Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Data operations in Power Automate allow you to manipulate, transform, and manage data in your automation flows more efficiently, without resorting to complicated code or loops. This article describes the advantages of data operations and provides best practices for using them effectively. Learn more in Use data operations.
The following data operations are available in Power Automate:
- Filter array: Filter an array based on specific conditions.
- Select: Transform the shape of an array by selecting specific fields or properties.
- Join: Combine multiple values into a single string with a specified delimiter.
- Compose: Generate a single output from a given input expression.
- Parse JSON: Parse a JSON string into a structured format for easier manipulation.
- Create HTML table: Convert an array into an HTML table format for easy presentation.
- Create CSV table: Convert an array into a CSV table format for easy export or sharing.
Advantages of using data operations
Using data operations in Power Automate offers several benefits, especially for complex data manipulation tasks.
Efficiency: Data operations are designed to handle data manipulation tasks efficiently, reducing the need for complex expressions and loops.
- The Filter array action lets you quickly filter data based on specific criteria without using conditions and loops.
- The Select action helps you transform the shape of your data by selecting only necessary fields. It simplifies the data structure and reduces the amount of data processed in subsequent steps.
- The Join action combines multiple values into a single string, which is useful for creating summaries or concatenating data for reports or notifications.
Improved data management: Data operations help you manage large datasets more effectively by allowing you to filter, transform, and combine data as needed.
- Actions such as Filter array, Select, Compose, and Parse JSON can be useful when you need to transform and manipulate data from external sources that have no built-in filtering or selection capabilities.
- The Filter array action helps manage large datasets by allowing you to process or analyze specific subsets of data.
- The Select action lets you focus on the essential parts of your data, making it easier to manage and understand. It also helps reduce the payload size when sending data to other systems or services.
- The Join action makes it easier to create readable and formatted strings from arrays for use in emails, reports, or logs, enhancing the clarity and presentation of your data.
Flexibility and customization: Data operations provide flexibility in how you manipulate and transform data, allowing you to customize the output to meet your specific needs.
- The Filter array action offers flexibility in defining complex filtering conditions using logical operators.
- The Select action can help you rename fields and create new structures, allowing for customized data outputs that fit your needs.
- The Join action lets you specify custom delimiters, giving you control over how the combined data is formatted.
Enhanced performance: Data operations can improve the performance of your flows by reducing the amount of data processed and transferred between actions.
- The Filter array action reduces the amount of data processed in subsequent steps, which can significantly improve the performance of your workflows.
- The Select action streamlines data by removing unnecessary fields, which can speed up data processing and reduce the risk of errors.
- The Join action simplifies the process of combining data, making it easier to generate summaries or formatted outputs quickly.
When it's better not to use data operations
While data operations are powerful tools for manipulating and transforming data, they might not be the best approach in every scenario.
When filtering and selecting data at the source is more efficient
When working with data sources such as Dataverse, it's often more efficient to filter and select data at the source rather than using data operations in your flow. For example, if you're retrieving data from Dataverse, you can use the Select columns and Filter rows actions directly in the Dataverse connector to limit the amount of data returned. This approach reduces the need for more filtering and selection steps in your flow, improving performance and reducing complexity.
When using variables is more appropriate
When working with data in Power Automate, you might wonder whether to use variables or data operations. The choice depends on the specific requirements of your flow and the nature of the data you're working with. Here are some guidelines to help you decide when to use variables and when to use data operations.
If you need to store and update data dynamically throughout the flow, using variables is more appropriate than using data operations. Variables are also better suited for maintaining state across different actions and conditions within the flow.
On the other hand, if you need to generate a static output or perform intermediate calculations that don't require updates, using the Compose action is more efficient. Compose is lightweight and doesn't require initialization or declaration, making it faster to set up.
Variables are useful when you need to:
Store and update values: Variables can hold data that might change as the flow progresses, such as counters. They can be updated multiple times, making them ideal for scenarios where data changes dynamically. Variables retain their value throughout the flow, which is useful for performing iterative operations.
Maintain state: Variables help in maintaining the state of data across different actions and conditions within the flow.
Perform calculations: You can use variables to perform arithmetic operations or concatenate strings.
Reuse values: Variables allow you to store a value once and reuse it multiple times throughout the flow, reducing redundancy.
The Compose action is useful when you need to:
Simplify expressions: Simplify complex expressions by breaking them down into smaller, manageable parts.
Store static values: Store values that don't change throughout the flow but need to be read many times.
Perform intermediate calculations: Perform intermediate calculations or transformations that don't need later updates.
Pass data between actions: Pass data between actions without the need to create a variable.
