Route filters allow you to consume a subset of supported services through Microsoft peering. This article guides you through configuring and managing route filters for ExpressRoute circuits.
Microsoft 365 services, such as Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and Skype for Business, are accessible through Microsoft peering. When Microsoft peering is configured in an ExpressRoute circuit, all prefixes related to these services are advertised through the BGP sessions. Each prefix has a BGP community value to identify the service it offers. For a list of BGP community values and their corresponding services, see BGP communities.
Connecting to all Azure and Microsoft 365 services can result in a large number of prefixes getting advertised through BGP, significantly increasing the size of your route tables. If you only need a subset of services offered through Microsoft peering, you can reduce your route table size by:
- Filtering out unwanted prefixes using route filters on BGP communities, a common networking practice.
- Defining route filters and applying them to your ExpressRoute circuit. A route filter is a resource that lets you select the services you plan to consume through Microsoft peering. ExpressRoute routers only send prefixes for the services identified in the route filter.
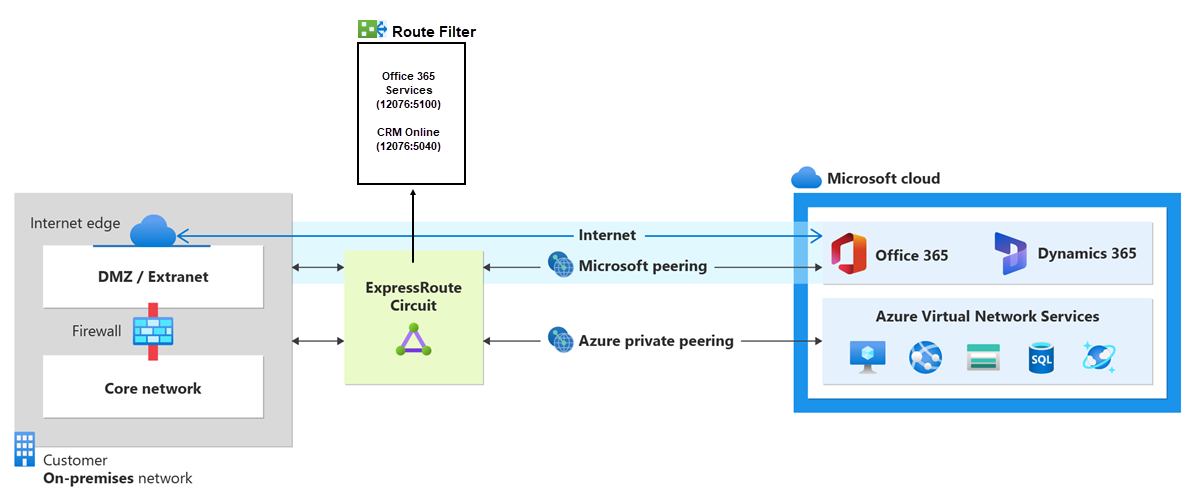
About route filters
When Microsoft peering is configured on your ExpressRoute circuit, Microsoft edge routers establish BGP sessions with your edge routers through your connectivity provider. No routes are advertised to your network until you associate a route filter.
A route filter lets you specify the services you want to consume through your ExpressRoute circuit's Microsoft peering. It acts as an allowed list of BGP community values. Once a route filter is defined and attached to an ExpressRoute circuit, all prefixes that map to the BGP community values are advertised to your network.
To attach route filters with Microsoft 365 services, you must be authorized to consume Microsoft 365 services through ExpressRoute. If you aren't authorized, the operation to attach route filters fail. For more information about the authorization process, see Azure ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365.
Important
Microsoft peering of ExpressRoute circuits configured before August 1, 2017, will have all Microsoft Office service prefixes advertised through Microsoft peering, even without route filters. For circuits configured on or after August 1, 2017, no prefixes will be advertised until a route filter is attached to the circuit.
Prerequisites
Review the prerequisites and workflows before starting the configuration.
- Ensure you have an active ExpressRoute circuit with Microsoft peering configured. For instructions, see:
- Create an ExpressRoute circuit and provisioned by your connectivity provider. The circuit must be in a provisioned and enabled state.
- Create Microsoft peering if you manage the BGP session directly, or have your connectivity provider create Microsoft peering for your circuit.
- You must have an active ExpressRoute circuit that has Microsoft peering provisioned. You can use the following instructions to accomplish these tasks:
- Create an ExpressRoute circuit and have the circuit enabled by your connectivity provider before you continue. The ExpressRoute circuit must be in a provisioned and enabled state.
