Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to discover MySQL database instances running on servers in your datacenter, using Azure Migrate appliance. The discovery process is agentless; no agents are installed on the target servers.
Supported regions
The following table lists the regions that support MySQL Discovery and Assessment in preview:
| Geography | Region |
|---|---|
| Asia Pacific | Southeast Asia |
| Australia | Australia East |
| Canada | Canada Central |
| Europe | North Europe West Europe |
| France | France Central |
| Japan | Japan East |
| Korea | Korea Central |
| United Kingdom | UK South |
| United States | Central US West US 2 |
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a free account.
Before you begin to discover MySQL database instances, use the below links to create an Azure Migrate project and deploy an appliance as per your requirements in one of the supported regions:
After you create a project, ensure you've completed the server discovery using the Azure Migrate appliance.
Ensure that you perform the discovery of software inventory by providing the server credentials to the appliance configuration manager.
Note
Only Azure Migrate projects created with public endpoint connectivity are supported. Private endpoint projects aren't supported in the preview.
Provide MySQL credentials
Open the appliance configuration manager, complete the prerequisite checks and registration of the appliance.
Navigate to the Manage credentials and discovery sources panel.
In Step 3: Select MySQL authentication credential type, provide a friendly name, input the MySQL username, and password and select Save.
Note
- Ensure that the user corresponding to the added MySQL credentials have the following privileges:
- Select permission on information_schema tables.
- Select permission on mysql.users table.
- For MySQL discovery, ensure the appliance's IP or domain is allowed by configuring the necessary firewall rules and MySQL user privileges. The bind-address in my.cnf should also be set to allow external connections if needed.
- Use the following commands to grant the necessary privileges to the MySQL user
GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'username@ip'; GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO 'username@ip'; GRANT SELECT (User, Host, Super_priv, File_priv, Create_tablespace_priv, Shutdown_priv) ON mysql.user TO 'username@ip'; GRANT SELECT ON information_schema.* TO 'username@ip'; GRANT SELECT ON performance_schema.* TO 'username@ip';- Ensure that the user corresponding to the added MySQL credentials have the following privileges:
You can review the discovered MySQL databases after around 24 hours of discovery initiation, through the Discovered servers view. To expedite the discovery of your MySQL instances follow the steps:
- After adding the MySQL credentials on the appliance configuration manager restart the discovery services on appliance.
