Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you use Azure CLI to set up Microsoft Entra authentication for an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster. You create variables that are used in commands that create an OAuth callback URL, an application registration and client secret, and update the application's permissions.
Prerequisites
- An existing Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster. If you don't have a cluster, see create a new cluster.
- Azure CLI 2.30.0 or later installed on your computer. Use
az --versionto find the installed version of Azure CLI. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI. You can also use Azure Cloud Shell with Bash to run commands. - OpenShift CLI installed on your computer or in your Bash Cloud Shell. For more information, see Install the OpenShift CLI.
Create variables
Retrieve your cluster-specific URLs that are used to configure the Microsoft Entra application.
Set the variables for resource group and cluster name. Replace <resourceGroupName> with your resource group's name and <aroClusterName> with your cluster's name.
resourceGroup=<resourceGroupName>
aroCluster=<aroClusterName>
Create the following variables that are used in other commands to complete the steps in this article.
domain=$(az aro show --resource-group $resourceGroup --name $aroCluster --query clusterProfile.domain --output tsv)
location=$(az aro show --resource-group $resourceGroup --name $aroCluster --query location --output tsv)
apiServer=$(az aro show --resource-group $resourceGroup --name $aroCluster --query apiserverProfile.url --output tsv)
webConsole=$(az aro show --resource-group $resourceGroup --name $aroCluster --query consoleProfile.url --output tsv)
Create the cluster's OAuth callback URL and store it in the variable oauthCallbackURL. The entraID at the end of the OAuth callback URL must match the OAuth identity provider name that you create later in the oidc.yaml file.
The format of the oauthCallbackURL is dependent on if you're using a custom domain.
If you have a custom domain like
contoso.com, run the following command.oauthCallbackURL=https://oauth-openshift.apps.$domain/oauth2callback/entraIDIf you're not using a custom domain, the
$domainis an eight character alphanumeric string that precedes the$location.aroapp.io.oauthCallbackURL=https://oauth-openshift.apps.$domain.$location.aroapp.io/oauth2callback/entraID
Create a Microsoft Entra application for authentication
Create a Microsoft Entra application and set a client secret for the application.
appId=$(az ad app create \
--display-name aro-auth \
--web-redirect-uris $oauthCallbackURL \
--query appId --output tsv)
clientSecret=$(az ad app credential reset --id $appId --query password --output tsv)
The values are stored in variables and clientSecret displays a console message that the command output contains credentials. The value is used later in this article and when you're finished you can clear the variable using the clientSecret="" command.
For more information about the commands to create the app and credentials, see az ad app create and az ad app credential reset.
Retrieve the tenant ID of the subscription that owns the application.
tenantId=$(az account show --query tenantId --output tsv)
Create a manifest file to define the optional claims to include in the ID Token
Application developers can use optional claims in their Microsoft Entra applications to specify which claims they want in tokens sent to their application.
You can use optional claims to:
- Select other claims to include in tokens for your application.
- Change the behavior of certain claims that Microsoft Entra ID returns in tokens.
- Add and access custom claims for your application.
You configure OpenShift to use the email claim and fall back to upn to set the Preferred Username by adding the upn as part of the ID token returned by Microsoft Entra ID.
Create a manifest.json file to configure the Microsoft Entra application.
cat > manifest-test-file.json<< EOF
{
"idToken": [
{
"name": "email",
"source": null,
"essential": false,
"additionalProperties": []
},
{
"name": "upn",
"source": null,
"essential": false,
"additionalProperties": []
}
]
}
EOF
Update the Microsoft Entra application's optionalClaims with a manifest
To use the manifest file and update the application's optionalClaims, run the following command.
az ad app update \
--id $appId \
--optional-claims @manifest.json
Update the Microsoft Entra application scope permissions
To be able to read the user information from Microsoft Entra ID, we need to define the proper scopes.
Add permission for the Microsoft Graph User.Read scope to enable sign in and read user profile. For more information, see User.Read.
az ad app permission add \
--api 00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000 \
--api-permissions e1fe6dd8-ba31-4d61-89e7-88639da4683d=Scope \
--id $appId
You can ignore the message to grant the consent unless you're authenticated as a Global Administrator for this Microsoft Entra ID. Standard domain users are asked to grant consent when they first sign in to the cluster with their Microsoft Entra credentials.
Assign users and groups to the cluster (optional)
Applications registered in a Microsoft Entra tenant are, by default, available to all users of the tenant who authenticate successfully. Microsoft Entra ID allows tenant administrators and developers to restrict an app to a specific set of users or security groups in the tenant.
Follow the instructions on the Microsoft Entra documentation to Restrict a Microsoft Entra app to a set of users.
Configure OpenShift OpenID authentication
Retrieve the kubeadmin credentials. Run the following command to find the password for the kubeadmin user.
kubeadminPassword=$(az aro list-credentials \
--name $aroCluster \
--resource-group $resourceGroup \
--query kubeadminPassword --output tsv)
Sign in to the OpenShift cluster's API server using the following command.
oc login $apiServer --username kubeadmin --password $kubeadminPassword
Create an OpenShift secret to store the Microsoft Entra application secret.
oc create secret generic openid-client-secret-azuread \
--namespace openshift-config \
--from-literal=clientSecret=$clientSecret
Create an oidc.yaml file to configure OpenShift OpenID authentication against Microsoft Entra ID.
cat > oidc.yaml<< EOF
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1
kind: OAuth
metadata:
name: cluster
spec:
identityProviders:
- name: entraID
mappingMethod: claim
type: OpenID
openID:
clientID: $appId
clientSecret:
name: openid-client-secret-azuread
extraScopes:
- email
- profile
extraAuthorizeParameters:
include_granted_scopes: "true"
claims:
preferredUsername:
- email
- upn
name:
- name
email:
- email
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/$tenantId
EOF
Apply the configuration to the cluster.
oc apply -f oidc.yaml
You get a response like the following example.
oauth.config.openshift.io/cluster configured
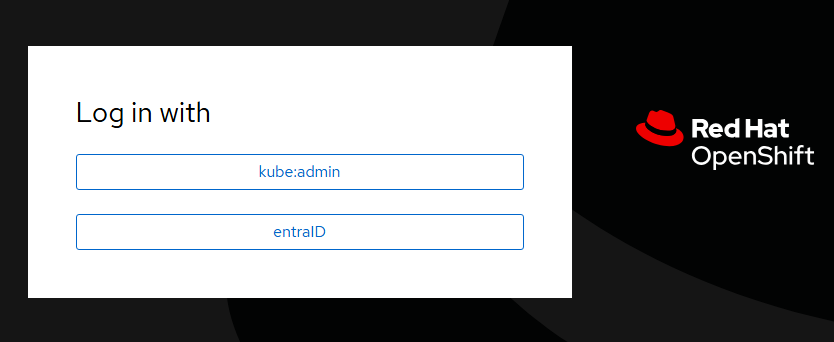
Verify sign in using Microsoft Entra ID
Sign out of the OpenShift Web Console and sign in again, and you'll see a new option to sign in with entraID. You might need to wait for a few minutes for the option to become available.