Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Teams AI library v2 is available in developer preview. Learn more about the new and improved developer experience, MCP support, and more.
A custom engine agent transforms system interactions. For developers, creating an exceptional user experience is crucial. This article details the steps, principles, and considerations for designing intuitive, user-centered interfaces that seamlessly integrate AI capabilities. The main goals are to simplify complex tasks, enhance productivity, and offer personalized experiences through adaptive learning. A custom engine agent includes features that enhance its functionality and integration within the Microsoft ecosystem:
- Generative AI integration: Uses advanced AI models for natural language processing and interaction.
- Bots: Allows building or extending bots with LLM and generative AI for high-quality chat experiences.
- Customizable orchestration: Provides extensive customization options for tailoring the agent's behavior and responses to specific use cases.
To achieve this, you must follow mandatory requirements and best practices. For more information, see validation guidelines for agents.
Ensure mandatory requirements for custom engine agent
The following requirements are mandatory for building the custom engine agent UX:
- Update the app manifest for custom engine agent.
- Stream the custom engine agent response to the user.
- Ensure the custom engine agent response contains citations.
- Ensure the custom engine agent response contains an AI label.
- Ensure that the custom engine agent is an intelligent conversational bot.
- Ensure that the custom engine agent offers prompt starters or a welcome card.
Note
- AI label, citation, feedback buttons, and sensitivity label are available for bots in personal chats, group chats, and channels.
Update the app manifest for custom engine agent
You must update the app manifest for the custom engine agent to define specific properties and configurations that characterize its capabilities and behavior.
Here's an example for updating the app manifest. You must add the botID property to the copilotAgents node in the app manifest.
App manifest update example:
"bots": [
{
"botId": "00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444",
// ... existing bot node fields
}
],
"copilotAgents": {
"customEngineAgents": [{ // New
"type": "bot", // Only option
"id": "00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444" // Validated against bots node
}]
},
Stream the custom engine agent response to the user
A custom engine agent uses LLM for complex user requests, which may delay responses. To prevent noticeable delays, the agent streams its responses, making them appear fast.

Use the following types of updates while streaming responses:
- Informative updates: Send information on the sub-steps as the agent generates the response before it sends the final response.
- Response streaming: Send the intermediate states of the final response while the LLM creates its full response.
You can use one of the following to stream the response:
- Use Teams AI library to add streaming to the agent.
- Call the Bot Framework APIs directly for streaming.
Note
- Streaming bot messages is available only for one-on-one chats and in public developer preview.
Ensure the custom engine agent response contains citations
Users must know the sources a custom engine agent uses to generate its final response. Identifying these resources allows users to validate and trust the agent's responses.
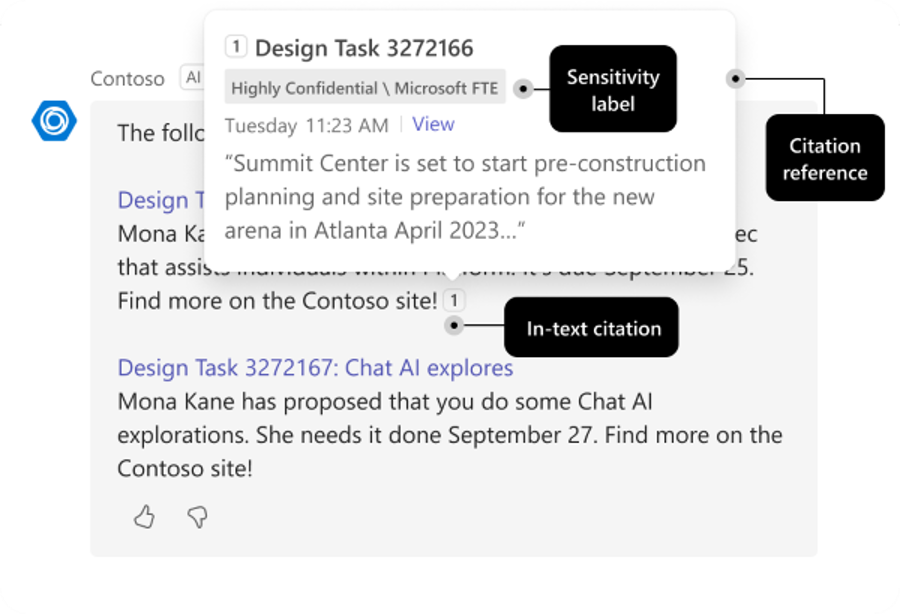
You can use one of the following to include citations for the resources used by the agent:
- Use Teams AI library citations module.
