Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can use Microsoft Entra ID security principals and role assignments for outbound connections from Azure AI Search to other Azure resources providing data, applied AI, or vectorization during indexing or queries.
To use roles on an outbound connection, first configure your search service to use either a system-assigned or user-assigned managed identity as the security principal for your search service in a Microsoft Entra tenant. Once you have a managed identity, you can assign roles for authorized access. Managed identities and role assignments eliminate the need for passing secrets and credentials in a connection string or code.
Prerequisites
A search service at the Basic tier or higher, any region.
An Azure resource that accepts incoming requests from a Microsoft Entra security principal that has a valid role assignment.
To create a managed identity, you must be an Owner or User Access Administrator roles. To assign roles, you must be an Owner, User Access Administrator, Role-based Access Control Administrator, or a member of a custom role with Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write permissions.
Supported scenarios
You can use managed identities for these scenarios.
| Scenario | System | User-assigned |
|---|---|---|
| Connect to indexer data sources 1 | Yes | Yes 2 |
| Connect to embedding and chat completion models in Azure OpenAI, Azure AI Foundry, and Azure Functions via skills/vectorizers 3 | Yes | Yes |
| Connect to Azure Key Vault for customer-managed keys | Yes | Yes |
| Connect to Debug sessions (hosted in Azure Storage) 1 | Yes | No |
| Connect to an enrichment cache (hosted in Azure Storage) 1, 4 | Yes | Yes 2 |
| Connect to a Knowledge Store (hosted in Azure Storage) 1 | Yes | Yes 2 |
1 For connectivity between search and storage, network security imposes constraints on which type of managed identity you can use. Only a system managed identity can be used for a same-region connection to Azure Storage, and that connection must be via the trusted service exception or resource instance rule. See Access to a network-protected storage account for details.
2 User-assigned managed identities can be used in data source connection strings. However, only the newer preview REST APIs and preview packages support a user-assigned managed identity in a connection string. Be sure to switch to a preview API if you set SearchIndexerDataUserAssignedIdentity as the identity in a data source connection.
3 Connections to Azure OpenAI, Azure AI Foundry, and Azure Functions via skills/vectorizers include: Custom skill, Custom vectorizer, Azure OpenAI embedding skill, Azure OpenAI vectorizer, AML skill and Azure AI Foundry model catalog vectorizer.
4 AI search service currently can't connect to tables on a storage account that has shared key access turned off.
Create a system managed identity
A system-assigned managed identity is a Microsoft Entra ID security principal that's automatically created and linked to an Azure resource, such as an Azure AI Search service.
You can have one system-assigned managed identity for each search service. It's unique to your search service and bound to the service for its lifetime.
When you enable a system-assigned managed identity, Microsoft Entra ID creates a security principal for your search service that's used to authenticate to other Azure resources. You can then use this identity in role assignments for authorized access to data and operations.
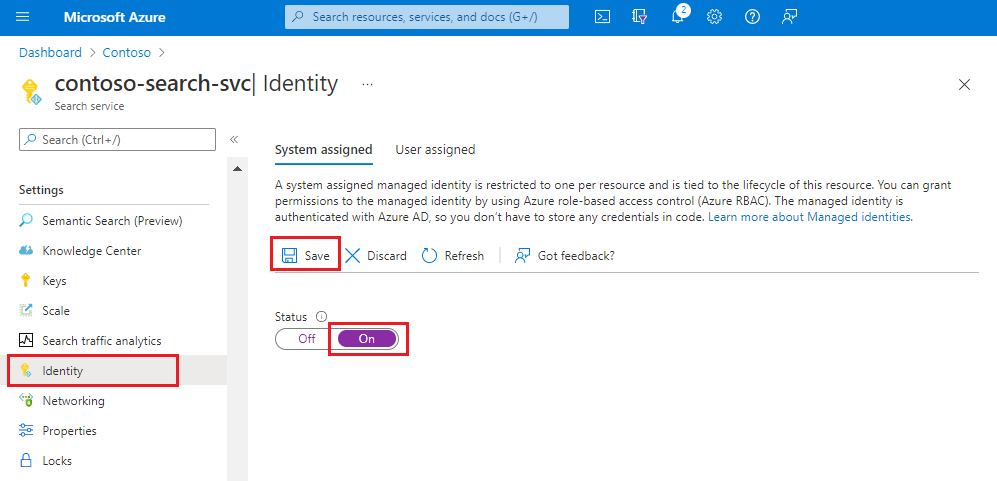
Sign in to the Azure portal and find your search service.
From the left pane, select Settings > Identity.
On the System assigned tab, under Status, select On.
Select Save.