- Create Microsoft peering if you manage the BGP session directly. Or, have your connectivity provider provision Microsoft peering for your circuit.
Azure Cloud Shell
Azure hosts Azure Cloud Shell, an interactive shell environment that you can use through your browser. You can use either Bash or PowerShell with Cloud Shell to work with Azure services. You can use the Cloud Shell preinstalled commands to run the code in this article, without having to install anything on your local environment.
To start Azure Cloud Shell:
| Option |
Example/Link |
| Select Try It in the upper-right corner of a code or command block. Selecting Try It doesn't automatically copy the code or command to Cloud Shell. |
 |
| Go to https://shell.azure.com, or select the Launch Cloud Shell button to open Cloud Shell in your browser. |
 |
| Select the Cloud Shell button on the menu bar at the upper right in the Azure portal. |
 |
To use Azure Cloud Shell:
Start Cloud Shell.
Select the Copy button on a code block (or command block) to copy the code or command.
Paste the code or command into the Cloud Shell session by selecting Ctrl+Shift+V on Windows and Linux, or by selecting Cmd+Shift+V on macOS.
Select Enter to run the code or command.
- Sign in to your Azure account and select your subscription
If you are using the Azure Cloud Shell, you sign in to your Azure account automatically after clicking 'Try it'. To sign in locally, open your PowerShell console with elevated privileges and run the cmdlet to connect.
Connect-AzAccount
If you have more than one subscription, get a list of your Azure subscriptions.
Get-AzSubscription
Specify the subscription that you want to use.
Select-AzSubscription -SubscriptionName "Name of subscription"
To successfully connect to services through Microsoft peering, you must complete the following configuration steps:
- You must have an active ExpressRoute circuit that has Microsoft peering provisioned. You can use the following instructions to accomplish these tasks:
- Create an ExpressRoute circuit and have the circuit enabled by your connectivity provider before you continue. The ExpressRoute circuit must be in a provisioned and enabled state.
- Create Microsoft peering if you manage the BGP session directly. Or, have your connectivity provider provision Microsoft peering for your circuit.
Azure Cloud Shell
Azure hosts Azure Cloud Shell, an interactive shell environment that you can use through your browser. You can use either Bash or PowerShell with Cloud Shell to work with Azure services. You can use the Cloud Shell preinstalled commands to run the code in this article, without having to install anything on your local environment.
To start Azure Cloud Shell:
| Option |
Example/Link |
| Select Try It in the upper-right corner of a code or command block. Selecting Try It doesn't automatically copy the code or command to Cloud Shell. |
 |
| Go to https://shell.azure.com, or select the Launch Cloud Shell button to open Cloud Shell in your browser. |
 |
| Select the Cloud Shell button on the menu bar at the upper right in the Azure portal. |
 |
To use Azure Cloud Shell:
Start Cloud Shell.
Select the Copy button on a code block (or command block) to copy the code or command.
Paste the code or command into the Cloud Shell session by selecting Ctrl+Shift+V on Windows and Linux, or by selecting Cmd+Shift+V on macOS.
Select Enter to run the code or command.
If you choose to install and use the CLI locally, this tutorial requires Azure CLI version 2.0.28 or later. To find the version, run az --version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install the Azure CLI.
Sign in to your Azure account and select your subscription
To begin your configuration, sign in to your Azure account. If you're using the "Try It", you're signed in automatically and can skip the sign in step. Use the following examples to help you connect:
az login
Check the subscriptions for the account.
az account list
Select the subscription for which you want to create an ExpressRoute circuit.
az account set --subscription "<subscription ID>"
Get a list of prefixes and BGP community values
Get a list of BGP community values. Find the BGP community values associated with services accessible through Microsoft peering on the ExpressRoute routing requirements page.
Use the following cmdlet to get the list of BGP community values and prefixes associated with services accessible through Microsoft peering:
Get-AzBgpServiceCommunity
Use the following cmdlet to get the list of BGP community values and prefixes associated with services accessible through Microsoft peering:
az network route-filter rule list-service-communities
Make a list of the values you want to use
List the BGP community values you want to use in the route filter.
Create a route filter and a filter rule
A route filter can have only one rule, which must be of type Allow. This rule can include a list of BGP community values.
Select Create a resource and search for Route filter:
Place the route filter in a resource group. Ensure the location matches the ExpressRoute circuit. Select Review + create and then Create.