- Incorporate citations into the Bot Framework API calls.
Note
- Citations with Adaptive Cards are available in public developer preview.
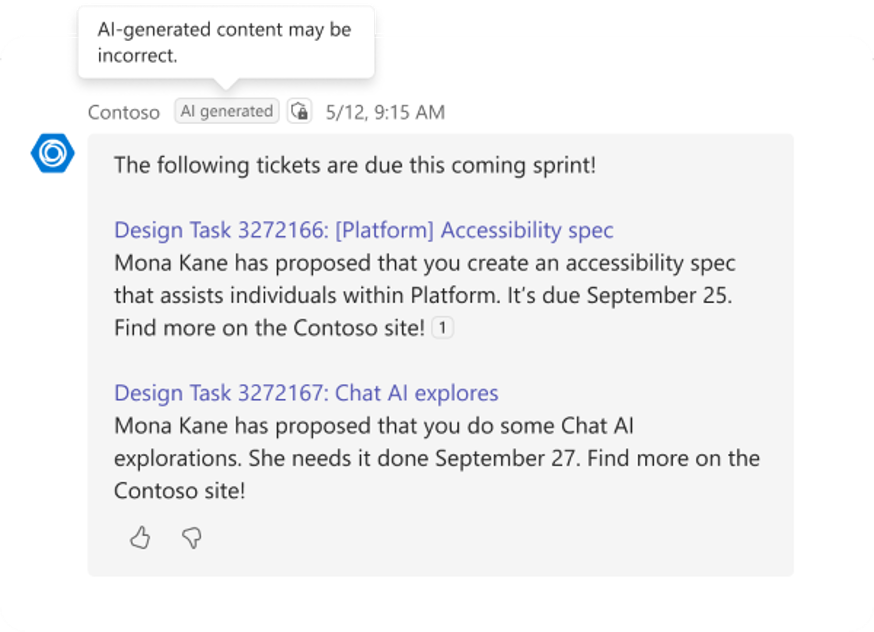
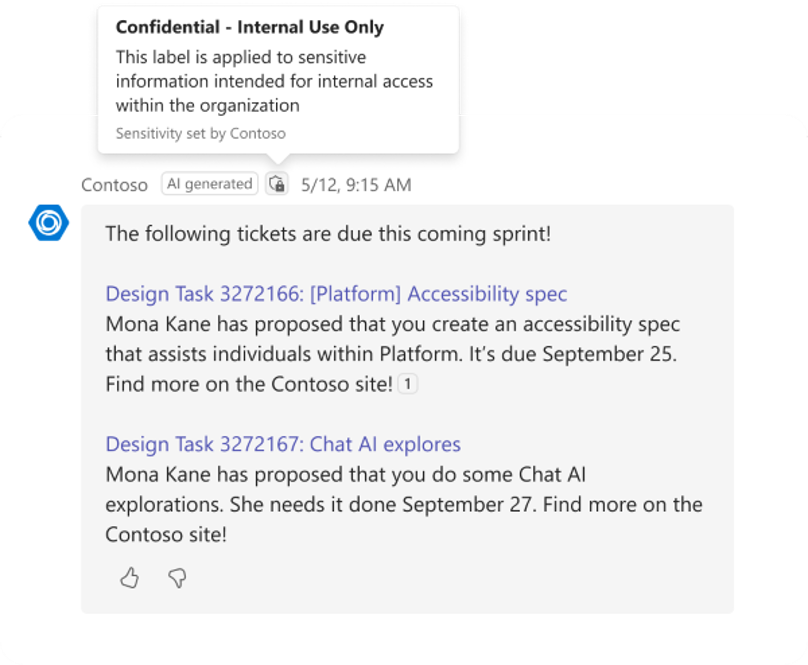
Ensure the custom engine agent response contains an AI label
A custom engine agent must identify that it uses AI. Informing users that a response is AI-generated helps build trust in the agent's capabilities. To ensure this, a custom engine agent must include a flag in each AI-generated response to indicate it was generated by AI. This flag automatically adds an AI label next to the response.
