Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
This feature is in preview.
The time-to-live (TTL) feature in Cosmos DB helps you manage your data's lifecycle by automatically deleting items after a specified period. In this guide, you modify the TTL value at the container and item level using the Fabric portal or an Azure SDK.
Prerequisites
An existing Fabric capacity
- If you don't have Fabric capacity, start a Fabric trial.
An existing Cosmos DB database in Fabric
- If you don't have one already, create a new Cosmos DB database in Fabric.
An existing container with data
- If you don't have one already, we suggest that you load the sample data container.
- Python 3.12 or later
- Node.js 22 or later
- .NET SDK 9.0 or later
Set at container level using the Fabric portal
First, use the Fabric portal to set the container-level TTL.
Open the Fabric portal (https://app.fabric.microsoft.com).
Navigate to your existing Cosmos DB database.
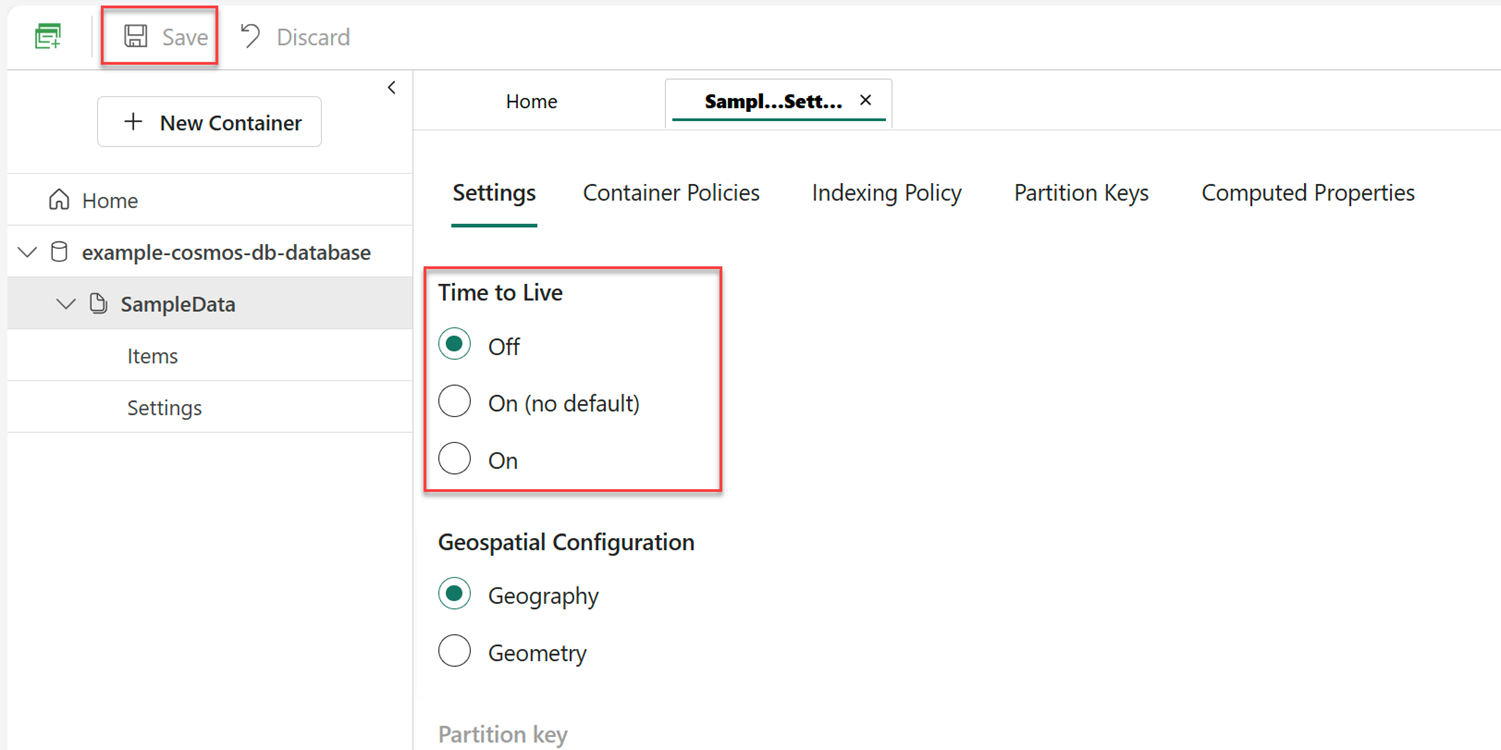
Select and expand your existing container. Then, select Settings.
In the Settings section, select the redundant Settings tab.
Locate the Time to Live setting.
Update the setting to a new value. For example, you can set the value to On (no default) to set the default time-to-live at the container level to
-1(infinity) where TTL is enabled but items don't expire by default.Select Save to persist your changes.
Tip
For more information on various time-to-live (TTL) configuration values, see time-to-live.
Set at item level
Next, update an item to set the TTL value at the item-level. Items within Cosmos DB are represented as JSON documents. The ttl property of each document is used to set the time-to-live of each specific item. The ttl property can either be set or not set and the corresponding value influences the behavior of TTL expiration.
[
{
"name": "Heatker Women's Jacket",
"category": "apparel"
},
{
"name": "Vencon Kid's Coat",
"category": "apparel",
"ttl": -1
},
{
"name": "Pila Swimsuit",
"category": "apparel",
"ttl": 3600
}
]
Set at container level using the Azure SDK
Now, use the Azure SDK to set the TTL at the container level to apply to all items.
database = client.get_database_client("<database-name>")
container = database.get_container_client("<container-name>")
# Set the container-level TTL to 7 days
database.replace_container(container, partition_key=PartitionKey(path='/<partition-key-path>'), default_ttl=60 * 60 * 24 * 7)
const container: Container = client.database('<database-name>').container('<container-name>');
const { resource: containerProperties } = await container.read();
if (!containerProperties) {
return;
}
// Set the container-level TTL to 7 days
containerProperties.defaultTtl = 60 * 60 * 24 * 7;
await container.replace(containerProperties);
Container container = client
.GetDatabase("<database-name>")
.GetContainer("<container-name>");
ContainerProperties properties = await container.ReadContainerAsync();
// Set the container-level TTL to 7 days
properties.DefaultTimeToLive = 60 * 60 * 24 * 7;
await container.ReplaceContainerAsync(properties);
Set at item level using the Azure SDK
Finally, use the Azure SDK again to set item-level TTL values to override the container-level value.
container = client.get_database_client("<database-name>").get_container_client("<container-name>")
# Set the item-level TTL to 1 day
item = {
"id": "ffffffff-5555-6666-7777-aaaaaaaaaaaa",
"name": "Pila Swimsuit",
"category": "apparel",
"ttl": 60 * 60 * 24
}
container.upsert_item(item)
const container: Container = client.database('<database-name>').container('<container-name>');
// Set the item-level TTL to 1 day
let item = {
id: 'ffffffff-5555-6666-7777-aaaaaaaaaaaa',
name: 'Pila Swimsuit',
category: 'apparel',
ttl: 60 * 60 * 24
};
await container.items.upsert(item);
Container container = client
.GetDatabase("<database-name>")
.GetContainer("<container-name>");
// Set the item-level TTL to 1 day
var item = new {
id = "ffffffff-5555-6666-7777-aaaaaaaaaaaa",
name = "Pila Swimsuit",
category = "apparel",
ttl = 60 * 60 * 24
};
await container.UpsertItemAsync(item);