Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you gain a comprehensive understanding of the different data sources and tools available for SAP data extraction, and how to select the most appropriate option based on your analytical goals. The content covers the structure and purpose of each data layer within SAP systems. It also highlights the integration capabilities towards Microsoft Fabric, and the considerations for reliability, performance, and business alignment.
Microsoft Fabric is a fully integrated, SaaS-based data platform that unifies data engineering, real-time analytics, data science, business intelligence, and governance into a single experience. Built on OneLake, Fabric centralizes data storage and enables seamless collaboration across roles—from data engineers to business users. At its core is OneLake, a unified data lake that centralizes storage and enables seamless data access across services. Fabric also integrates AI capabilities through Copilot and Azure AI Studio, empowering users to derive insights faster and more intuitively. Designed for simplicity, scalability, and collaboration, Microsoft Fabric helps organizations streamline their analytics workflows, reduce complexity, and accelerate their AI transformation journey
Enterprises are increasingly adopting Microsoft Fabric as the foundation of their data landscape to unify business applications, IoT telemetry, and AI workloads. By consolidating all analytics workloads into a single environment, Microsoft Fabric accelerates insight delivery and eliminates data silos. SAP systems are one of the most critical data sources as they contain data supporting core business operations and can also be integrated into the unified platform. This integration enriches enterprise data and enables a more holistic view of business performance. You can build powerful dashboards that explore trends and highlight issues, reflecting end-to-end business processes using data from across systems and departments, regardless of its source. This is made possible by having all relevant data unified in a single platform.
Important
Before you begin any data extractions from SAP systems, always verify your organization’s SAP licensing entitlements. Certain extraction methods can require other licenses or specific usage rights.
Data sources in SAP system
SAP offers multiple layers of data access, each serving different analytical and reporting needs. This section introduces the main types of data sources available in an SAP landscape, explaining what they are and how they work.
Tables and views
SAP Tables are the foundational layer of data storage in the SAP system. Every transaction processed in SAP, from a goods receipt to an invoice or sales order, gets stored in a set of structured tables in the underlying relational database (such as HANA, Oracle, or SQL Server). These tables contain the raw, transactional data of your business. In modern versions of SAP systems there's one-to-one representation of the ABAP tables to the database tables. In older releases that’s not always the case and accessing pool/cluster tables at the database level isn't possible. Using tables requires in-depth knowledge of SAP’s data model, otherwise you risk misinterpreting the business context.
Core Data Services views / extractors
Core Data Services (CDS) Views and Extractors provide a business-oriented, multidimensional view of transactional data directly within the operational SAP system. These sources offer predefined logic that reflects how data is used in day-to-day processes, such as sales, purchasing, or finance. Instead of accessing raw tables, CDS Views and Extractors expose data in a way that aligns with business meaning. For example, showing only active orders or including relevant descriptions and calculated fields.
Business Warehouse InfoObjects / InfoProviders
InfoObjects and InfoProviders are part of the SAP Business Warehouse (BW) semantic layer. They form the multidimensional model based on facts and dimensions to use in modeling and reporting across all layers of BW architecture. As data moves through the layers it's continuously transformed, cleansed, and enriched. As a result, the data in the final data mart is consistent and prepared for use in enterprise dashboards and reports.
BW queries
Queries are the main interface for consuming data stored in SAP BW. They define business-ready metrics such as key revenue, cost, or quantity measures by applying calculations, filters, and aggregations on top of InfoProviders. Queries are also tightly integrated with SAP's authorization model and optimized for performance.
Choose the right data source
Selecting the right data source depends on the ultimate objective and how much of existing transformation you want to reuse. As explained in the previous section SAP systems offer several layers of data access, each suited to different stages in the data journey, from raw transactions to fully modeled business metrics. Transactional data is stored in a highly normalized form, meaning information is divided across many smaller, related tables to reduce redundancy and improve efficiency. These tables reflect the raw output of business processes, exactly as it's generated in the system. Such design promotes data integrity but makes reporting and analytics more complex.
In moving from base tables toward higher layers, each step adds more structure, consistency, and alignment with business meaning. CDS Views and BW Extractors shape the transactional data into multidimensional format by applying basic joins, filters, and business logic to simplify analytics and reporting. These objects can present different perspectives on the same underlying data, depending on the reporting need. For example, one view can focus on open sales orders while another highlights delivered items. This flexibility allows the same dataset to support multiple analytical scenarios without duplicating the raw data.