Examples of AI label:
Example of AI-generated label:
Example of sensitivity label:
You can use one of the following to include AI label in the agent's response:
- Use Teams AI library to add the AI label to all AI-generated messages automatically.
- Set the flag in the Bot Framework API for message activities.
Ensure that the custom engine agent is an intelligent conversational bot
A custom engine agent must track a conversation's context and history to provide an intelligent interaction. The agent must meet the user's expectation by being aware of the conversation's context and allowing them to refer to previous messages and responses.
You can use one of the following to ensure intelligent context-based conversation:
Use Teams AI library to manage and pass conversational history and context to the LLM.
Use Bot Framework SDK to:
- Manage context and conversation history: Ensure that the agent can track the context and conversation history.
- Identify conversation location: Ensure the agent is aware of the platform on which the conversation is ongoing, such as on Teams, copilot.com, in a meeting side panel, or a group chat.
- Store and pass conversation history: Determine the means of storage and pass some of the conversation history to the agent.
- Understand user references: Ensure that when a user sends a message, the agent must understand what the user is referring to. You can build this understanding in the agent using LLM and the recent conversation history. The agent mustn't need the user to reestablish context with every message.
Ensure that the custom engine agent offers prompt starters or a welcome card
A custom engine agent must assist users by offering prompt suggestions on how to best utilize the agent. This helps users overcome challenges during both initial and subsequent interactions with the agent.
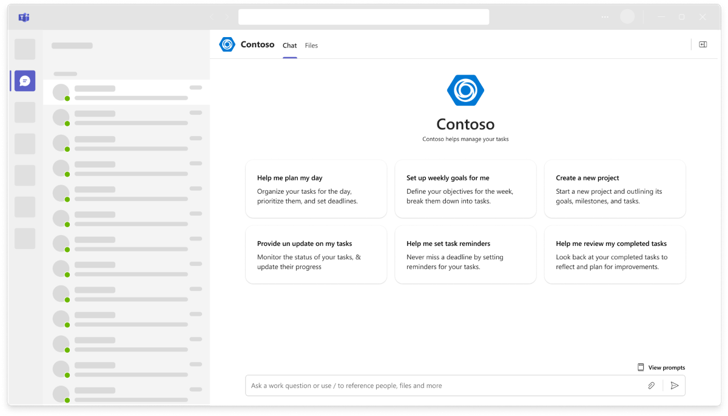
- Prompt starters: Prompt starters are the initial prompts users see when a custom engine agent is added to a new conversation, whether it's a one-on-one chat, a new session, or a group chat. These prompts must be tailored to the user's context and the specific conversation thread.
- Contextual prompts: Contextual prompts are dynamic recommendations from a custom engine agent during user interactions. These prompts appear via contextual flyouts, such as View Prompts in one-on-one chats and @mention flyouts in group chats. These suggestions are updated to stay relevant to the ongoing conversation.
- Suggested action: Suggested actions are prompts that appear as pills above the compose box in one-on-one chats and as action buttons in group chats. They are suggestions for actions a user might take in response to the agent's message and must be customized to match the response.
