Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
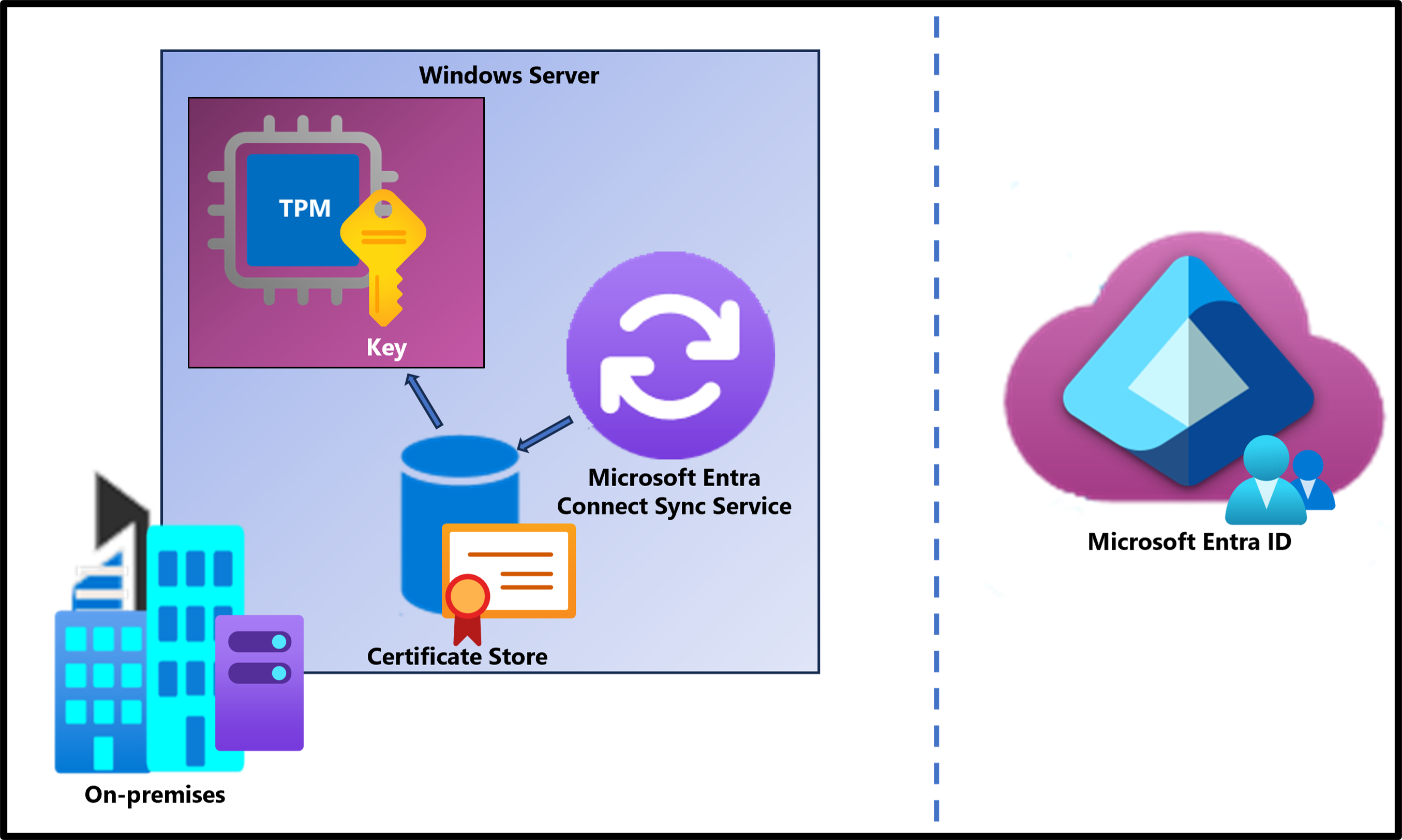
Microsoft Entra Connect uses the Microsoft Entra Connector account to authenticate and sync identities from Active Directory to Microsoft Entra Connect. This account uses a username and password to authenticate requests.
