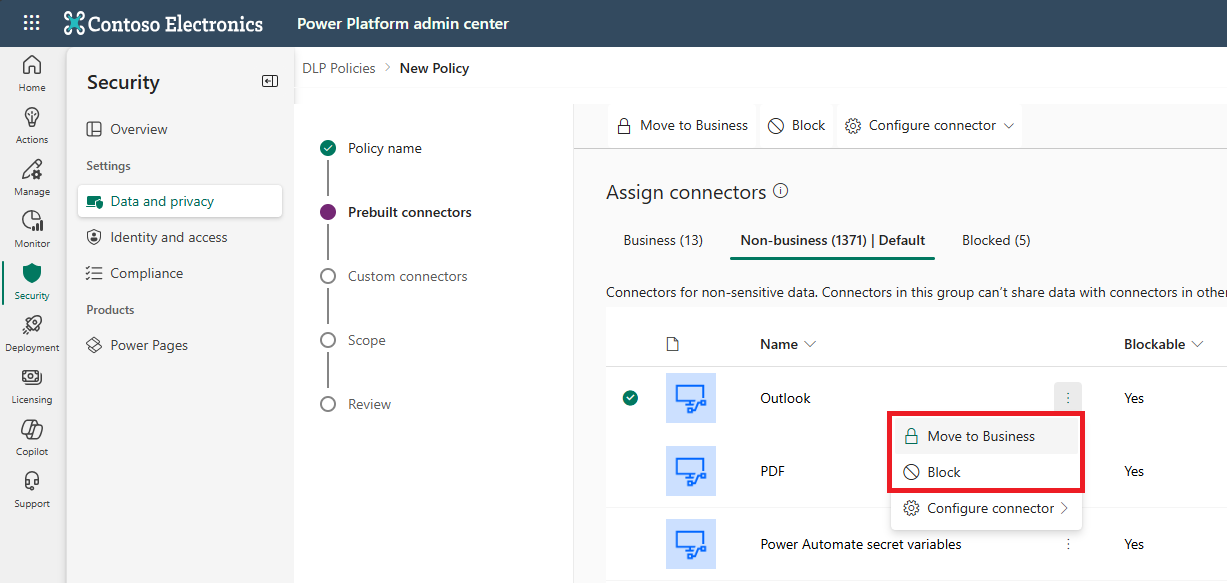
Protect your business data by creating and enforcing policies that classify the desktop flow's action groups as Business or Non-business and to mark actions or action groups as Blocked.
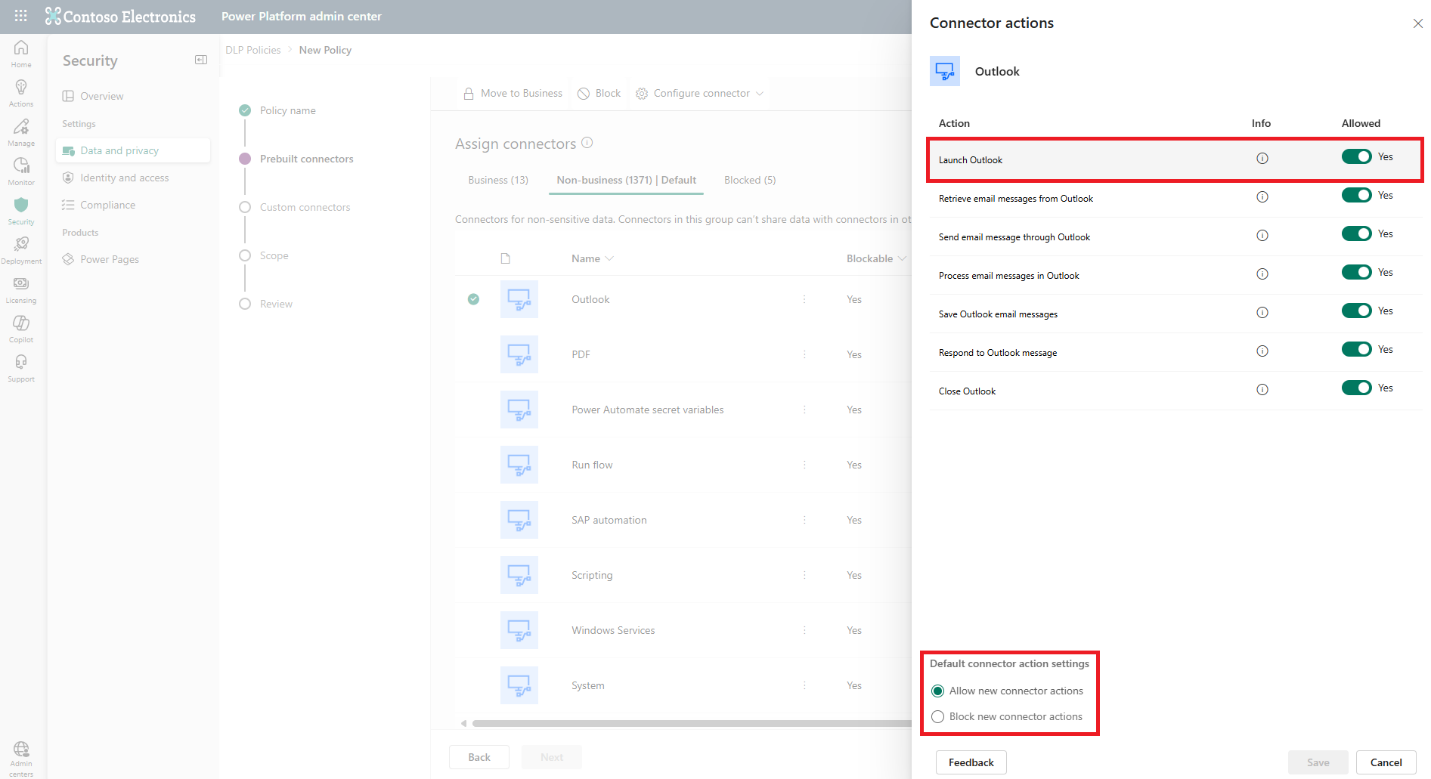
For more fine-grained control, select More actions > Configure connector > Connector actions to allow or block individual actions within a given group. Set the Default connector action settings to allow or block any new connector actions added to the connector in the future.
Learn more about data loss prevention (DLP) policies in desktop flows.
Capture audit logs
Use Dataverse auditing to track changes and access to tables related to desktop flows.
Enable Dataverse auditing at both the environment level and for the specific automation-related tables where you intend to capture logs.
Learn more about managing Dataverse auditing.