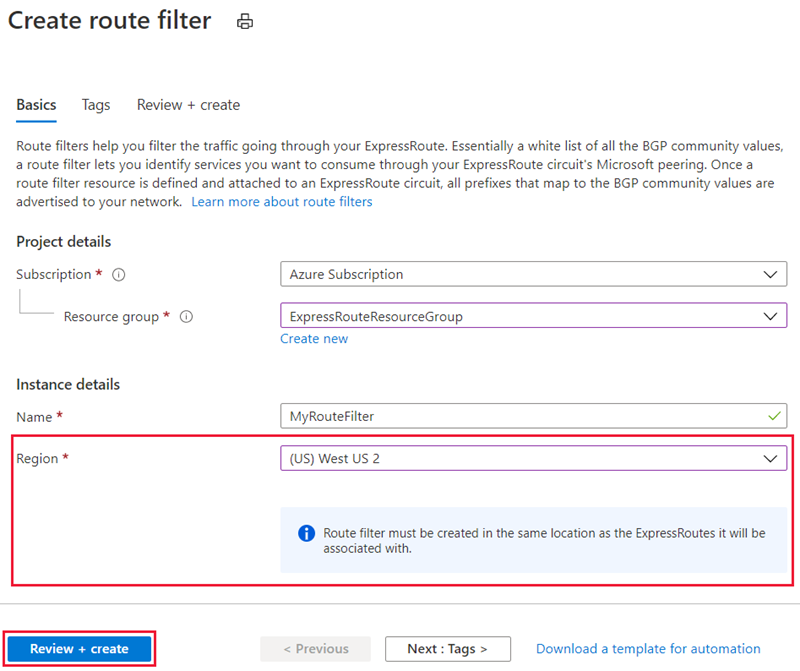
Create a filter rule
To add and update rules, select the managed rule tab for your route filter.
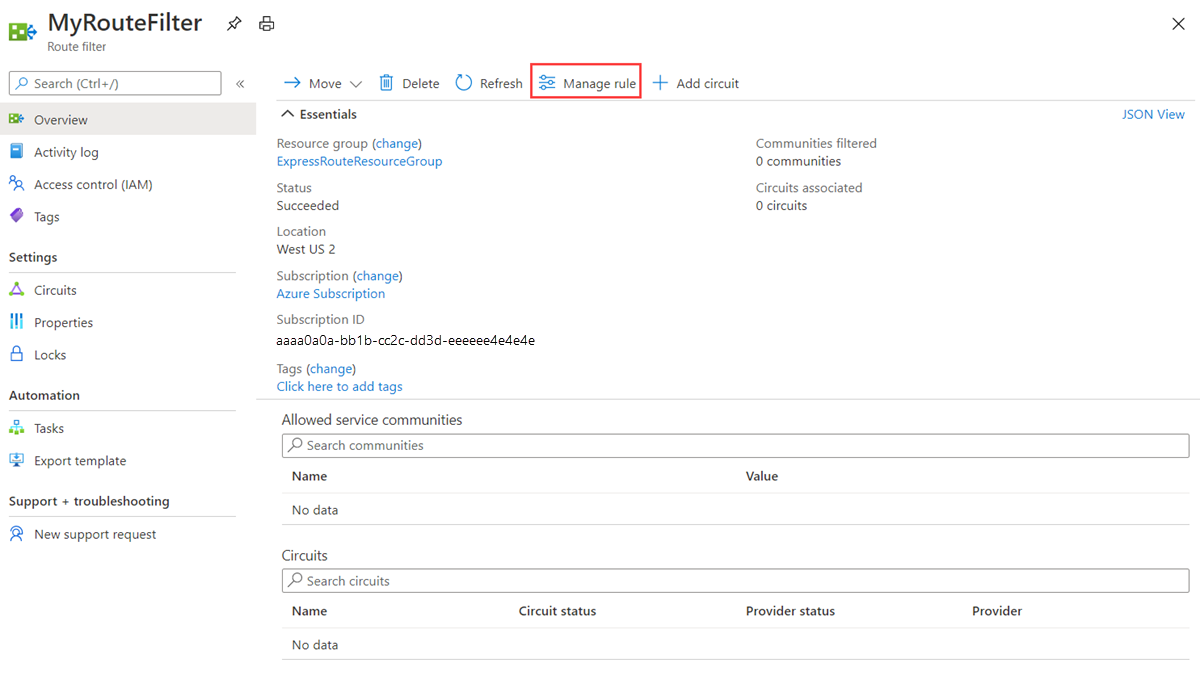
Then select the services you want to connect to from the drop-down list and save the rule.