To enhance the security of the service, we're rolling out an application identity that uses Oauth 2.0 client credential flow with certificate credentials. In this new method, Microsoft Entra or an administrator creates a single tenant non-Microsoft application in Microsoft Entra ID and uses one of the following relevant certificate management options for the credentials.
Microsoft Entra Connect provides three options for application and certificate management:
- Managed by Microsoft Entra Connect (default)
- Bring Your Own Application (BYOA)
- Bring Your Own Certificate (BYOC)
Note
The Application Administrator role grants the ability to consent for application permissions, with the exception of application permissions for Azure AD Graph and Microsoft Graph. This means that the application administrator can still consent to application permissions for other apps, notably the AWS first-party app and SSPR first-party app.
This role also grants the ability to manage application credentials. User assigned to this role can add credentials to an application (notably the Connect Sync) and use those credentials to impersonate the application's identity. This might be an elevation of privilege over what the user can do via their role assignments.
Managed by Microsoft Entra Connect (default)
Microsoft Entra Connect manages the application and certificate, which includes creation, rotation, and deletion of the certificate. The certificate is stored in the CURRENT_USER store. For optimal protection of the certificate's private key, we recommend that the machine should use a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) solution to establish a hardware-based security boundary.
When a TPM is available, key service operations are performed within a dedicated hardware environment. In contrast, if a TPM can't be used, Microsoft Entra Connect defaults to storing the certificate in the default Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider and marks the private key as nonexportable for extra protection. Without the hardware isolation provided by a TPM, only software safeguards secure the private key, which doesn't achieve the same level of protection.
For more information on TPM technology, see Trusted Platform Module technology overview.
We recommend the Microsoft Entra Connect certificate management (default) option because we manage the keys and automatically rotate the certificate on expiry.
Microsoft Entra Connect Sync uses the scheduler to check if the certificate is due for rotation and then automatically rotate the certificate. If the scheduler is suspended, automatic certificate rotation can't happen even though Microsoft Entra Connect Sync manages the certificate.
Bring Your Own Application
In the Bring Your Own Application (BYOA) setup, administrator manages the application that Microsoft Entra Connect Sync uses to authenticate to Microsoft Entra ID, the application permissions, and the certificate credential that the application uses.
The administrator registers a Microsoft Entra app and creates a service principal. The application needs the required permissions configured. To configure the required permissions on the application, you can use Microsoft Graph API or PowerShell. In this section, we'll use Microsoft Graph API.
ConnectSyncAppIdrefers to the application (client) ID of the application for which we want to configure permissions.SynchronizationServiceAppIdrefers to the application (client) ID for Microsoft Entra AD Synchronization Service. The value is6bf85cfa-ac8a-4be5-b5de-425a0d0dc016for all clouds.PasswordResetServiceAppIdrefers to the application (client) ID for Microsoft password reset service. The value is93625bc8-bfe2-437a-97e0-3d0060024faafor all clouds except Arlington where it's2e5ecfc8-ea79-48bd-8140-c19324acb278.
Open Graph explorer and sign in using Application Administrator or Global Administrator credentials.