Further along the data journey, BW objects take over the responsibility for storing, structuring, and preparing data for enterprise reporting. InfoObjects and InfoProviders together form a standardized foundation for analytics across departments and tools. At the top, queries expose curated datasets, complete with predefined filters, calculations, and key figures, ready to be consumed by dashboards and external analytics platforms.
As a general recommendation, the higher the level you access in the data stack, the more content and business logic you can reuse. Instead of manually joining base tables to create a consolidated view of sales orders, you can apply dedicated objects delivered by SAP, which already include relevant joins, filters, and field mappings. This approach significantly reduces development effort and ensures consistency with how data is used within the system. However, it also means to accept the built-in transformations such as filtering out certain document statuses. If other fields are needed, changes must be made at the source level, for example by extending the CDS View.
The following table provides examples of common scenarios and recommends the most suitable SAP data source in each case. The use of a specific object is a design decision and should always be evaluated based on available options, data requirements, and system capabilities.
| Scenario / Intent | Recommended data source |
|---|---|
| I want to access raw transactional tables and apply custom transformations and business logic myself. | SAP Tables |
| I don’t have detailed knowledge of SAP’s underlying data model and want to reuse the existing structure and relationships from the transactional system. | CDS Views / BW Extractors |
| I need to build dashboards based on transactional data, but prefer to work with a curated, business-aligned model. | CDS Views / BW Extractors |
| My organization already has a BW system with validated data models, and I want to use those as the basis for reporting. | BW InfoObjects / InfoProviders |
| I need a secure reporting layer with predefined restrictions and business-specific key figures, ready for consumption in BI tools. | BW Queries |
Summary of connectivity options
The following table summarizes the available connectivity options to SAP systems.
| Connector | Sources | Use case | ETL Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP BW (Application Server or Message Server) | SAP BW, SAP BW/4HANA SAP S/4HANA |
Access to multidimensional analytic layer | Microsoft Fabric (Dataflow Gen2) |
| SAP HANA | SAP HANA, SAP HANA Cloud SAP Datasphere SAP BW-on-HANA SAP BW/4HANA |
Access to multidimensional analytic layer Access to SQL artifacts (tables, views) Access to HANA Calculation Views exposed by SAP BW-on-HANA or BW/4HANA |
Microsoft Fabric (Dataflow Gen2, Pipeline, Copy Job) |
| SAP Table (Application Server or Message Server) | SAP S/4HANA SAP ECC |
SAP data dictionary (DDIC) tables, views ABAP CDS Views |
Microsoft Fabric (Pipeline) |
| SAP CDC | SAP S/4HANA SAP ECC |
SAP data dictionary (DDIC) tables, views ABAP CDS Views |
Azure Data Factory (Data flow) |
| SAP BW OpenHub (Application Server or Message Server) | SAP BW | Access to data in BW InfoProviders (ADSOs) | Microsoft Fabric (Pipeline) |
| OData | SAP SuccessFactors SAP C4C SAP S/4HANA SAP ECC |
OData Services | Microsoft Fabric (Dataflow Gen2, Pipeline) |
| ODBC | SAP HANA, SAP HANA Cloud SAP Datasphere |
Access to SQL artifacts (tables, views) | Microsoft Fabric (Dataflow Gen2, Pipeline) |
| Open Mirroring | SAP S/4HANA SAP ECC (based on third party features) |
SAP data dictionary (DDIC) tables, views ABAP CDS Views |
Microsoft Fabric |
| Premium Outbound Integration | SAP S/4HANA SAP ECC SAP BW, SAP BW/4HANA (and other solutions as per Datasphere connectivity options) |
SAP data dictionary (DDIC) tables, views ABAP CDS Views SAP ODP |
SAP Datasphere |
SAP data extraction tools and solutions
This section provides an overview of available tools and solutions for you to consider when extracting SAP data to Microsoft Fabric.
SAP data extraction using Microsoft Fabric
You can use pipelines and dataflows in Microsoft Fabric to extract and transform data from various SAP data sources.