A route filter can have only one rule, and the rule must be of type Allow. This rule can have a list of BGP community values associated with it. The command az network route-filter create only creates a route filter resource. After you create the resource, you must then create a rule and attach it to the route filter object.
To create a route filter resource, run the following command:
New-AzRouteFilter -Name "MyRouteFilter" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup" -Location "West US"
To create a route filter rule, run the following command:
$rule = New-AzRouteFilterRuleConfig -Name "Allow-EXO-D365" -Access Allow -RouteFilterRuleType Community -CommunityList 12076:5010,12076:5040
Run the following command to add the filter rule to the route filter:
$routefilter = Get-AzRouteFilter -Name "MyRouteFilter" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
$routefilter.Rules.Add($rule)
Set-AzRouteFilter -RouteFilter $routefilter
A route filter can have only one rule, and the rule must be of type 'Allow'. This rule can have a list of BGP community values associated with it. The command az network route-filter create only creates a route filter resource. After you create the resource, you must then create a rule and attach it to the route filter object.
To create a route filter resource, run the following command:
az network route-filter create -n MyRouteFilter -g MyResourceGroup
To create a route filter rule, run the following command:
az network route-filter rule create --filter-name MyRouteFilter -n CRM --communities 12076:5040 --access Allow -g MyResourceGroup
Attach the route filter to an ExpressRoute circuit
Attach the route filter to a circuit by selecting the + Add Circuit button and choosing the ExpressRoute circuit from the drop-down list.
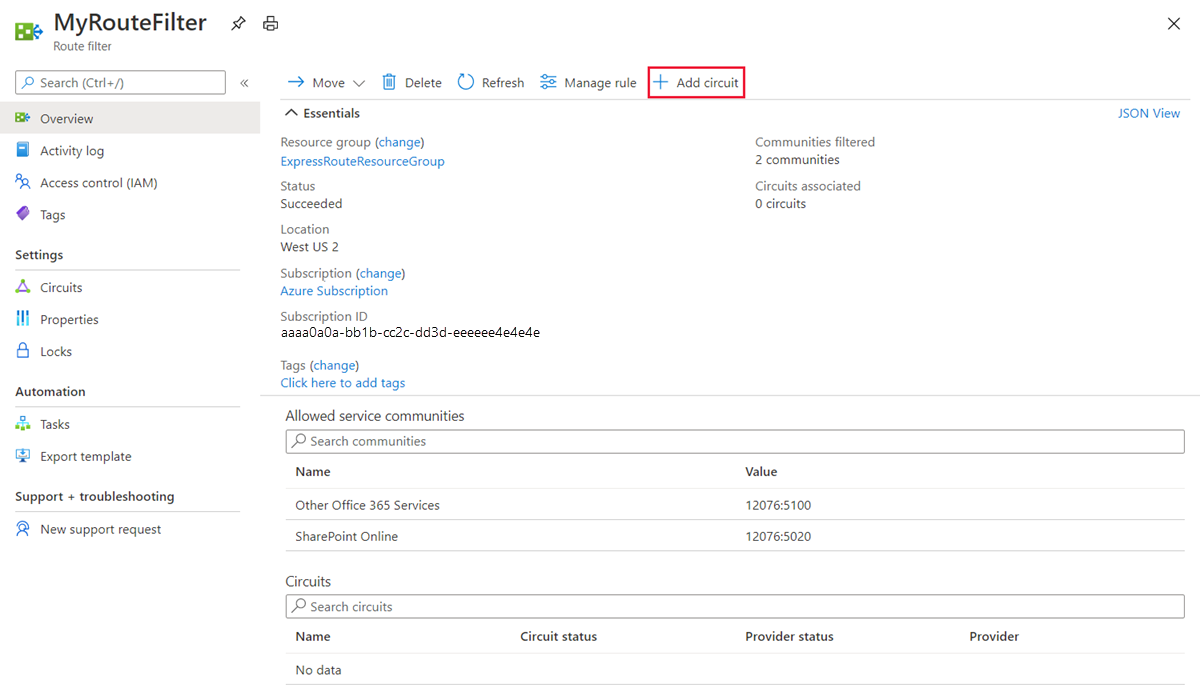
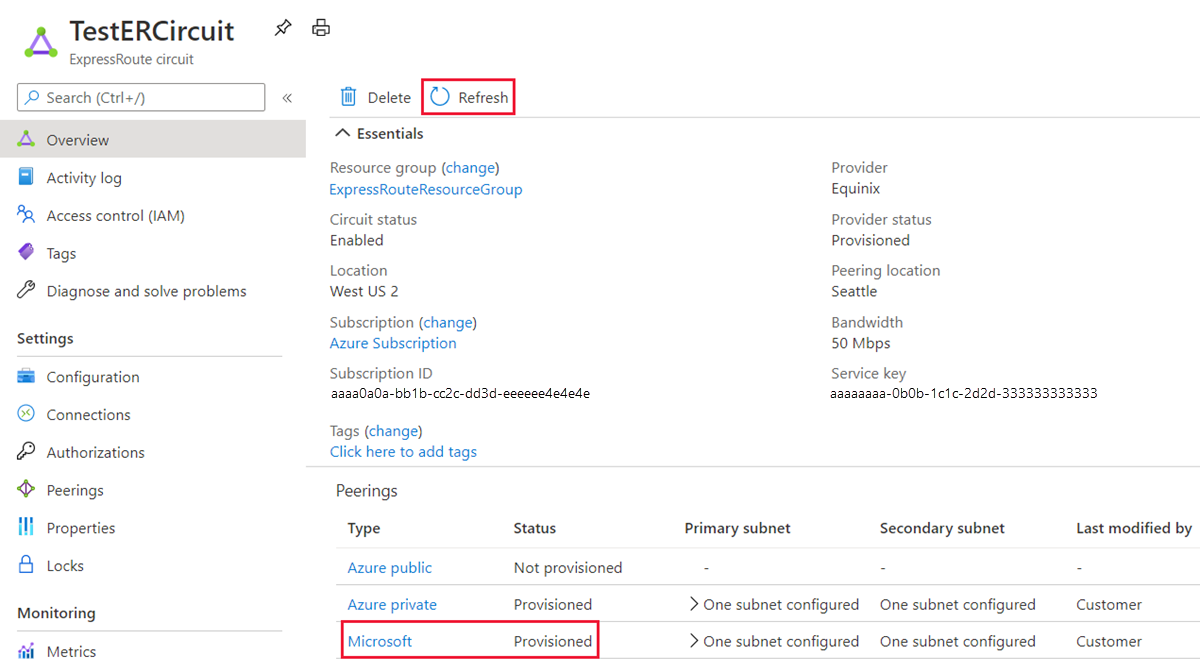
If your connectivity provider configures peering for your ExpressRoute circuit, refresh the circuit from the ExpressRoute circuit page before selecting the + Add Circuit button.
Run the following command to attach the route filter to the ExpressRoute circuit, assuming you have only Microsoft peering:
$ckt = Get-AzExpressRouteCircuit -Name "ExpressRouteARMCircuit" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
$index = [array]::IndexOf(@($ckt.Peerings.PeeringType), "MicrosoftPeering")
$ckt.Peerings[$index].RouteFilter = $routefilter
Set-AzExpressRouteCircuit -ExpressRouteCircuit $ckt