Get the service principal ID for Microsoft Entra AD Synchronization Service. We'll refer to this as
SynchronizationServiceSPIdGET /servicePrincipals/(appId=’{SynchronizationServiceAppId}’)?$select=idGet the app role ID for
ADSynchronization.ReadWrite.All permission. We'll refer to this asSynchronizationServiceAppRoleIdGET /servicePrincipals/(appId=’{SynchronizationServiceAppId}’)?$select=appRolesSynchronizationServiceAppRoleIdis the id property of the app role in the response where value=ADSynchronization.ReadWrite.AllGet the service principal ID for Microsoft password reset service. We'll refer to this as
PasswordResetServiceSPId. Note that the service principal might not exist in the tenant.GET /servicePrincipals/(appId=’{PasswordResetServiceAppId}’)?$select=idGet the app role IDs for
PasswordWriteback.OffboardClient.All,PasswordWriteback.RegisterClientVersion.AllandPasswordWriteback.RefreshClient.Allpermissions. This step is relevant only if password reset service principal exists in the tenant. We'll refer to these asPasswordResetServiceServiceOffboardClientAppRoleId,PasswordResetServiceServiceRegisterClientAppRoleId,PasswordResetServiceServiceRefreshClientAppRoleIdrespectively.PasswordResetServiceServiceOffboardClientAppRoleIdis the id of the app role in the response where value=PasswordWriteback.OffboardClient.AllPasswordResetServiceServiceRegisterClientAppRoleIdis the id of the app role in the response where value=PasswordWriteback.RegisterClientVersion.AllPasswordResetServiceServiceRefreshClientAppRoleIdis the id of the app role in the response where value=PasswordWriteback.RefreshClient.All
Update application
requiredResourceAccessto configure required permissions for Microsoft Entra AD Synchronization Service and Microsoft password reset service.PATCH /applications(appId='{ConnectSyncAppId}') { "requiredResourceAccess": [ { "resourceAppId": "{PasswordResetServiceAppId}", "resourceAccess": [ { "id": “{PasswordResetServiceServiceOffboardClientAppRoleId}", "type": "Role" }, { "id": “{PasswordResetServiceServiceRegisterClientAppRoleId}", "type": "Role" }, { "id": “{PasswordResetServiceServiceRefreshClientAppRoleId}", "type": "Role" } ] }, { "resourceAppId": "{SynchronizationServiceAppId}", "resourceAccess": [ { "id": "{SynchronizationServiceAppRoleId}", "type": "Role" } ] } ] }Assign app roles to the Connect Sync application service principal:
Add an app role assignment for
ADSynchronization.ReadWrite.AllPOST /servicePrincipals(appId='{ConnectSyncAppId}')/appRoleAssignments { "principalId": “{ConnectSyncSPId}”, "resourceId": “{SynchronizationServiceSPId}”, "appRoleId": "{SynchronizationServiceAppRoleId}" }
If password writeback is enabled on the Connect Sync server, add the three app role assignments for password reset service.
Add app role assignment for
PasswordWriteback.OffboardClient.AllPOST /servicePrincipals(appId='{ConnectSyncAppId}')/appRoleAssignments { "principalId": “{ConnectSyncSPId}”, "resourceId": “{PasswordResetServiceSPId}”, "appRoleId": "{PasswordResetServiceServiceOffboardClientAppRoleId}" }
Add app role assignment for
PasswordWriteback.RegisterClientVersion.AllPOST /servicePrincipals(appId='{ConnectSyncAppId}')/appRoleAssignments { "principalId": “{ConnectSyncSPId}”, "resourceId": “{PasswordResetServiceSPId}”, "appRoleId": "{PasswordResetServiceServiceRegisterClientAppRoleId}" }Add app role assignment for value=
PasswordWriteback.RefreshClient.AllPOST /servicePrincipals(appId='{ConnectSyncAppId}')/appRoleAssignments { "principalId": “{ConnectSyncSPId}”, "resourceId": “{PasswordResetServiceSPId}”, "appRoleId": “{PasswordResetServiceServiceRefreshClientAppRoleId}” }
The administrator is responsible for creating the certificate, rotation, and deletion of unused or expired certificates. The certificate must be stored in the LOCAL_MACHINE store.
The administrator is responsible for securing the private key of the certificate and ensuring that only Microsoft Entra Connect Sync can access the private key for signing.
We recommend that you use a TPM or a Hardware Security Module (HSM) to provide a hardware-based security boundary, as opposed to the default. To check the status of the TPM, use the Get-TPM PowerShell cmdlet.
If you use Hyper-V virtual machines (VMs), you can enable the TPM by selecting Security > Enable Trusted Platform Module. You can do this step only on generation 2 VMs. Generation 1 VMs can't be converted to generation 2 VMs. For more information, see Generation 2 VM security settings for Hyper-V and Enable trusted launch on existing Azure Gen2 VMs.
Bring Your Own Certificate
In the Bring Your Own Certificate (BYOC) setup, the administrator manages the certificate credential that the application uses. The administrator is responsible for creating the certificate, rotation, and deletion of unused or expired certificates. The certificate must be stored in the LOCAL_MACHINE store.
The administrator is responsible for securing the private key of the certificate and ensuring that only Microsoft Entra Connect Sync can access the private key for signing.
We recommend that you use a TPM or a Hardware Security Module (HSM) to provide a hardware-based security boundary, as opposed to the default. To check the status of the TPM, use the Get-TPM PowerShell cmdlet.