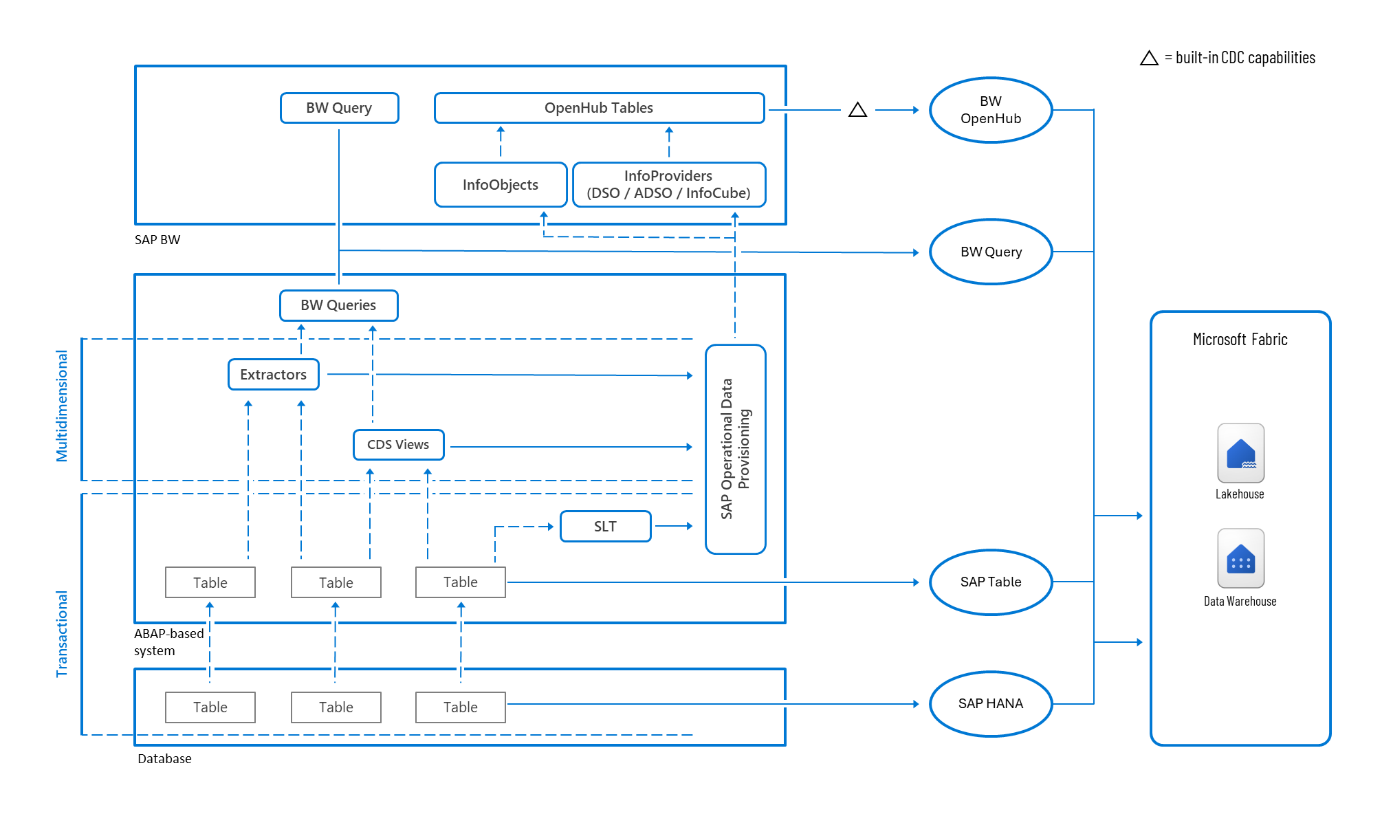
Figure 1: SAP data connectivity options within Microsoft Fabric.
SAP Table connector
The SAP Table connector connects to ABAP-based SAP systems and enables snapshot extraction of table data. It supports data filtering using a simple ABAP-like syntax. For larger data volumes, you can apply built-in partitioning based on selected columns such as posting timestamp to divide the table into smaller chunks. The connector is available through pipelines in Microsoft Fabric.
SAP HANA connector
The SAP HANA connector lets you connect to SAP HANA database. It supports two access layers: the multidimensional analytic layer that's based on HANA calculation views, and the transactional layer that provides access to data stored in tables and views.
When connecting through Dataflow Gen2, designed for semantic modeling and analytics, the SAP HANA connector typically accesses the multidimensional layer. Calculation views work similarly to SAP BW queries and are often used directly access curated data and KPIs following built-in logic.
