Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes the AppCAT CLI command usage.
Commands
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| appcat analyze | This subcommand enables running source code analysis on input source code or on a binary. |
| appcat transform | This subcommand enables converting XML rules to YAML. |
| appcat version | This subcommand prints the tool version. |
appcat analyze
The following sections provide a detailed description of the available appcat analyze command line parameters.
Required parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--input |
The path to the application source code or a binary file for analysis. Use a comma-separated list for multiple values: --input <input1>,<input2>,.... The default value is []. |
--output |
The directory where the analysis results are stored. |
Optional parameters
| Category | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Source & target technologies | ||
--list-sources |
Displays the available migration source technologies. | |
--list-targets |
Displays the available migration target technologies. | |
--source, -s |
Specifies the source technologies for analysis. Use a comma-separated list for multiple values - for example, --source <source1>,<source2>,.... Use the --list-sources argument to list all available sources. |
|
--target, -t |
Specifies the target technologies for analysis. Use a comma-separated list for multiple values - for example, --target <target1>,<target2>,.... Use the --list-targets argument to list all available targets. |
|
| Analysis options | ||
--analyze-known-libraries |
Enables analysis of known open-source libraries - specified in AppCAT's maven.default.index - during source code analysis. The default value is false. |
|
--custom-maven-settings |
Specifies the path to a custom Maven settings file. | |
--dry-run |
Checks whether the flags are valid without actually running the analysis. The default value is false. |
|
--mode, -m |
Sets the analysis mode. Must be one of full - source + dependencies, to analyze the source code and list dependencies - or source-only. The default value is full. |
|
--packages |
Specifies the application class packages to be evaluated. Use a comma-separated list for multiple values - for example, --packages <package1>,<package2>,.... The default value is []. |
|
| Rule options | ||
--code-snips-number |
Limits the displayed number of incidents with code snippets in a file. 0 means no limit, so all incidents with code snippets in a file are displayed. -1 means no code snippets are displayed. The default value is 0. |
|
--enable-default-rulesets |
Enables the execution of default rulesets. The default value is true. Use --enable-default-rulesets=false to disable. |
|
--label-selector, -l |
Applies rules based on a specified label selector expression - for example, (konveyor.io/target=azure-aks && konveyor.io/source). |
|
--rules |
Specifies rule files or directories. Use a comma-separated list for multiple values - for example, --rules <rule1>,<rule2>,.... The default value is []. |
|
| Proxy settings | ||
--http-proxy |
Defines an HTTP proxy URL for downloading open-source software (OSS) libraries from the Maven repository. | |
--https-proxy |
Defines an HTTPS proxy URL for downloading OSS libraries from the Maven repository. | |
--no-proxy |
Specifies URLs to exclude from proxy usage when downloading OSS libraries from the Maven repository. | |
| Report & output formatting | ||
--bulk |
Combines results when running multiple analyze commands in bulk. The default value is false. |
|
--context-lines-number |
Sets the number of source code lines included in the output for each detected incident. The default value is 100. |
|
--incident-selector |
Filters incidents based on a custom variable expression - for example, (!package=io.konveyor.demo.config-utils). |
|
--output-format |
Chooses the output format. Either yaml or json. The default value is yaml. |
|
--overwrite |
Overwrites the existing output directory. The default value is false. |
|
--skip-static-report |
Skips generating a static analysis report. The default value is false. |
Supported sources
The --list-sources parameter shows the following source technologies:
| Source name | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Java | Best practices for migrating Java applications. | java |
| Java EE | Best practices for migrating Java EE technology. | java-ee |
| OpenJDK | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK. | openjdk |
| OpenJDK 8 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 8. | openjdk8 |
| OpenJDK 9 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 9. | openjdk9 |
| OpenJDK 10 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 10. | openjdk10 |
| OpenJDK 11 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 11. | openjdk11 |
| OpenJDK 12 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 12. | openjdk12 |
| OpenJDK 13 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 13. | openjdk13 |
| OpenJDK 14 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 14. | openjdk14 |
| OpenJDK 15 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 15. | openjdk15 |
| OpenJDK 16 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 16. | openjdk16 |
| OpenJDK 17 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 17. | openjdk17 |
| OpenJDK 18 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 18. | openjdk18 |
| OpenJDK 19 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 19. | openjdk19 |
| OpenJDK 20 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 20. | openjdk20 |
| OpenJDK 21 | Best practices for migrating applications with OpenJDK 21. | openjdk21 |
| Oracle JDK | Best practices for migrating applications with Oracle JDK. | oraclejdk |
| Oracle JDK 7 | Best practices for migrating applications with Oracle JDK 7. | oraclejdk7 |
| RMI | Best practices for migrating Java applications that use RMI technology. | rmi |
| RPC | Best practices for migrating Java applications that use RPC technology. | rpc |
| Spring 5 | Best practices for migrating applications that use Spring 5 technology. | spring5 |
| Spring Boot | Best practices for migrating Spring Boot technology. | springboot |
| EAP | Best practices for migrating Java applications that use JBoss EAP technology. | eap |
| EAP 7 | Best practices for migrating Java applications that use JBoss EAP 7 technology. | eap7 |
Support targets
The --list-targets parameter shows the following target technologies:
| Target name | Description | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Azure App Service | Best practices for deploying an app to Azure App Service. | azure-appservice |
| Azure Kubernetes Service | Best practices for deploying an app to Azure Kubernetes Service. | azure-aks |
| Azure Container Apps | Best practices for deploying an app to Azure Container Apps. | azure-container-apps |
| Cloud Readiness | General best practices for making an application Cloud (Azure) ready. | cloud-readiness |
| Linux | General best practices for making an application Linux ready. | linux |
| OpenJDK 11 | General best practices for running a Java 8 application with Java 11. | openjdk11 |
| OpenJDK 17 | General best practices for running a Java 11 application with Java 17. | openjdk17 |
| OpenJDK 21 | General best practices for running a Java 17 application with Java 21. | openjdk21 |
Configure ignore files
In the AppCAT CLI install path, you can configure the .appcat-ignore file to exclude specified folders or paths when running the appcat analyze command.
