Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse is a data architecture platform for storing, managing, and analyzing structured and unstructured data in a single location. In this guide, you access your mirrored Cosmos DB in Microsoft Fabric data in a lakehouse. You then use a notebook to perform a basic query of that date.
Prerequisites
An existing Fabric capacity
- If you don't have Fabric capacity, start a Fabric trial.
An existing Cosmos DB database in Fabric
- If you don't have one already, create a new Cosmos DB database in Fabric.
An existing container with data
- If you don't have one already, we suggest that you load the sample data container.
Open the SQL analytics endpoint for the database
Start by accessing the SQL analytics endpoint for the Cosmos DB in Fabric database to ensure that mirroring ran successfully at least once.
Open the Fabric portal (https://app.fabric.microsoft.com).
Navigate to your existing Cosmos DB database.
Important
For this guide, the existing Cosmos DB database has the sample data set already loaded. The remaining query examples in this guide assume that you're using the same data set for this database.
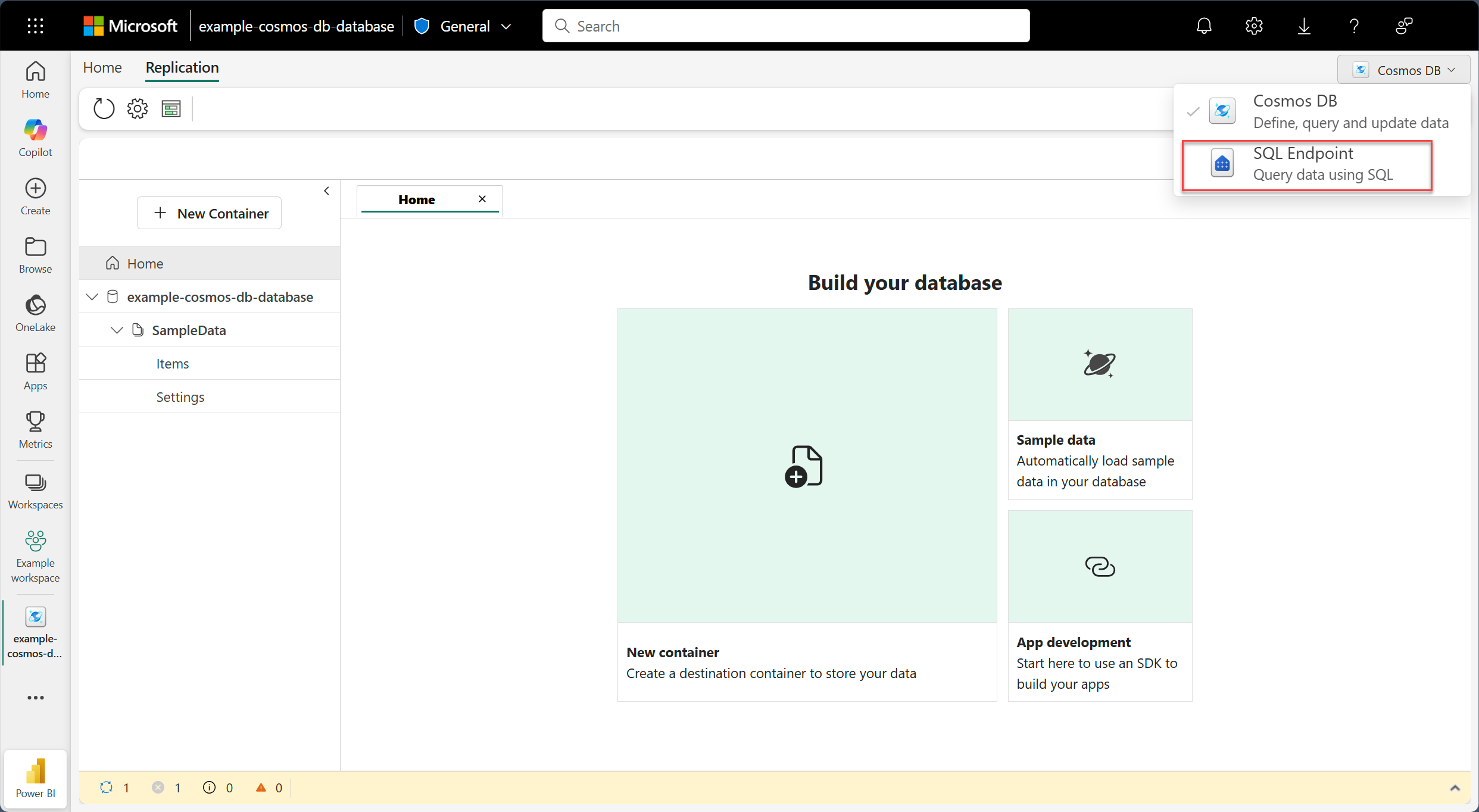
In the menu bar, select the Cosmos DB list and then select SQL Endpoint.