Compound utterance guidelines for agents
Agents must support at least three unique compound utterances by handling three or more parameters. Guidelines for agents provide detailed information on parameter description and ways to enhance message extension to retrieve information through compound utterances.
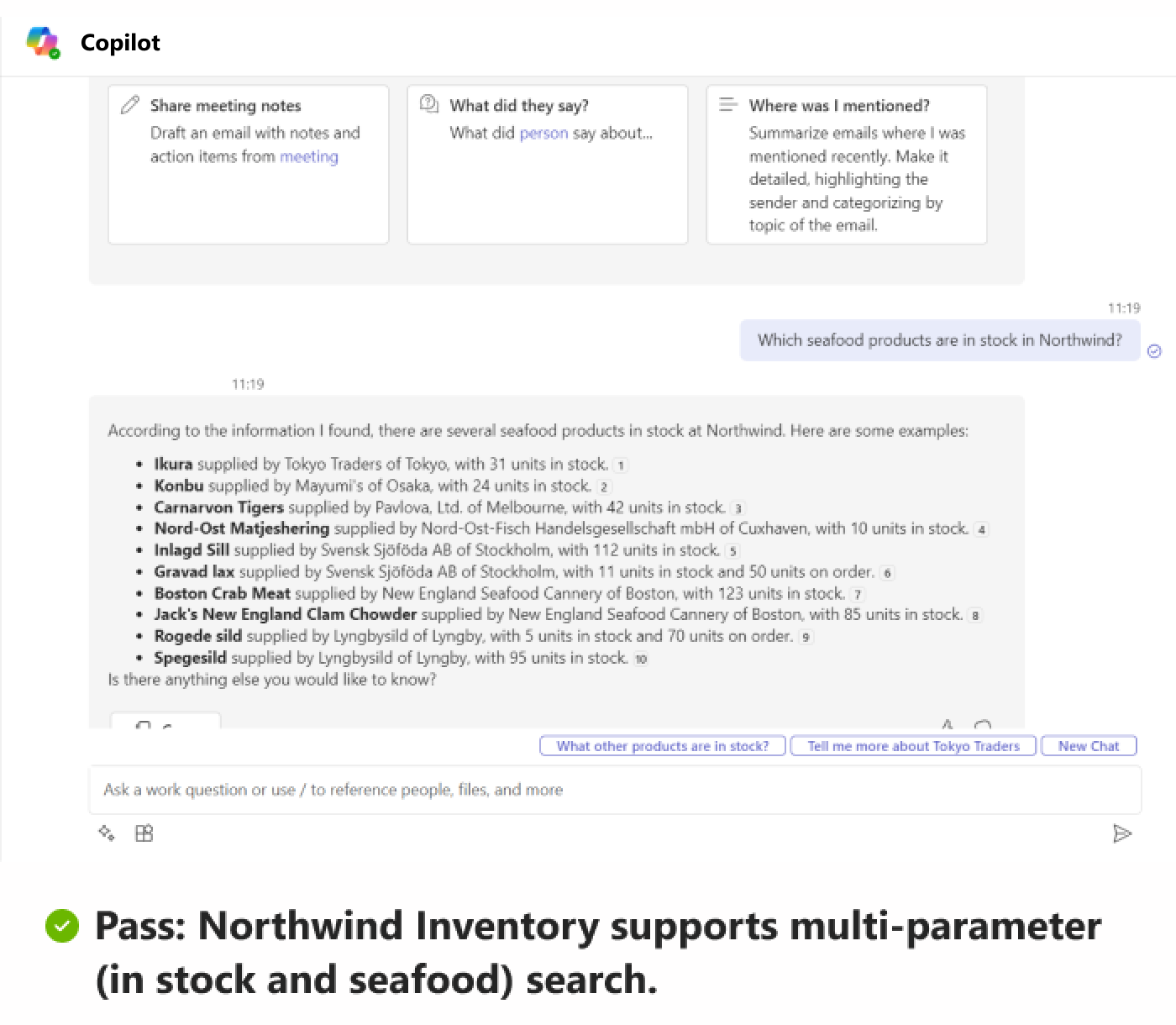
Best practices for custom engine agent
The following best practices can help enhance the overall effectiveness of a custom engine agent.