Global parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--disable-telemetry |
Disables telemetry. |
--log-level |
Sets the log level. The default value is 4. |
--no-cleanup |
Prevents cleanup of temporary resources after execution. |
Examples
Analyze a source code directory:
appcat analyze --input <path-to-source> --output <path-to-output>Analyze a source code directory with specific source and target technologies:
appcat analyze \ --input <path-to-source> \ --output <path-to-output> \ --source springboot \ --target azure-aks,azure-appservice,azure-container-appsAnalyze a source code directory with extra custom rules:
appcat analyze --input <path-to-source> --output <path-to-output> --rules <path-to-rules>Analyze a source code directory using only custom rules, without default rulesets:
appcat analyze \ --input /path/to/source \ --output /path/to/output \ --enable-default-rulesets=false \ --rules /path/to/rulesAnalyze and add more application analysis to an existing output directory and static report:
appcat analyze \ --input=<path-to-source-A>,<path-to-source-B>,<path-to-source-C> \ --output=<path-to-output-ABC> \ --target=<target-name> appcat analyze --bulk \ --input=<path-to-source-D> \ --output=<path-to-output-ABC> \ --target=<target-name> appcat analyze \ --bulk \ --input=<path-to-source-E> \ --output=<path-to-output-ABC> \ --target=<target-name>Analyze a source code directory and keep the detected context lines with custom line numbers:
appcat analyze \ --input <path-to-source> \ --output <path-to-output> \ --context-lines-number <line-number>
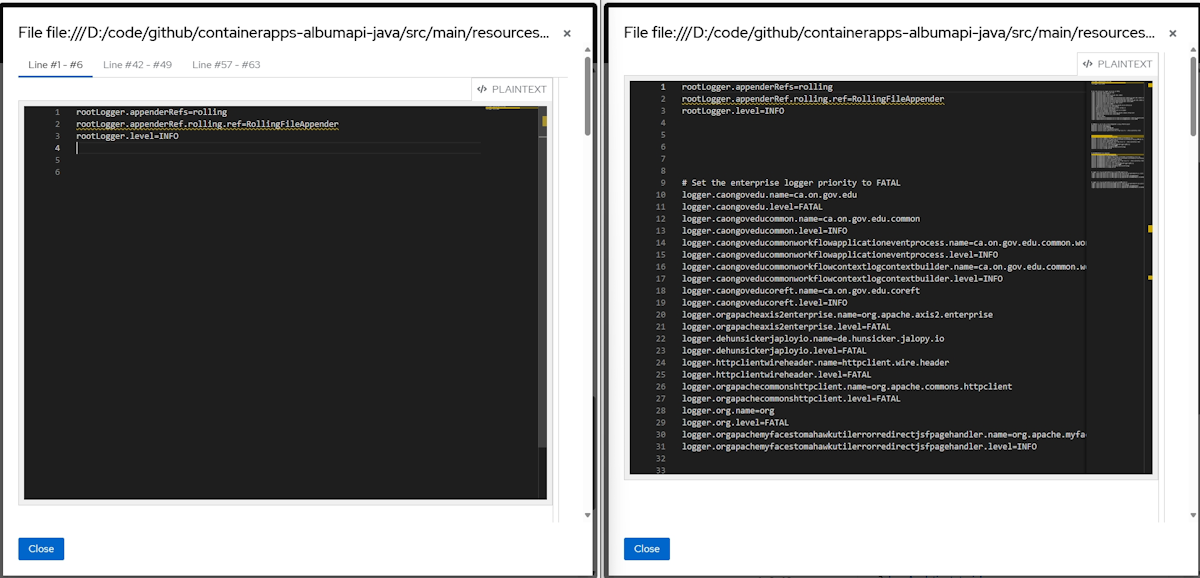
The following screenshot shows an example of using --context-lines-number 3:
appcat transform
Converts Windup XML rules to YAML.
Required parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--rules |
Converts XML rules to YAML. |
Global parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--disable-telemetry |
Disables telemetry |
--log-level |
Sets the log level. The default value is 4. |
--no-cleanup |
Prevents cleanup of temporary resources after execution. |
Examples
The following example converts a windup XML rule to YAML:
appcat transform rules --input <path-to-rule> --output <path-to-output-folder>
appcat version
Prints the tool version.
appcat version