If you use Hyper-V virtual machines (VMs), you can enable the TPM by selecting Security > Enable Trusted Platform Module. You can do this step only on generation 2 VMs. Generation 1 VMs can't be converted to generation 2 VMs. For more information, see Generation 2 VM security settings for Hyper-V and Enable trusted launch on existing Azure Gen2 VMs.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to implement authentication by using application identity.
Important
New Microsoft Entra Connect Sync versions are available only via the Microsoft Entra admin center.
Following up on the What's New communication, new versions of Microsoft Entra Connect Sync are available only on the Microsoft Entra Connect pane within the Microsoft Entra admin center and will no longer be released to the Microsoft Download Center.
- Microsoft Entra Connect version 2.5.3.0 or greater for manual onboarding.
- Microsoft Entra Connect version 2.5.76.0 or greater for automatic onboarding
- Microsoft Entra account with at least a Hybrid Identity Administrator role.
- Optional: TPM 2.0 present and ready to use (highly recommended for security).
The following extra requirements are needed for the BYOC certificate management option:
- A certificate is created in an HSM or TPM by using a Cryptography API: Next Generation provider. The private key is marked as nonexportable. A warning event 1014 is emitted if TPM isn't used. The following certificate configurations are supported:
KeyLength: 2048KeyAlgorithm: RSAKeyHashAlgorithm: SHA256
- The created certificate is stored in the
LOCAL_MACHINEstore. - Grant the Microsoft Entra Connect Sync account permission to perform signing by using the private key.
The following extra requirements are needed for the BYOA application management option:
- The customer creates a certificate as instructed in the preceding BYOC prerequisites.
- The customer registers an application in Microsoft Entra ID and creates a service principal. The necessary permissions are granted to the application.
- The customer registers the certificate with the application.
View the current authentication configuration
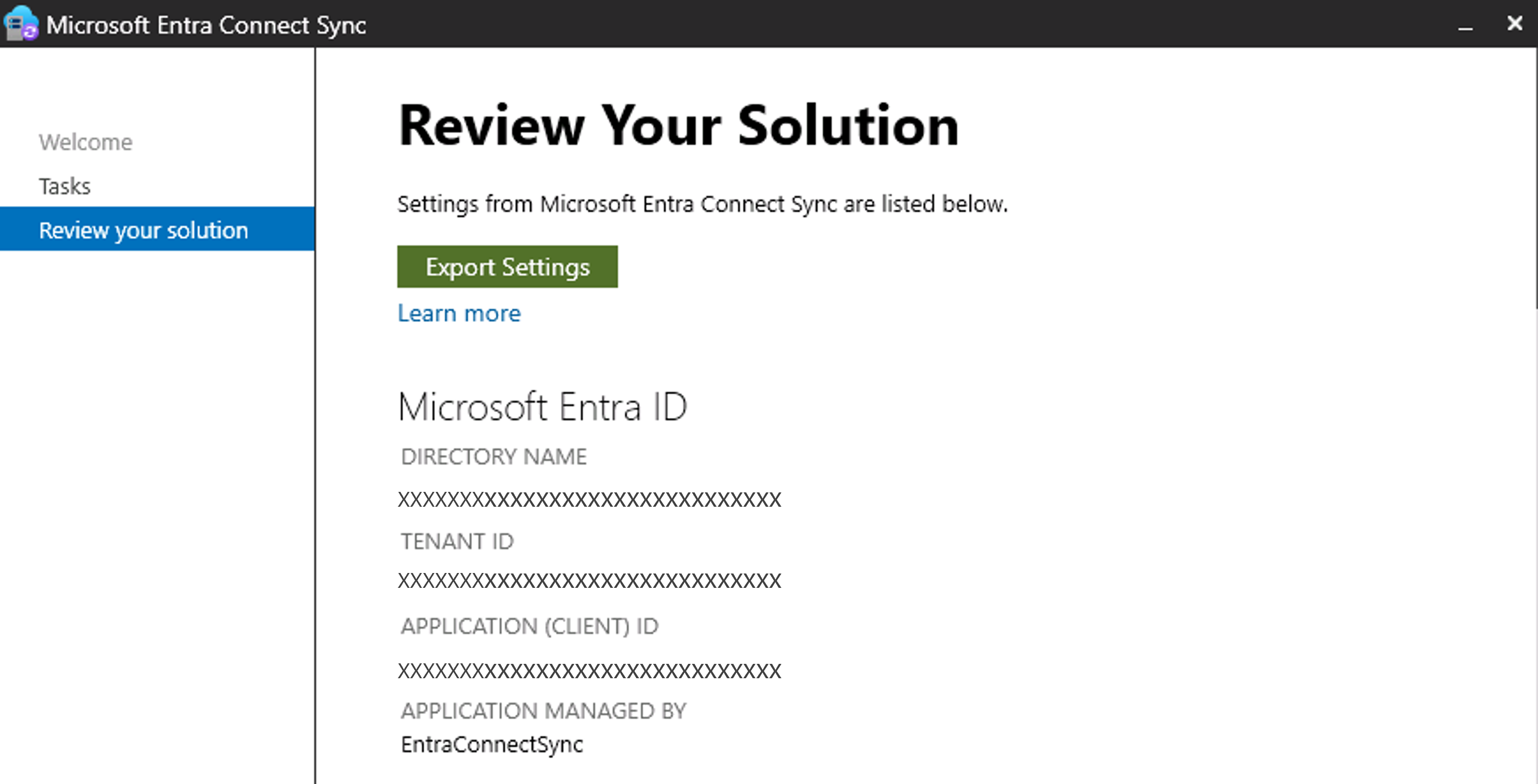
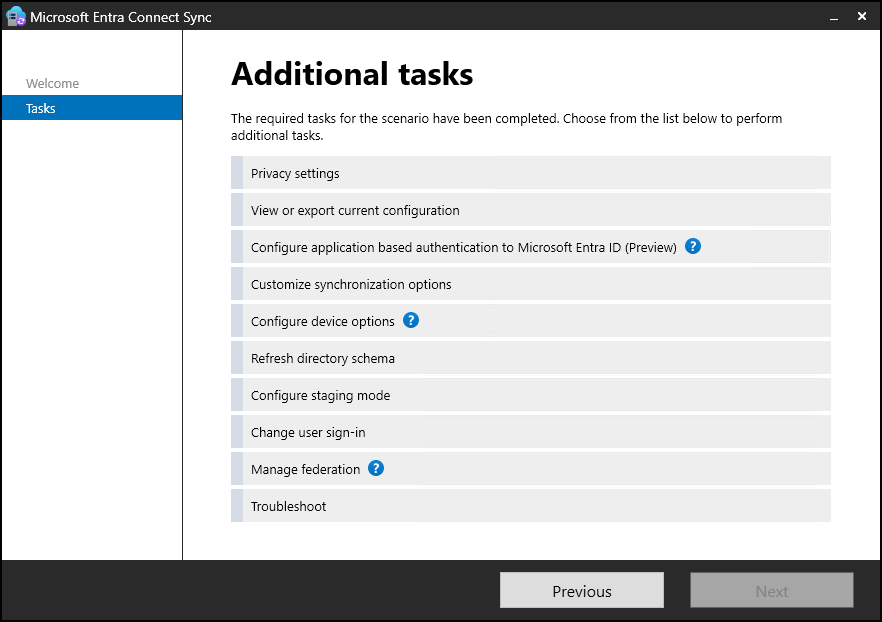
To view the current authentication configuration, run the Wizard and go to Tasks, and then select View or export current configuration.
If the server is configured to use application-based authentication, you should be able to see the application (client) ID as shown in the following screenshot.