In contrast, when the connector is used within a Microsoft Fabric pipeline, built for ETL and large-scale data ingestion, it defaults to accessing database tables and SQL views. This approach works well when working with larger amounts of data thanks to other data partitioning capabilities that allow large datasets to be split and processed in parallel, improving performance and scalability.
Generic ODBC
Generic ODBC connectivity enables connectivity to a wide range of databases, including but not limited to SAP HANA. It provides flexible access to underlying tables and views that make it suitable for scenarios where direct access to raw, transactional data is needed. When used with an SAP HANA database, the Generic ODBC connector connects to the transactional layer, allowing users to query data from base tables and SQL views.
SAP BW connector
The SAP BW connector is designed to access the multidimensional analytic layer in SAP systems. It's used to deliver business-ready datasets and contains predefined measures, hierarchies, filters, and authorizations, making the data easy to interpret and consume in reporting and analytics tools. The connector provides a reliable way to extract curated and semantically rich data, which aligns closely with enterprise reporting standards. The connector supports BW queries from SAP BW and BW/4HANA, and the embedded analytic layer in SAP S/4HANA, which you can use to access SAP CDS Views.
SAP BW OpenHub
The SAP BW OpenHub connector enables data extraction from OpenHub destinations in SAP BW systems. OpenHub destinations are used to expose BW-managed data for external consumption. Any object supported by the SAP Data Transfer Process (DTP) can serve as a source for OpenHub, including DataStore Objects (DSOs), InfoCubes, and DataSources. This makes it a flexible option for exporting structured, transformed data.
The connector supports delta extraction, which captures only records that have changed since the last successful load. Delta handling is managed by the SAP BW system based on the logic defined in the DTP, typically using timestamps, request IDs, or change log positions. Once configured, the system applies the delta logic automatically, reducing the need for manual tracking or custom implementation.
OData connector
Data extraction can also be handled by OData services, which expose business data from SAP systems through a standardized, REST-based protocol. This approach is suited for accessing data made available via SAP Gateway services, like those in SAP S/4HANA and SAP Business Suite. SAP provides a rich set of preconfigured OData services covering many core business objects and processes. In addition, custom or standard CDS Views can be exposed as OData endpoints, that offer a flexible way to retrieve semantically rich and well-structured data.