- Ensure that agent's response contains feedback button.
- Enable Teams Azure AD single sign-on.
- Enable the custom engine agent to understand conversational history and context.
- Offer dynamic and contextual suggestion prompts.
Ensure that agent's response contains feedback button
Develop the capability in the custom engine agent to receive user feedback. This could enable the collection of valuable insights from users, which can be analyzed to identify areas for improvement. By incorporating this feedback, the bot's responses can be continuously refined and enhanced, leading to a more effective and user-friendly interaction experience.
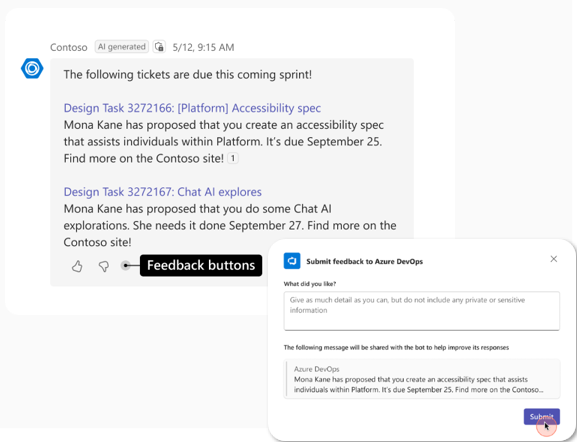
To collect the user feedback, you must:
- Provide feedback buttons with every response.
- Provide the feedback received from the user to the agent.
- Use the feedback to improve the quality of agent's responses.
You can use one of the following to enable feedback collection and usage:
- Use Teams AI library to add the feedback button property to the AI module. This property adds a feedback button to each AI-generated message automatically.
- Use the feedback flag in the Bot Framework API to add the feedback button for each message.
Note
Customizable feedback forms are available in public developer preview.
Enable Teams Azure AD single sign-on
You can add single sign-on (SSO) authentication to your custom engine agent. For more information, see enable SSO for your app.
Enable the custom engine agent to understand conversational history and context
You can design your custom engine agent to understand and refer to conversational history and context. It helps to ensure that every interaction is relevant and tailored to the user's specific needs. The agent can refer to the context and offer responses that are accurate and contextually appropriate. For more information, see messages in bot conversations.
Offer dynamic and contextual suggestion prompts
Enhance your custom engine agent experience with intelligent and context-aware prompts. The agent can offer context-relevant prompts dynamically.
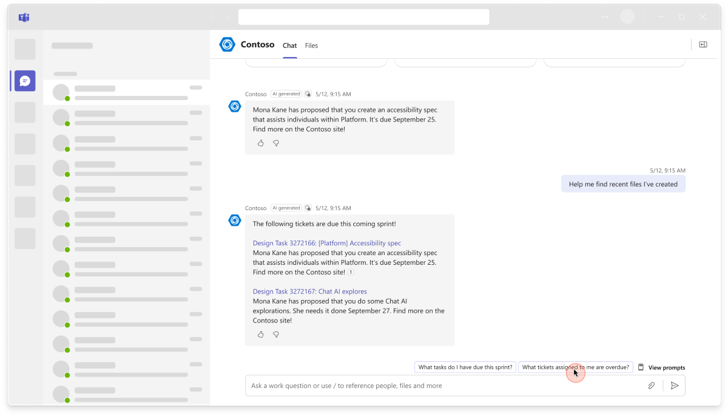
To achieve this, the agent must leverage the conversation context and history, and prompt suggestions can be timely and fit for the query.
See also
Platform Docs