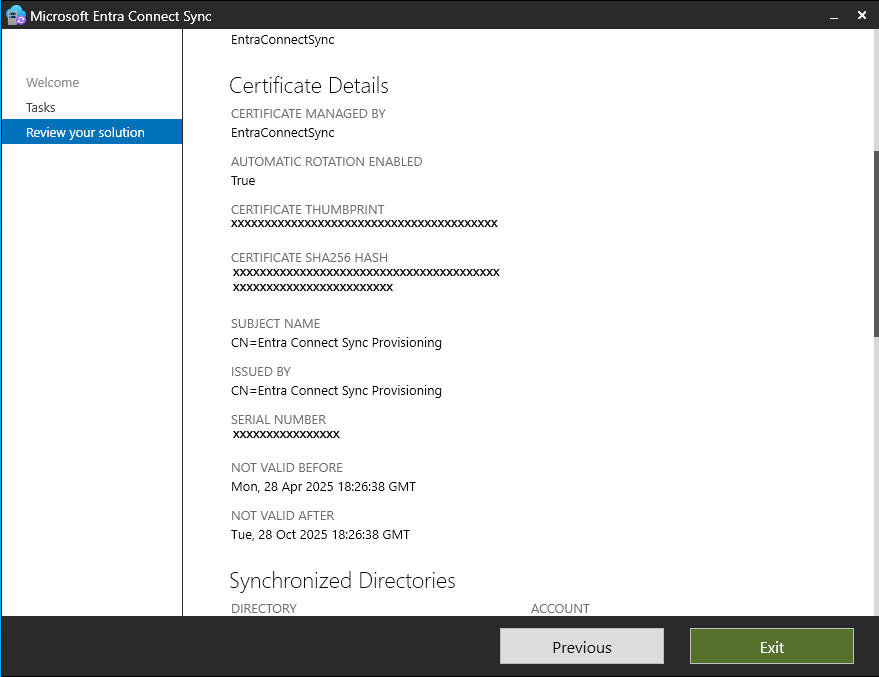
Scroll down to the certificate details. The following table provides information about the certificate.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Certificate managed by | Whether Microsoft Entra Connect Sync or BYOC manages the certificate |
| Automatic rotation enabled | Whether automatic rotation or manual rotation is enabled |
| Certificate thumbprint | Unique identifier for the certificate |
| Certificate SHA256 hash | A fingerprint for the certificate generated by using the SHA-256 hashing algorithm |
| Subject name | Identifies the entity associated with the certificate |
| Issued by | Who is the issuer of the certificate |
| Serial number | Uniquely identifies the certificate among certificates by the same issuer |
| Not valid before | The first date that the certificate is valid |
| Not valid after | The last date that the certificate is valid |
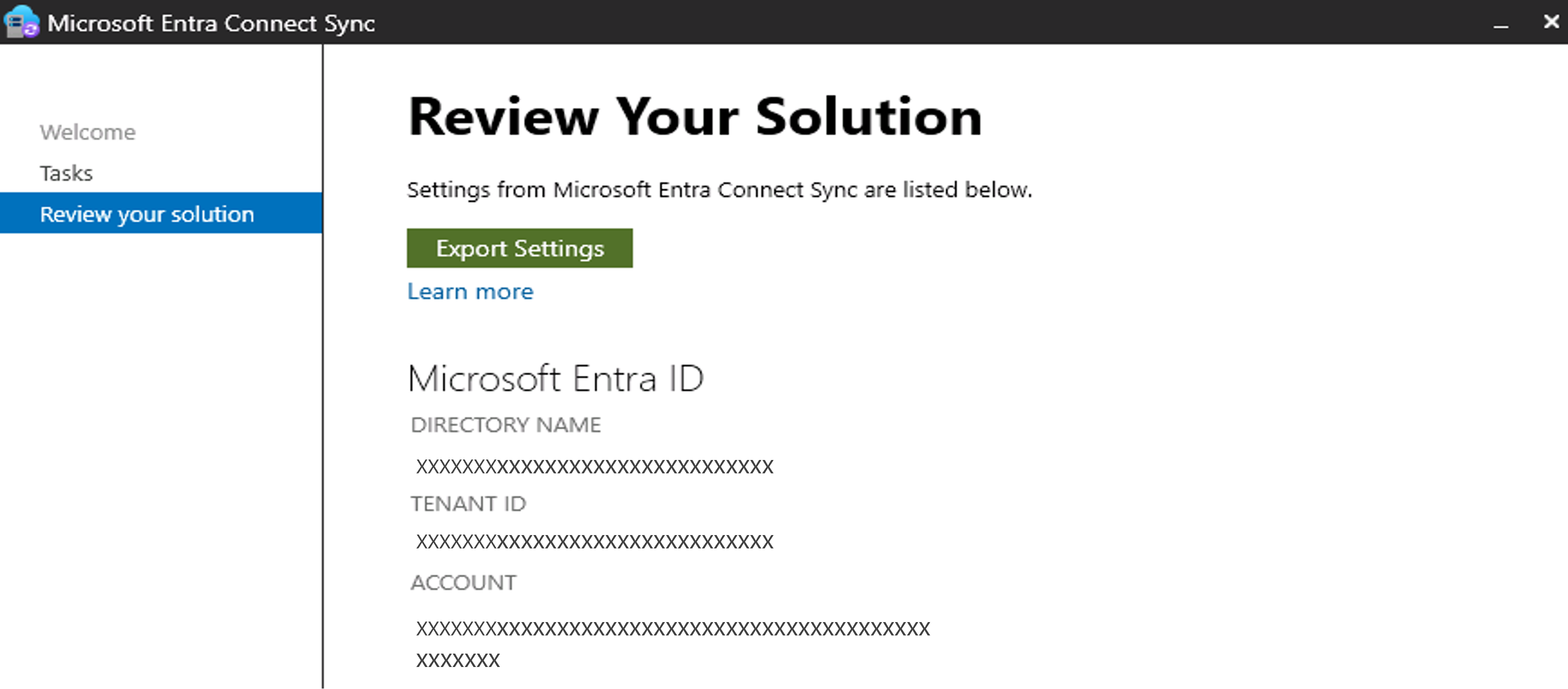
If the server is using username and password, you should be able to see the account name as shown in the following screenshot.
Installation and upgrade (managed by Microsoft Entra Connect)
The Microsoft Entra Connect Sync managed application and credential is automatically set up during initial installation or manual interactive upgrades. To confirm that Microsoft Entra Connect is using the application identity, you can view the current authentication configuration.
Onboard to application-based authentication
Automatic
Starting with version 2.5.76.0 or higher, the service will automatically configure application authentication within a six-hour window if the service is using username and password to authenticate to Microsoft Entra ID.