SAP data extraction using Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory is a cloud-based data integration service that enables you to build and schedule pipelines for moving and transforming data across diverse systems. Many data connectors, including SAP-specific ones like SAP Table and SAP BW, are already available in Microsoft Fabric. If SAP integration is a new workload you plan to onboard and you're considering Microsoft Fabric for analytics, it's strongly recommend to also use it for data integration. This way, you benefit from a more unified experience across data ingestion, transformation, and analytics all within a single platform. However, if you already have SAP pipelines built in Azure Data Factory or need to use the SAP CDC connector, there’s no immediate need to replatform. Existing pipelines and dataflows can be integrated with OneLake.
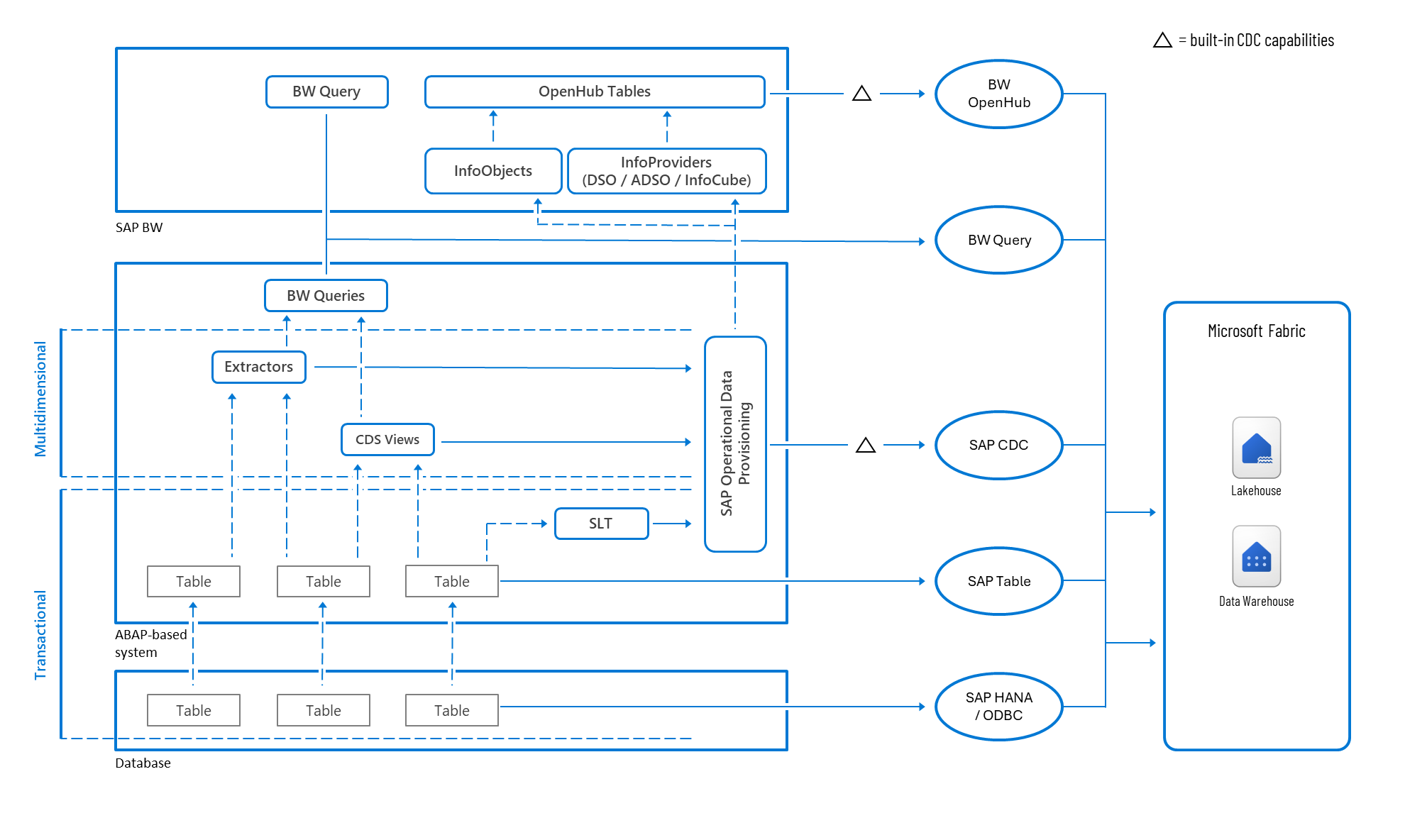
Figure 2: SAP to Microsoft Fabric data connectivity options within Azure Data Factory.
SAP CDC connector
The SAP CDC connector enables incremental data extraction from SAP systems using the SAP Operational Data Provisioning framework, available in ABAP environments. The ODP framework automatically tracks deltas in the source system and storing them in a delta queue. Each time the connector runs, it retrieves only the new or changed records since the last extraction, based on a subscription maintained by the framework.
It supports a wide range of SAP data sources, including:
- BW Extractors
- Core Data Services (CDS) Views
- SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT)
- BW InfoProviders
- SAP HANA Information Views
It also supports data filtering and partitioning to optimize performance and control data volume during extraction.
When the target is a relational data store, the SAP CDC connector automatically applies inserts, updates, and deletes to keep the destination synchronized with the source. This built-in delta merge process ensures that downstream systems always reflect the latest state of the SAP data without requiring manual reconciliation.
Note
While Microsoft fully supports the SAP CDC connector as a reliable solution for data extraction, before using the SAP CDC connector, consult the relevant SAP Note: 3255746 - Unpermitted usage of ODP Data Replication APIs to determine if it's relevant for your current SAP licensing.
Learn more about SAP CDC connector in Azure Data Factory
SAP data extraction using SAP Datasphere
SAP Datasphere is SAP’s enterprise-grade solution for extracting and transforming data across heterogeneous systems. It supports connections to third-party services and enables flexible data movement strategies tailored to enterprise needs.