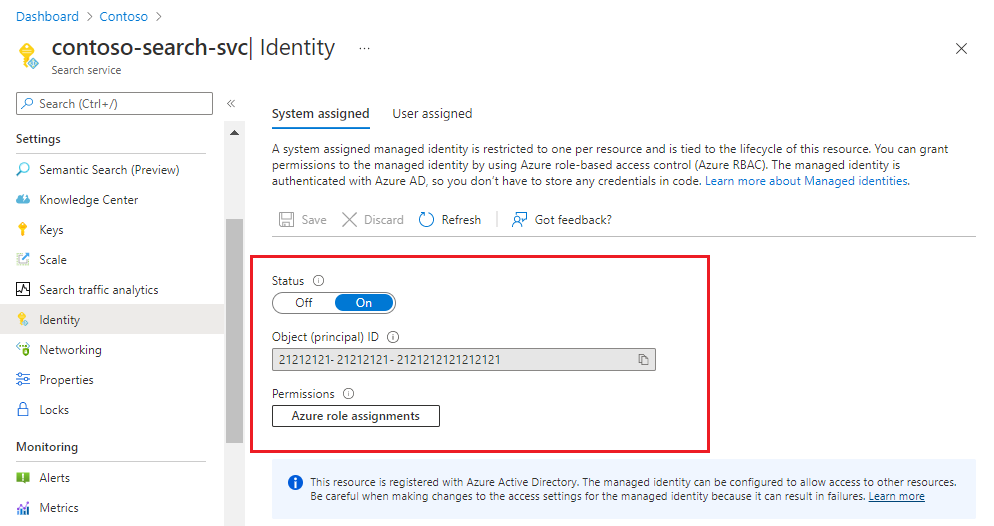
After you save the settings, the page updates to show an object identifier that's assigned to your search service.
Create a user-assigned managed identity
A user-assigned managed identity is an Azure resource that can be scoped to subscriptions, resource groups, or resource types.
You can create multiple user-assigned managed identities for more granularity in role assignments. For example, you might want separate identities for different applications and scenarios. As an independently created and managed resource, it's not bound to the service itself.
The steps for setting up a user-assigned managed identity are as follows:
In your Azure subscription, create a user-assigned managed identity.
On your search service, associate the user-assigned managed identity with your search service.
On other Azure services you want to connect to, create a role assignment for the identity.
Associating a user-assigned managed identity with an Azure AI Search service is supported in the Azure portal, Search Management REST APIs, and SDK packages that provide the feature.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the upper-left corner of your dashboard, select Create a resource.
Use the search box to find User Assigned Managed Identity, and then select Create.
Select the subscription, resource group, and region. Give the identity a descriptive name.
Select Create and wait for the resource to finish deploying.
It takes several minutes before you can use the identity.
On your search service page, select Settings > Identity.
On the User assigned tab, select Add.
Select the subscription and the user-assigned managed identity you previously created.
Assign a role
Once you have a managed identity, assign roles that determine search service permissions on the Azure resource.
Read permissions are needed for indexer data connections and for accessing a customer-managed key in Azure Key Vault.
Write permissions are needed for AI enrichment features that use Azure Storage for hosting debug session data, enrichment caching, and long-term content storage in a knowledge store.
The following steps illustrate the role assignment workflow. This example is for Azure OpenAI. For other Azure resources, see Connect to Azure Storage, Connect to Azure Cosmos DB, or Connect to Azure SQL.
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account, and go to your Azure OpenAI resource.
Select Access control from the left menu.
Select Add and then select Add role assignment.
Under Job function roles, select Cognitive Services OpenAI User and then select Next.
Under Members, select Managed identity and then select Members.
Filter by subscription and resource type (Search services), and then select the managed identity of your search service.
Select Review + assign.
Connection string examples
Recall from the scenarios description that you can use managed identities in connection strings to other Azure resources. This section provides examples. You can use generally available REST API versions and Azure SDK packages for connections using a system-assigned managed identity.
Tip
You can create most of these objects in the Azure portal, specifying either a system or user-assigned managed identity, and then view the JSON definition to get the connection string.
Here are some examples of connection strings for various scenarios.
Blob data source (system managed identity):
An indexer data source includes a credentials property that determines how the connection is made to the data source. The following example shows a connection string specifying the unique resource ID of a storage account.
A system managed identity is indicated when a connection string is the unique resource ID of a Microsoft Entra ID-aware service or application. A user-assigned managed identity is specified through an identity property.
"credentials": {
"connectionString": "ResourceId=/subscriptions/{subscription-ID}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-account-name};"
}
Blob data source (user managed identity):
User-assigned managed identities can also be used in indexer data source connection strings. However, only the newer preview REST APIs and preview packages support a user-assigned managed identity in a data source connection string. Be sure to switch to a preview version if you set SearchIndexerDataUserAssignedIdentity as the identity in a data source connection.