Manual
If application authentication wasn't automatically configured, you can switch to application-based authentication manually.
If you want to configure application-based authentication using the default option (Managed by Microsoft Entra Connect), you can use the wizard. However, if you want to configure application-based authentication using BYOC or BYOA, you must use PowerShell.
- Start the Microsoft Entra Connect wizard
- Go to Additional tasks > Configure application-based authentication to Microsoft Entra ID and then follow the prompts.
Certificate rotation
Microsoft Entra Connect warns if the certificate rotation is due. That is, if expiration is less than or equal to 150 days. It emits an error if the certificate is already expired. You can find these warnings (Event ID 1011) and errors (Event ID 1012) in the Application event log.
This message is emitted at the scheduler frequency if the scheduler isn't suspended. Run Get-ADSyncSchedulerSettings to see if the scheduler is suspended.
Automatic
If Microsoft Entra Connect manages the certificate, no action is required from you unless the scheduler is suspended, Microsoft Entra Connect Sync adds the new certificate credential to the application, and tries to remove the old certificate credential.
If it fails to remove the old certificate credential, an error event appears in the Application logs in the Event Viewer.
If you see this error, run the following cmdlet in PowerShell to clean up the old certificate credential from Microsoft Entra. The cmdlet takes the CertificateId value of the certificate that must be removed, which you can obtain from the log or the Microsoft Entra admin center.