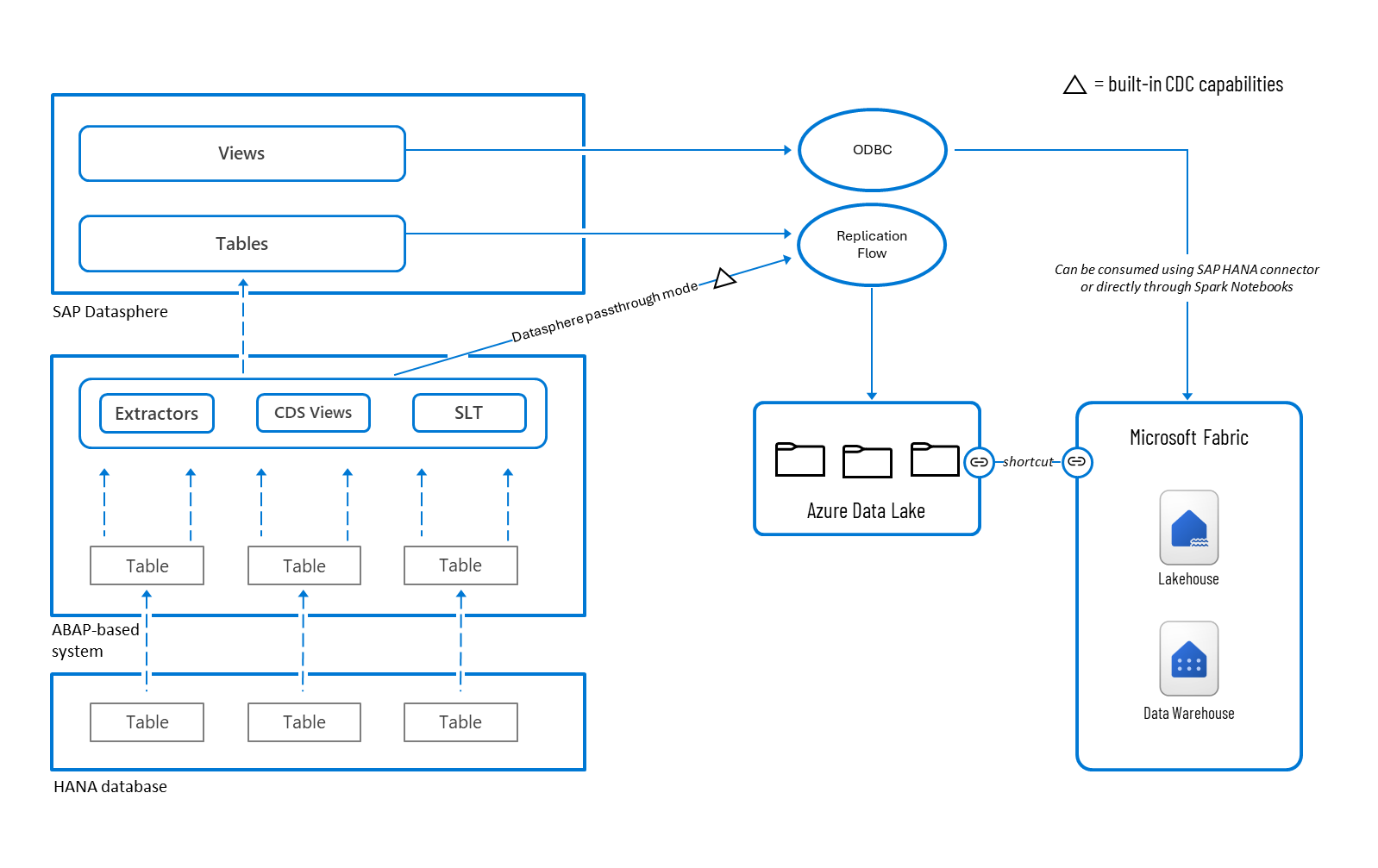
Figure 3: SAP to Microsoft Fabric data connectivity options within SAP Datasphere.
Premium Outbound Integration
Using Premium Outbound Integration, customers can configure replication flows to extract data from SAP source systems and ingest it into Azure Data Lake Gen2. The data source could be an object within SAP Datasphere, but this integration also allows data to be extracted directly from the source system without being stored in SAP Datasphere.
Once the data lands in Azure Data Lake Gen2, it can be exposed in Microsoft Fabric lakehouses using shortcuts. These shortcuts provide seamless, read-only access to the ingested data without duplicating storage, enabling powerful analytics and transformation workflows directly within Fabric.
ODBC connection
ODBC connectivity allows customers to consume views in SAP Datasphere directly from Spark notebooks in Microsoft Fabric, enabling real-time data exploration, transformation, and advanced analytics without the need for replication. The SAP HANA connector can also be used to ingest data into Microsoft Fabric lakehouses using pipelines and dataflows.