- In your Azure Migrate project navigate to Servers, databases and Web apps blade. On this tab locate Appliances in the right side of Assessment tools section.
- Select the number projected against total. This will take you to the Appliances blade. Select the appliance where the credentials were added.
- Select the Refresh services link available at the bottom of the appliance screen. This will restart all the services and MySQL instances will start appearing in the inventory after the refresh.
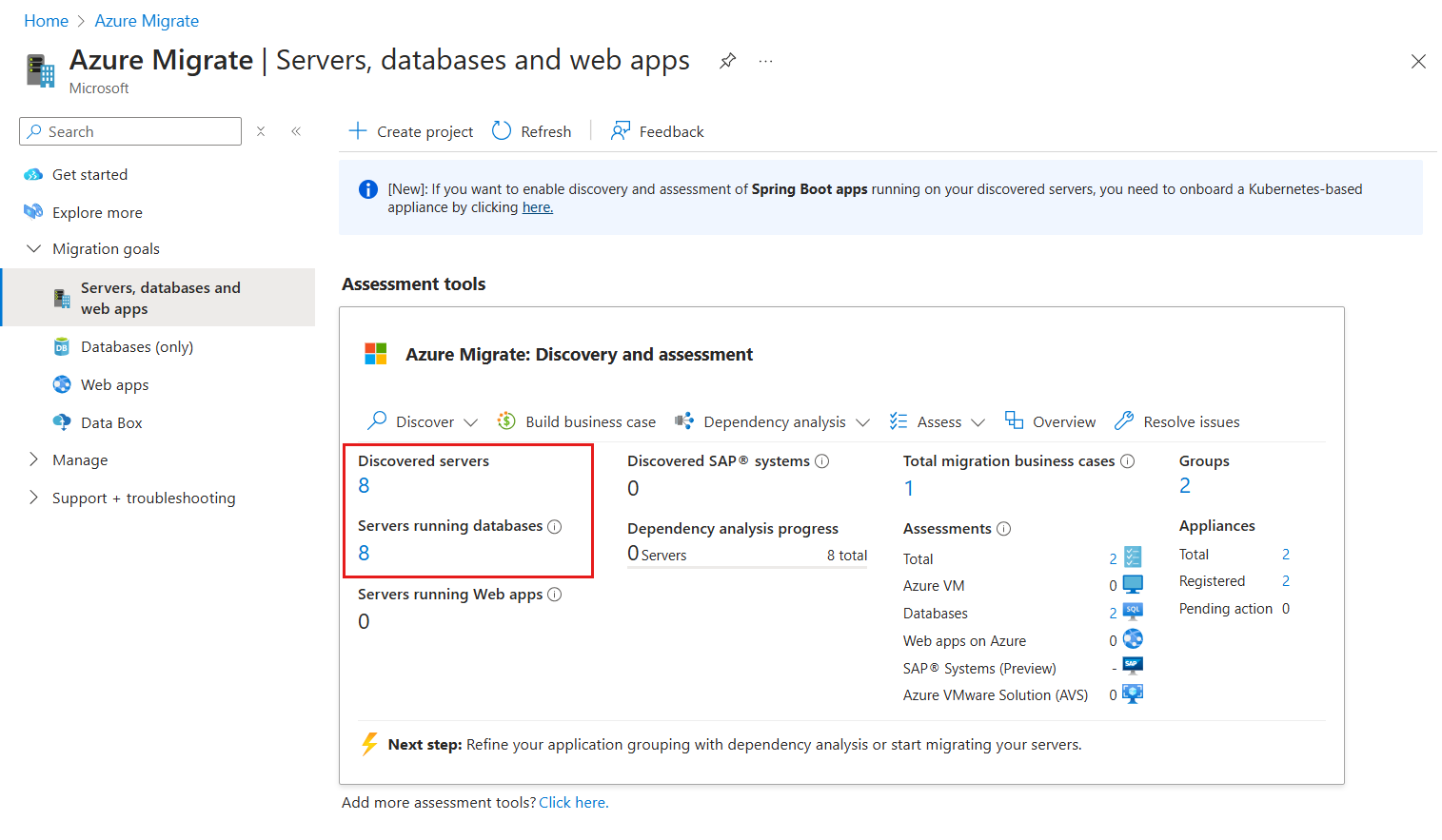
On the Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment tile on the Hub page, select the number below the Discovered servers.
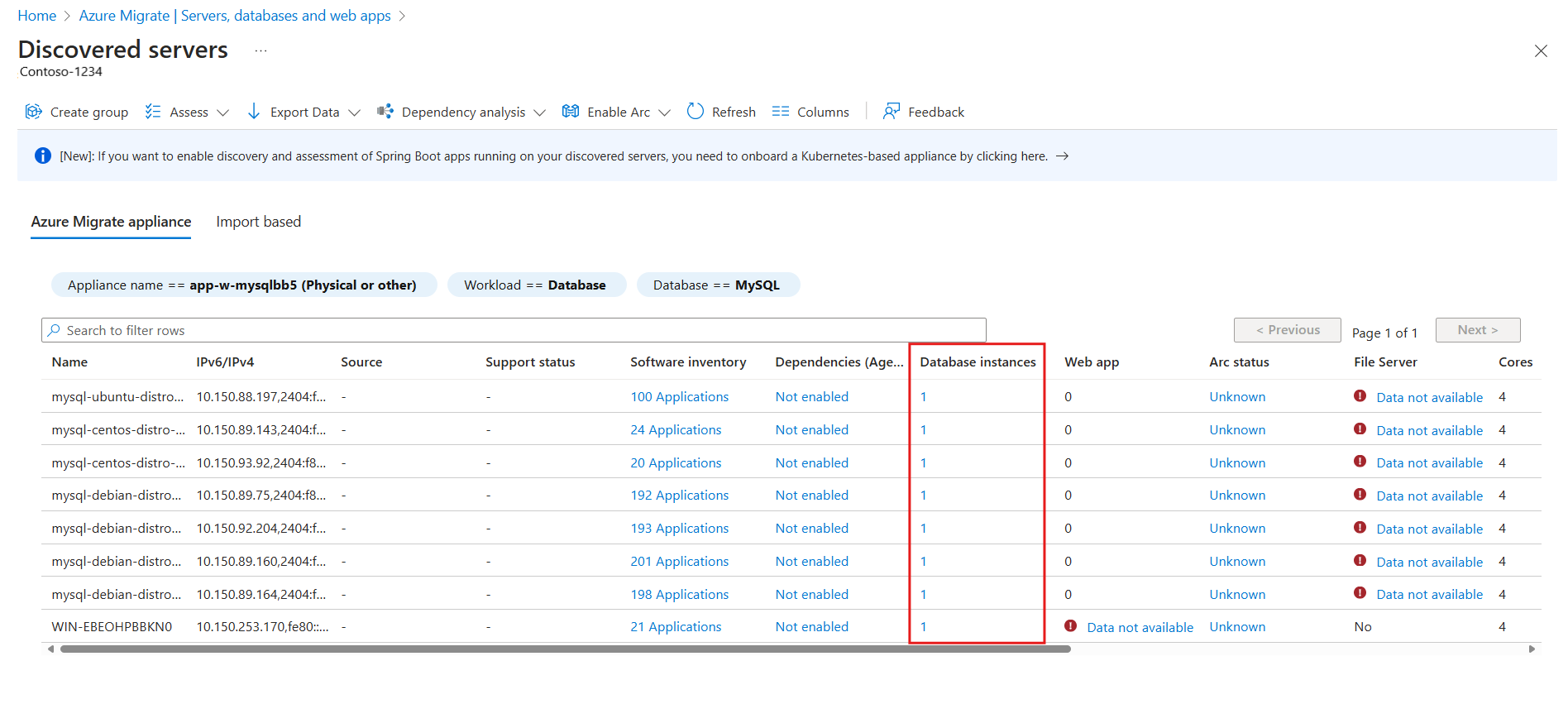
Select the filters Workload == Databases and Database type == MySQL to view the list of all servers that are running MySQL database instances in your environment.
To view basic information of the MySQL database instances in each of the discovered servers, select the number in the Database instances column for the corresponding server.
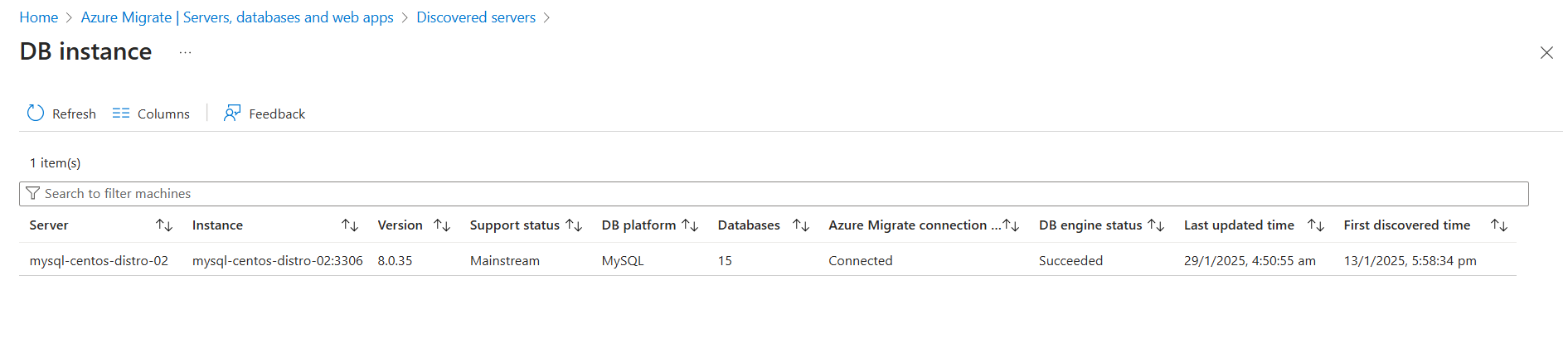
Review the following information on the DB instance page:
- MySQL server and instance name
- MySQL edition, version, and version support status
- Number of user databases in the instance
- Azure Migrate connection status, DB engine status, first discovered time, and last updated time
Tip
Select Columns to filter the data.
Next steps
- Learn how to create and run a MySQL assessment.
- Learn more about how MySQL assessments are calculated.