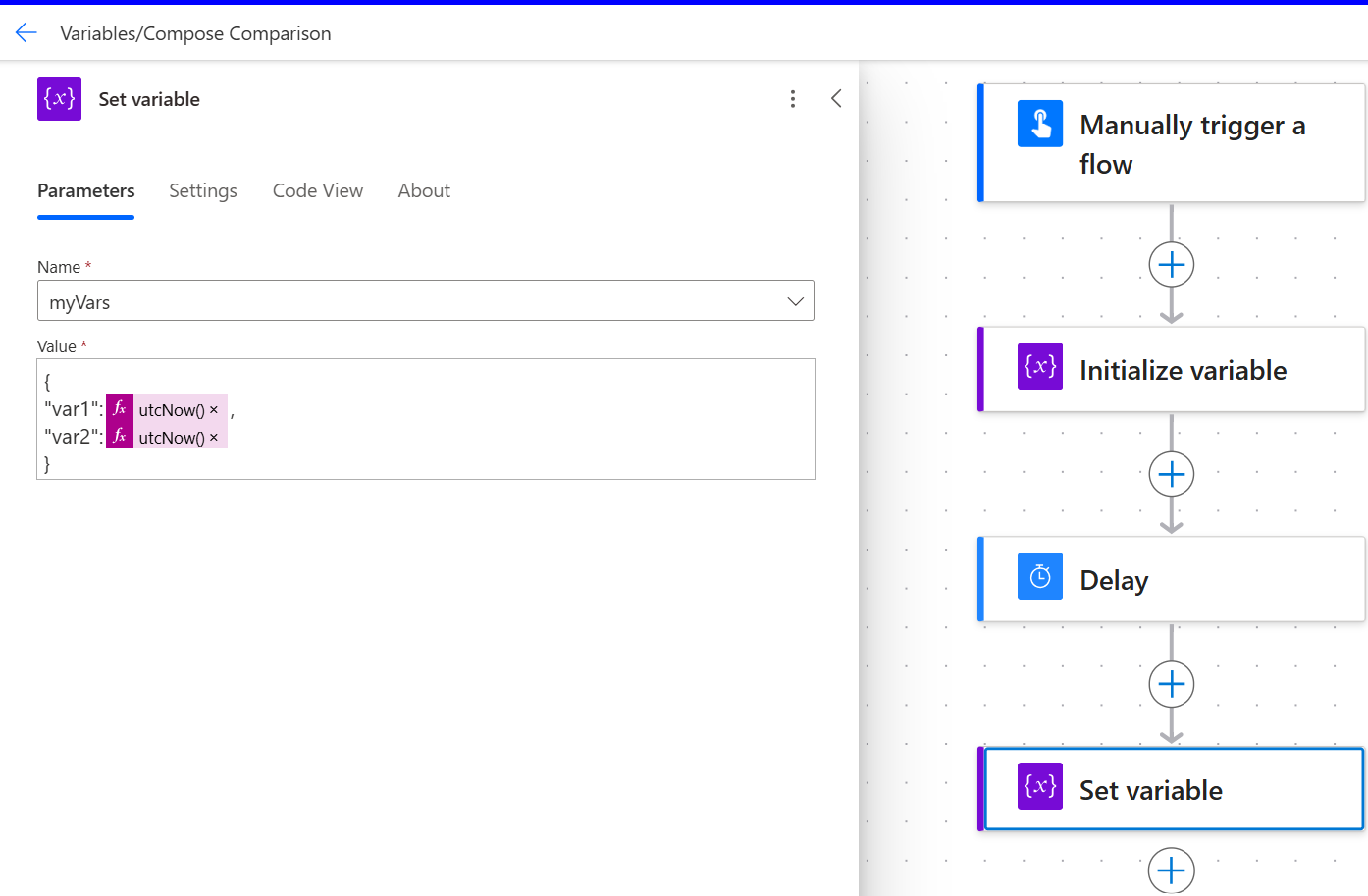
JSON variables vs individual variables
When you're working with a set of variables that are updated within the same logical blocks in the flow, use JSON variables instead of individual variables to reduce the number of actions in the flow.
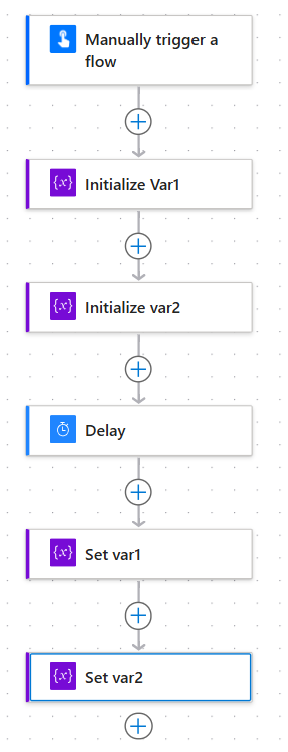
Using separate variables for each value requires multiple actions: two Initialize variable actions and two Set variable actions, adding steps in the flow.
Using a single object variable in JSON format requires one Initialize variable action and one Set variable action, reducing the number of steps in the flow.