Once you're able to successfully navigate to the SQL analytics endpoint, this navigation step confirms that mirroring ran successfully at least once.
Connect database to a lakehouse
Next, use Lakehouse to extend the number of tools you can use to analyze your Cosmos DB data. In this step, create a lakehouse and connect it to your mirrored data.
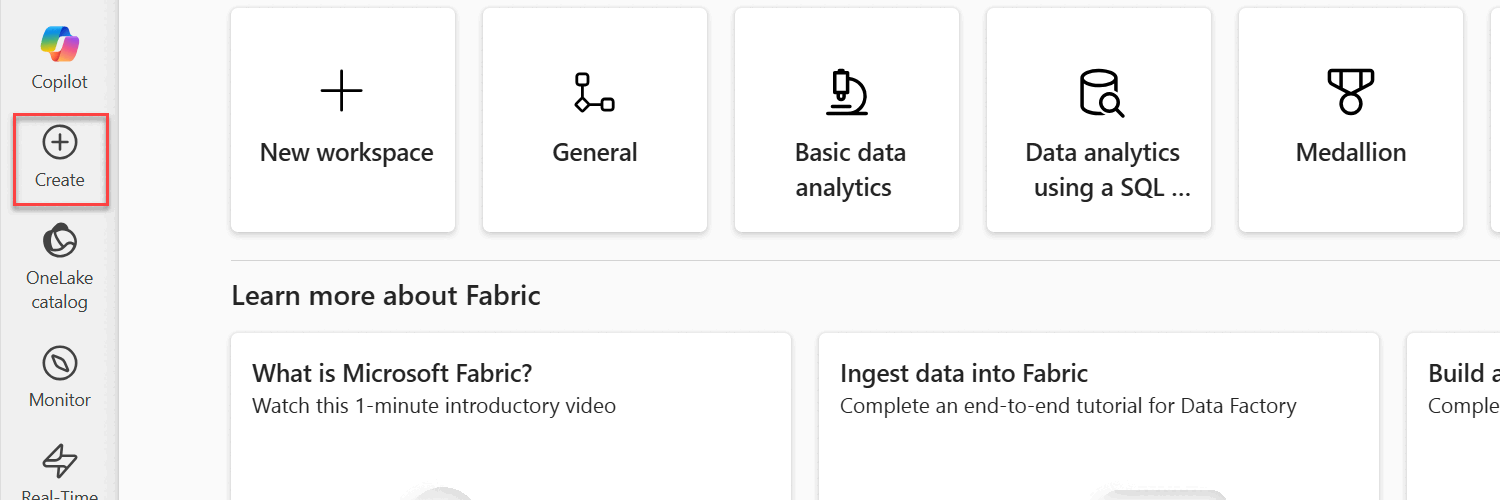
Navigate to the Fabric portal home page.
Select the Create option.
If the option to create an Lakehouse account isn't initially available, select See all.
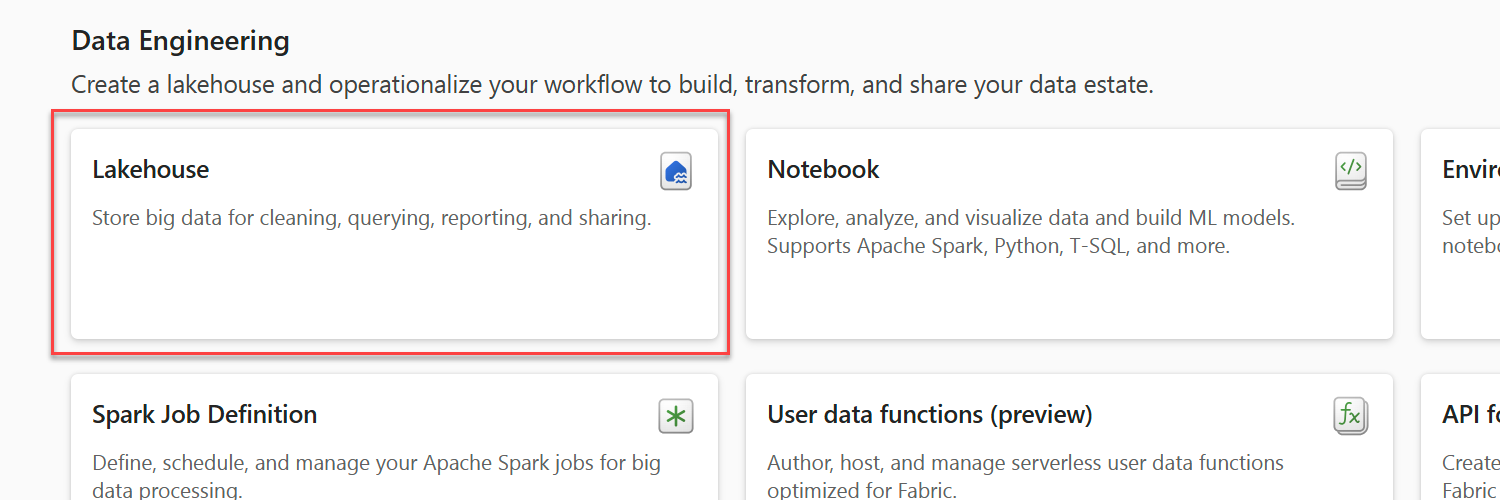
Within the Data Engineering category, select Lakehouse.
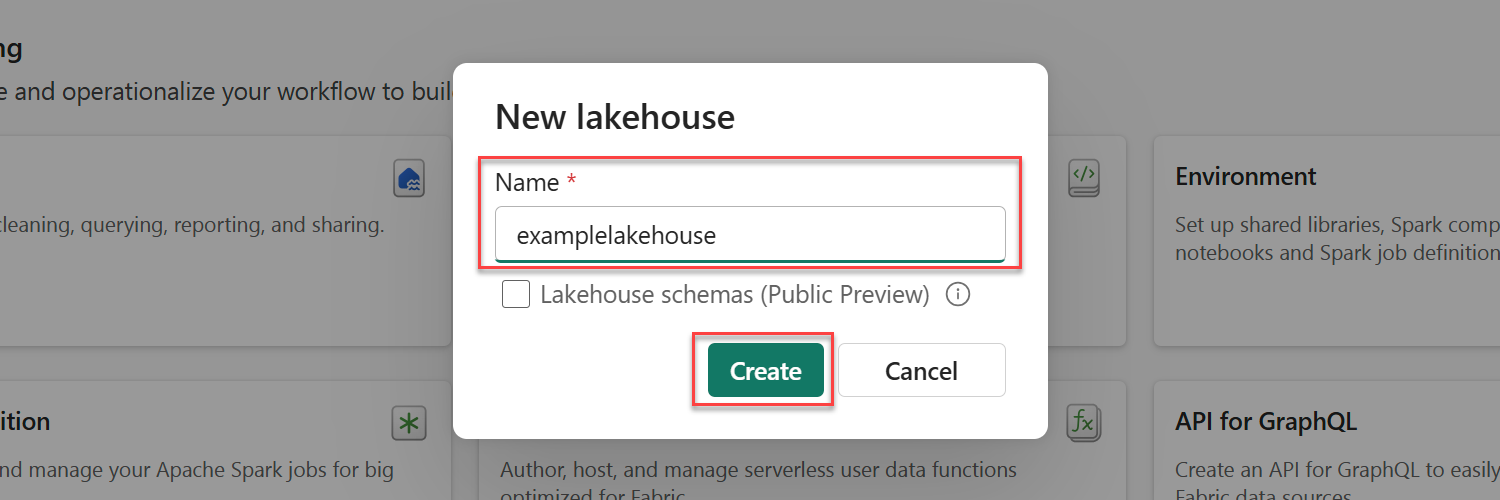
Give the lakehouse a unique name and then select Create.
In the newly created lakehouse's menu, select the Get data option, and then select New shortcut.
Follow the sequential instructions in the various New shortcut dialogs to select your existing mirrored Cosmos DB database, and then select your target table.
Important
This guide assumes that you're selecting the SampleData table that's available when you mirror a Cosmos DB database that has the sample data set preloaded.
Run a Spark query in a notebook
Finally, use Spark within a notebook to write Python queries for your mirrored data that is connected to the lakehouse. For this last step, create a notebook and then run a baseline Spark query using the Transact SQL (T-SQL) language syntax.
In the lakehouse menu, select the Open notebook category and then select New notebook.
In the newly created notebook, create a new PySpark (Python) cell.
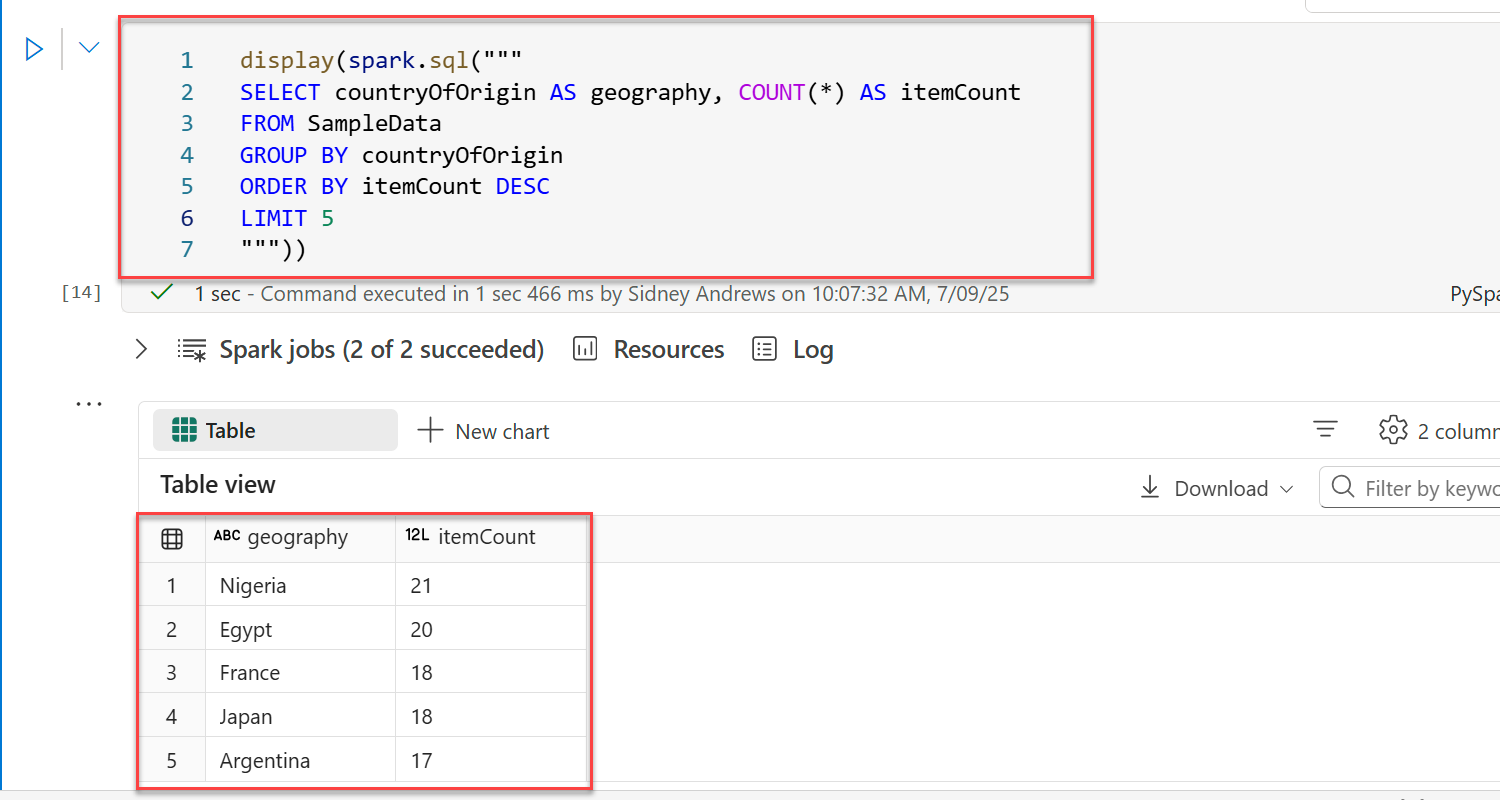
Test a SQL query using a combination of the
displayandspark.sqlfunctions in PySpark. Enter this code into the cell.display(spark.sql(""" SELECT countryOfOrigin AS geography, COUNT(*) AS itemCount FROM SampleData GROUP BY countryOfOrigin ORDER BY itemCount DESC LIMIT 5 """))Important
This query uses data found in the sample data set. For more information, see sample data set.
Run the notebook cell.
Observe the output from running the notebook cell. The results are rendered in tabular format.
geographyitemCountNigeria 21 Egypt 20 France 18 Japan 18 Argentina 17