Run the following command to attach the route filter to the ExpressRoute circuit:
az network express-route peering update --circuit-name MyCircuit -g ExpressRouteResourceGroupName --name MicrosoftPeering --route-filter MyRouteFilter
Common tasks
To get the properties of a route filter
View the properties of a route filter by opening the resource in the portal.
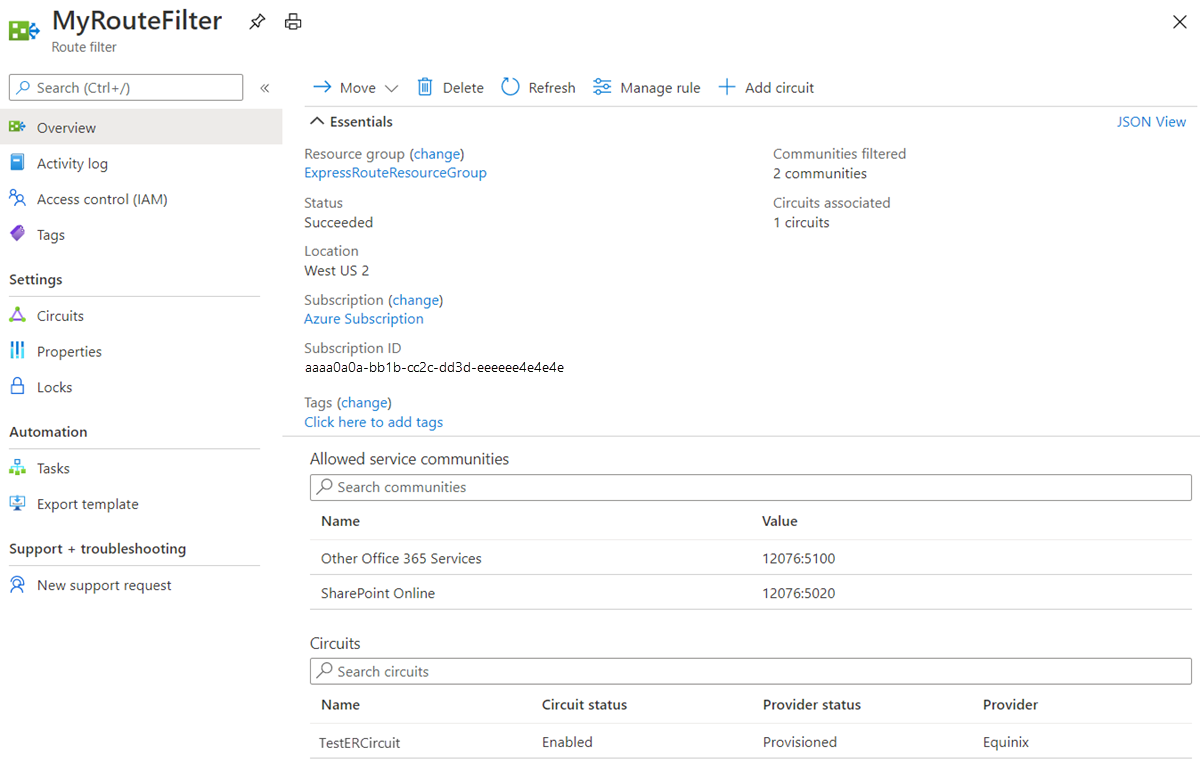
To get the properties of a route filter, use the following steps:
Run the following command to get the route filter resource:
$routefilter = Get-AzRouteFilter -Name "MyRouteFilter" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
Get the route filter rules for the route-filter resource by running the following command:
$routefilter = Get-AzRouteFilter -Name "MyRouteFilter" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
$rule = $routefilter.Rules[0]
To get the properties of a route filter, use the following command:
az network route-filter show -g ExpressRouteResourceGroupName --name MyRouteFilter
To update the properties of a route filter
Update the list of BGP community values attached to a circuit by selecting the Manage rule button.
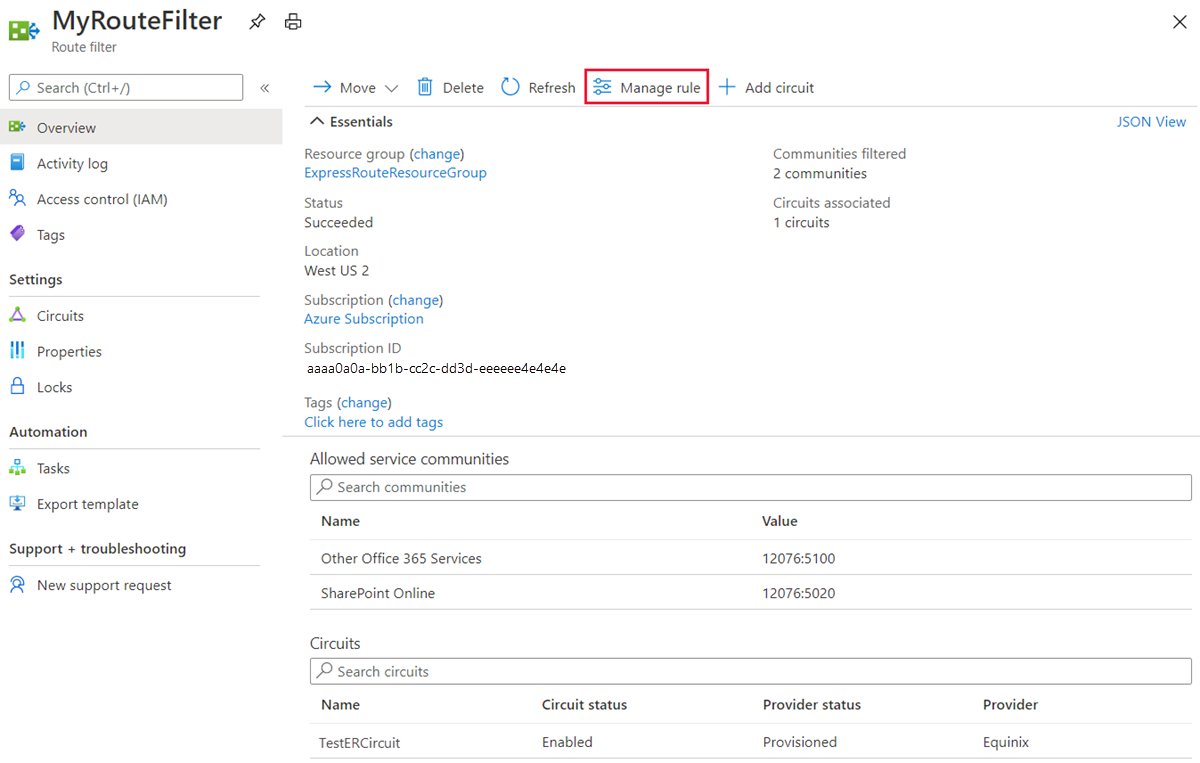
Select the service communities you want and then select Save.