Partner solutions
A growing ecosystem of trusted partners brings specialized expertise in extracting data from complex SAP environments such as SAP S/4HANA and SAP BW/4HANA into Microsoft Fabric. These partners go beyond standard connectors by delivering custom-built add-ons that address enterprise-specific requirements.
| Partner solution | Open Mirroring | Lakehouse Integration | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAB | Supported | Supported | Link |
| ASAPIO | Supported | Supported | Link |
| Theobald | Supported | Supported | Link |
| Simplement | Supported | Supported | Link |
| SNP Glue | Supported | Supported | Link |
Learn more about partner solutions supporting Open Mirroring.
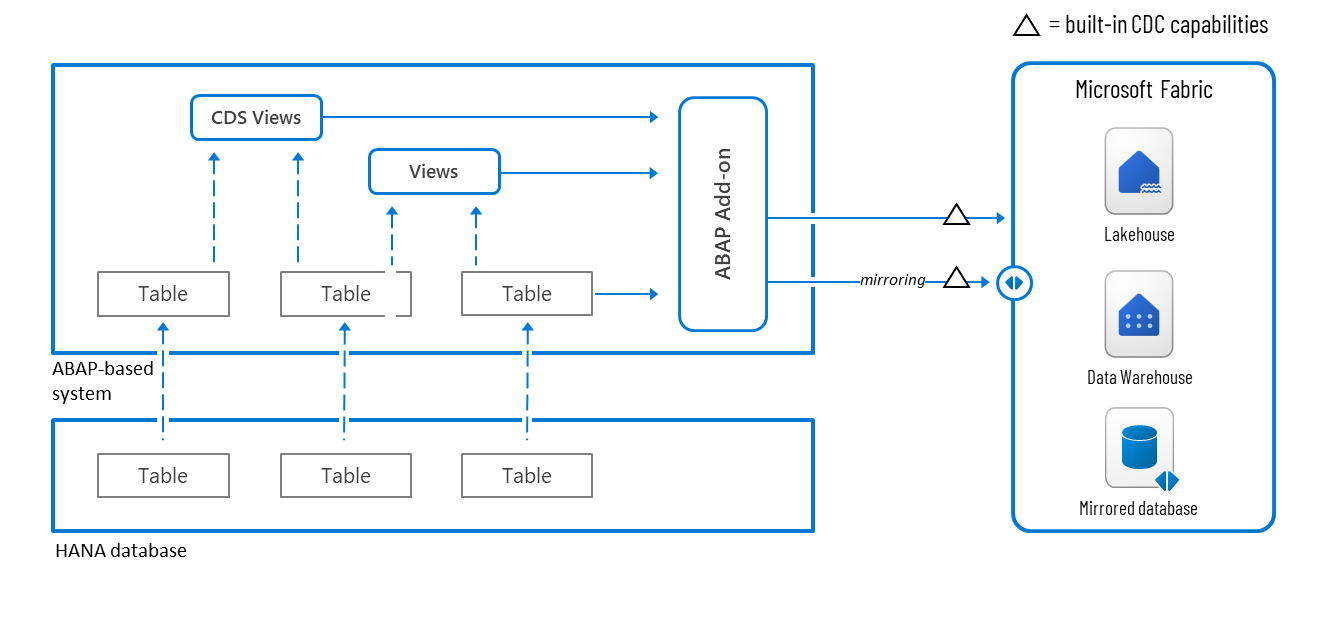
Figure 4: SAP to Microsoft Fabric data connectivity options using partner solutions.
Partner solutions usually support two integration patterns:
Open Mirroring
Partner solutions apply a set of native Microsoft Fabric APIs to synchronize source datasets with mirrored databases in Fabric. This approach ensures that the target tables remain a consistent and up-to-date copy of the source, as the mirroring engine automatically process and merges changes.
Learn more about Open Mirroring in Microsoft Fabric.
Lakehouse
Direct lakehouse integration allows partners to ingest data into Fabric in both full and incremental modes. While this method offers flexibility and control, it usually requires another processing to handle deduplication and consolidation of records before the data is ready for downstream analytics.
Resources
SAP Knowledge Center – data integration
Overview and architecture of the SAP CDC capabilities
What’s new with SAP connectivity in Microsoft Fabric – July 2025