Remove-EntraApplicationKey -CertificateId <certificateId>
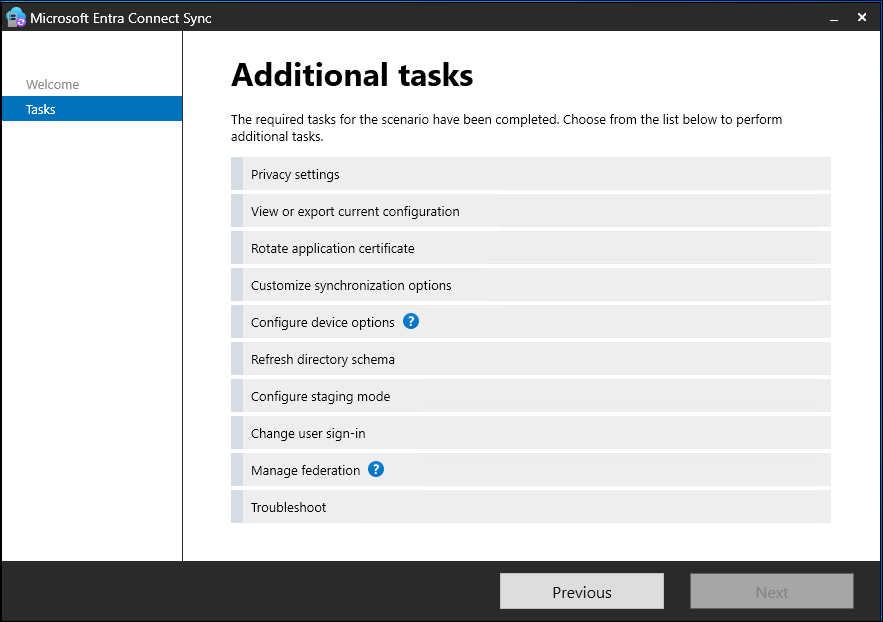
Manual
If your configuration isn't eligible for automatic certificate rotation, you can rotate the certificate at any point in time, even if the current certificate is still not due for rotation or the current certificate expired.
- Start the Microsoft Entra Connect wizard
- Go to Additional tasks > Rotate application certificate and then follow the prompts.
Script to generate the SHA256 hash of the certificate
# Get raw data from X509Certificate cert
$certRawDataString = $cert.GetRawCertData()
# Compute SHA256Hash of certificate
$sha256 = [System.Security.Cryptography.SHA256]::Create()
$hashBytes = $sha256.ComputeHash($certRawDataString)
# Convert hash to bytes for PowerShell (Core) 7.1+:
$certHash = [System.Convert]::ToHexString($hashBytes)
# Convert hash to bytes for older PowerShell:
$certHash = ($hashBytes|ForEach-Object ToString X2) -join ''
Certificate revocation process
For self-signed certificates, either Microsoft Entra Managed or BYOC, an administrator must perform manual revocation by removing the keyCredential value from Microsoft Entra ID. An on-demand rotation of the certificate is also an option.
For BYOC certificates issued by a Certificate Authority registered with Microsoft Entra, the administrator can follow the certificate revocation process.
Remove a legacy service account
After you transition to application-based authentication and Microsoft Entra Connect Sync is working as expected, we strongly recommend that you remove the legacy DSA username and password service account by using PowerShell. If you use a custom account that can't be removed, deprivilege it and remove the DSA role from it.
Follow these steps to remove the legacy service account.
Add the service account username and password.
$HACredentialYou're prompted to enter the Microsoft Entra administrator
UserPrincipalNamevalue and the password. Enter the username and password.Next, remove the service account.
Remove-ADSyncAADServiceAccount -AADCredential $HACredential -Name <$serviceAccountName>The
ServiceAccountNamevalue is the first part of theUserPrincipalNamevalue of the service account used in Microsoft Entra ID. You can find this user in the list of users in the Microsoft Entra admin center. If the UPN isaringdahl@fabrikam.com, usearingdahlas theServiceAccountNamevalue.
Roll back to a legacy service account by using PowerShell
If you want to go back to the legacy service account, you can use PowerShell to revert to using the service account to promptly mitigate the issue. Use the following steps to roll back to the service account.
As part of the rollback, we'll be re-creating the DSA account. This new account might take up to 15 minutes to take effect, so you might get an "Access Denied" error when you reenable the sync cycle.
Disable the scheduler to ensure that no sync cycles run until this change is completed.
Set-ADSyncScheduler -SyncCycleEnabled $falseAdd the service account. You're prompted to enter the Microsoft Entra administrator
UserPrincipalNamevalue and the password. Enter the credentials.Add-ADSyncAADServiceAccountGet the current authentication mechanism and confirm that the
ConnectorIdentityTypevalue is back toServiceAccount.Get-ADSyncEntraConnectorCredentialReenable the scheduler to begin the synchronization service.
Set-ADSyncScheduler -SyncCycleEnabled $true