If the route filter is already attached to a circuit, updates to the BGP community list automatically propagate prefix advertisement changes through the BGP session established. You can update the BGP community list of your route filter using the following command:
$routefilter = Get-AzRouteFilter -Name "MyRouteFilter" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
$routefilter.rules[0].Communities = "12076:5030", "12076:5040"
Set-AzRouteFilter -RouteFilter $routefilter
If the route filter is already attached to a circuit, updates to the BGP community list automatically propagate prefix advertisement changes through the BGP session established. You can update the BGP community list of your route filter using the following command:
az network route-filter rule update --filter-name MyRouteFilter -n CRM -g ExpressRouteResourceGroupName --add communities '12076:5040' --add communities '12076:5010'
To detach a route filter from an ExpressRoute circuit
Detach a circuit from the route filter by right-clicking on the circuit and selecting Dissociate.
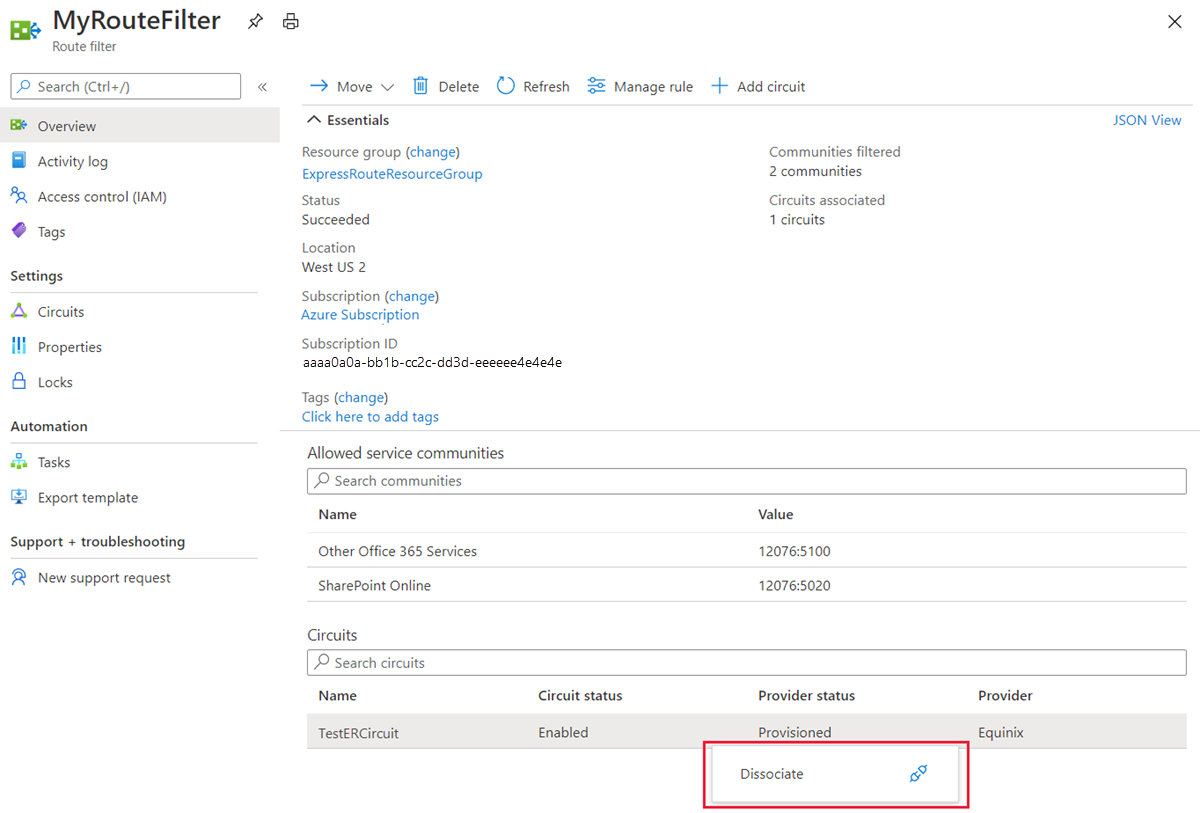
Once a route filter is detached from the ExpressRoute circuit, no prefixes are advertised through the BGP session. You can detach a route filter from an ExpressRoute circuit using the following command:
$ckt.Peerings[0].RouteFilter = $null
Set-AzExpressRouteCircuit -ExpressRouteCircuit $ckt
Once a route filter is detached from the ExpressRoute circuit, no prefixes are advertised through the BGP session. You can detach a route filter from an ExpressRoute circuit using the following command:
az network express-route peering update --circuit-name MyCircuit -g ExpressRouteResourceGroupName --name MicrosoftPeering --remove routeFilter
Clean up resources
Delete a route filter by selecting the Delete button. Ensure the route filter isn't associated with any circuit before doing so.
