Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Diagnostic logs provide insight into operations that occur in your Azure AI Search resource. In contrast to Activity Logs that track operations performed on Azure resources at the subscription level, known as the control plane, diagnostic logging monitors operations on the search service itself. Diagnostic logging is essential for effective oversight of service operations like indexing and queries.
This article explains how to enable diagnostic logging and find information about system and user operations on an Azure AI Search resource.
Note
Azure AI Search doesn't log the identity of the person or app accessing content or operations on the search service. If you require this level of monitoring, you need to implement it in your client application.
Prerequisites
- An Azure Log Analytics workspace in the same subscription.
Enable diagnostic logging
Sign in to the Azure portal and find your search service.
Under Monitoring > Diagnostic settings, select Add diagnostic setting.
Provide a descriptive name that identifies the service and level of logging, such as "my-search-service-all-logs" or "my-search-service-audit-logs".
Under Logs, choose a category:
- Audit logs capture user or app interactions with data or the settings of the service, but don't include user or groups identities.
- Operation logs capture information about operations on a search service.
- allLogs collect everything.
Verbose logging can be expensive to store and complex to manage and store. You might want to start with allLogs and then switch to more scoped logging if it meets your information requirements. For more information about these categories, see Diagnostic settings in Azure Monitor.
For a destination, we recommend Send to Log Analytics workspace so that you can run Kusto queries against the data. Provide an existing Log Analytics workspace to store your logs.
Save the settings.
Repeat these steps if you require a more comprehensive data collection strategy.
Each diagnostic setting you create requires separate storage. If you use the Azure portal to review logs, the first diagnostic setting is used by default. You can navigate to specific workspaces for visualization support.
Note
If you're using key-based authentication, Azure AI Search can't monitor individual user access to content on the search service. If you require this level of monitoring, you need to implement it in your client application.
View logs in Log Analytics
Follow these instructions to explore log analytics data for your search service.
Under Monitoring, select Logs. Query hub opens by default. You can try the available queries, or close the hub and open a query window in KQL mode to run queries written in the Kusto Query Language (KQL).
In a query window, you can run Kusto queries against your logs.
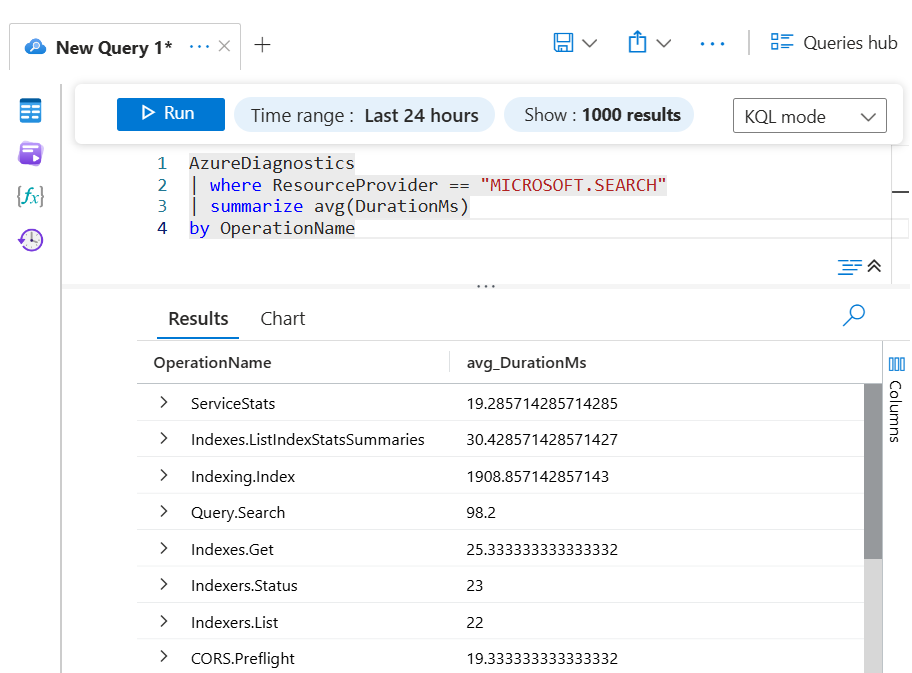
Sample Kusto queries
Here are a few basic Kusto queries you can use to explore your log data.
Run this query for all diagnostic logs from Azure AI Search services over the specified time period:
AzureDiagnostics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.SEARCH"
Run this query to see the 10 most recent logs:
AzureDiagnostics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.SEARCH"
| take 10
Run this query to group operations by Resource:
AzureDiagnostics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.SEARCH" |
summarize count() by Resource
Run this query to find the average time it takes to perform an operation:
AzureDiagnostics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.SEARCH"
| summarize avg(DurationMs)
by OperationName
Run this query to view the volume of operations over time split by OperationName with counts binned for every 10 seconds.
AzureDiagnostics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.SEARCH"
| summarize count()
by bin(TimeGenerated, 10s), OperationName
| render areachart kind=unstacked