A search service user identity is specified in the identity property.
"credentials": {
"connectionString": "ResourceId=/subscriptions/{subscription-ID}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-account-name};"
},
. . .
"identity": {
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Azure.Search.DataUserAssignedIdentity",
"userAssignedIdentity": "/subscriptions/{subscription-ID}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/{user-assigned-managed-identity-name}"
}
A knowledge store definition includes a connection string to Azure Storage. The connection string is the unique resource ID of your storage account. Notice that the string doesn't include containers or tables in the path. These are defined in the embedded projection definition, not the connection string.
"knowledgeStore": {
"storageConnectionString": "ResourceId=/subscriptions/{subscription-ID}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/storage-account-name};"
}
An indexer creates, uses, and remembers the container used for the cached enrichments. It's not necessary to include the container in the cache connection string. You can find the object ID on the Identity page of your search service in the Azure portal.
"cache": {
"enableReprocessing": true,
"storageConnectionString": "ResourceId=/subscriptions/{subscription-ID}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-account-name};"
}
A debug session runs in the Azure portal and takes a connection string when you start the session. You can paste a string similar to the following example.
"ResourceId=/subscriptions/{subscription-ID}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-account-name}/{container-name};",
A custom skill targets the endpoint of an Azure function or app hosting custom code.
uriis the endpoint of the function or app.authResourceIdtells the search service to connect using a managed identity, passing the application ID of the target function or app in the property.
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Custom.WebApiSkill",
"description": "A custom skill that can identify positions of different phrases in the source text",
"uri": "https://contoso.count-things.com",
"authResourceId": "<Azure-AD-registered-application-ID>",
"batchSize": 4,
"context": "/document",
"inputs": [ ... ],
"outputs": [ ...]
}
Connection examples for models
For connections made using managed identities, this section shows examples of connection information used by a search service to connect to a model on another resource. A connection through a system managed identity is transparent; the identity and roles are in place, and the connection succeeds if they are properly configured. In contrast, a user managed identity requires extra connection properties.
Azure OpenAI embedding skill and Azure OpenAI vectorizer:
An Azure OpenAI embedding skill and vectorizer in AI Search target the endpoint of an Azure OpenAI hosting an embedding model. The endpoint is specified in the Azure OpenAI embedding skill definition and/or in the Azure OpenAI vectorizer definition.
The system-managed identity is used automatically if "apikey" and "authIdentity" are empty, as demonstrated in the following example. The "authIdentity" property is used for user-assigned managed identity only.
System-managed identity example:
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Text.AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill",
"description": "Connects a deployed embedding model.",
"resourceUri": "https://url.openai.azure.com/",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-ada-002",
"modelName": "text-embedding-ada-002",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "text",
"source": "/document/content"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "embedding"
}
]
}
Here's a vectorizer example configured for a system-assigned managed identity. A vectorizer is specified in a search index.
"vectorizers": [
{
"name": "my_azure_open_ai_vectorizer",
"kind": "azureOpenAI",
"azureOpenAIParameters": {
"resourceUri": "https://url.openai.azure.com",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-ada-002",
"modelName": "text-embedding-ada-002"
}
}
]
User-assigned managed identity example:
A user-assigned managed identity is used if "apiKey" is empty and a valid "authIdentity" is provided.
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Text.AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill",
"description": "Connects a deployed embedding model.",
"resourceUri": "https://url.openai.azure.com/",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-ada-002",
"modelName": "text-embedding-ada-002",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "text",
"source": "/document/content"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "embedding"
}
],
"authIdentity": {
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Azure.Search.DataUserAssignedIdentity",
"userAssignedIdentity": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourcegroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<user-assigned-managed-identity-name>"
}
}
Here's a vectorizer example configured for a user-assigned managed identity. A vectorizer is specified in a search index.
"vectorizers": [
{
"name": "my_azure_open_ai_vectorizer",
"kind": "azureOpenAI",
"azureOpenAIParameters": {
"resourceUri": "https://url.openai.azure.com",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-ada-002",
"modelName": "text-embedding-ada-002"
"authIdentity": {
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Azure.Search.DataUserAssignedIdentity",
"userAssignedIdentity": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourcegroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<user-assigned-managed-identity-name>"
}
}
}
]
Check for firewall access
If your Azure resource is behind a firewall, make sure there's an inbound rule that admits requests from your search service and from the Azure portal.
For same-region connections to Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, use a system managed identity and the trusted service exception. Optionally, you can configure a resource instance rule to admit requests.
For all other resources and connections, configure an IP firewall rule that admits requests from Azure AI Search. See Indexer access to content protected by Azure network security features for details.