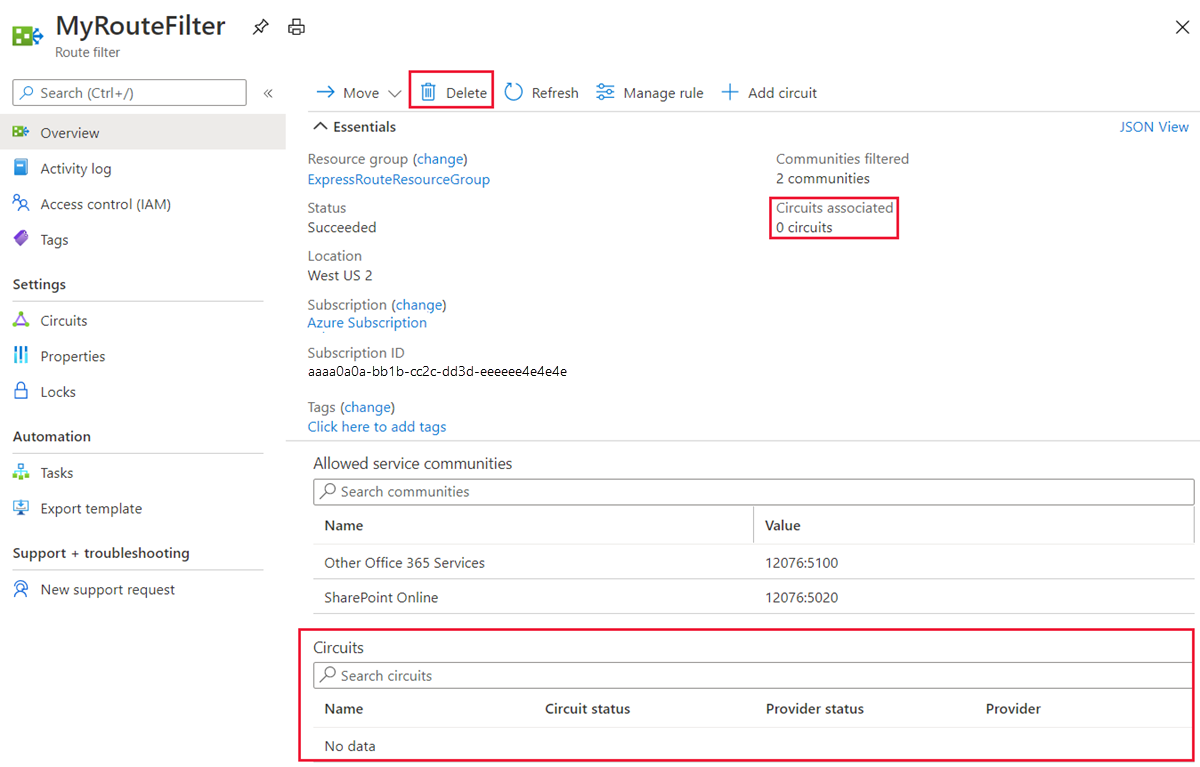
You can only delete a route filter if it isn't attached to any circuit. Ensure that the route filter isn't attached to any circuit before attempting to delete it. You can delete a route filter using the following command:
Remove-AzRouteFilter -Name "MyRouteFilter" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
You can only delete a route filter if it isn't attached to any circuit. Ensure that the route filter isn't attached to any circuit before attempting to delete it. You can delete a route filter using the following command:
az network route-filter delete -n MyRouteFilter -g MyResourceGroup
Next Steps
For information about router configuration samples, see:











