Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Copilot can help you generate Terraform configurations that define your Azure infrastructure. Describe the infrastructure you want to deploy, and Copilot generates a Terraform configuration using the AzureRM provider. The configuration automatically includes both the main resources and any required dependencies to ensure the configuration is deployable. You can define the output by iteratively making subsequent prompts.
In this article, you learn how to use Copilot in Azure from the Azure portal and GitHub Copilot for Azure in Visual Studio Code. We also provide sample Terraform prompts for you to use as-is or edit as desired.
Tip
For best results, keep your prompt to fewer than eight primary Terraform resource types. Copilot performs well with common configurations. Complex or large-scale architectures may produce incomplete or less accurate results.
Note
Copilot currently supports AzureRM provider resources extensively. Support for the AzAPI provider is evolving and may not be fully available yet. If the required resource type isn't supported, Copilot either falls back to a sample structure or explains the limitations.
Use Copilot in Azure from the Azure portal
Open the Azure portal.
Select the Copilot icon in the upper right corner.
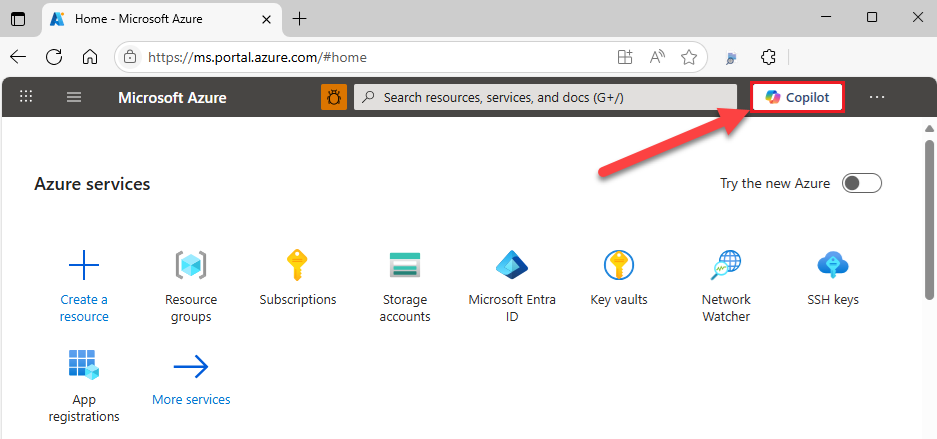
Enter a Terraform-related prompt such as the following example.
Create a Terraform configuration for a Cognitive Services instance named "mycognitiveservice" and the S0 pricing tierPress <Enter>.
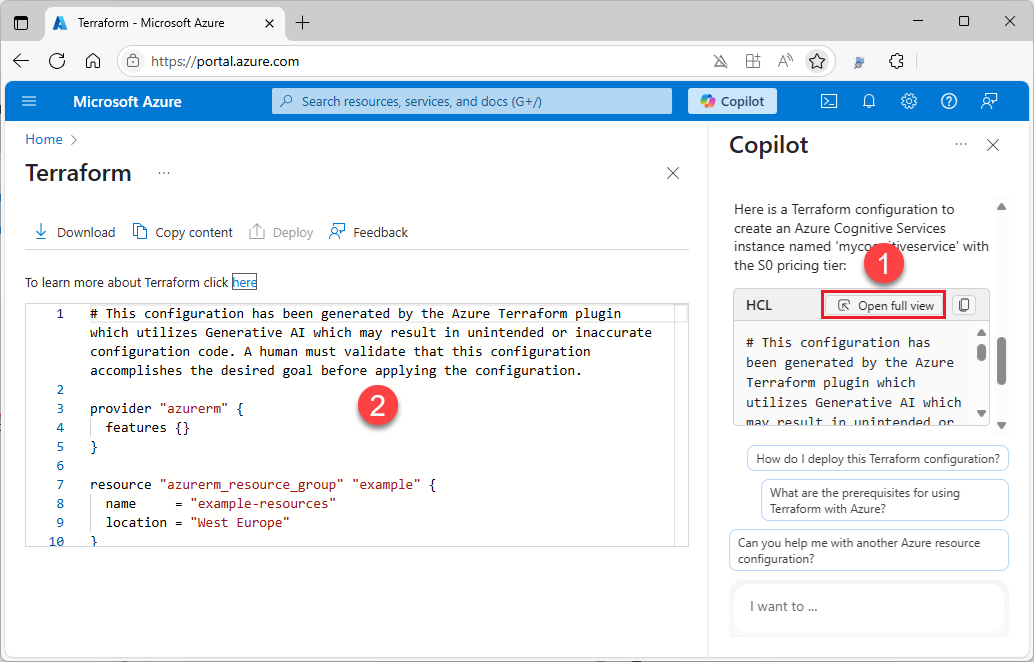
Once Copilot in Azure responds, you can select Open Full View to view the configuration code block in full-screen mode.
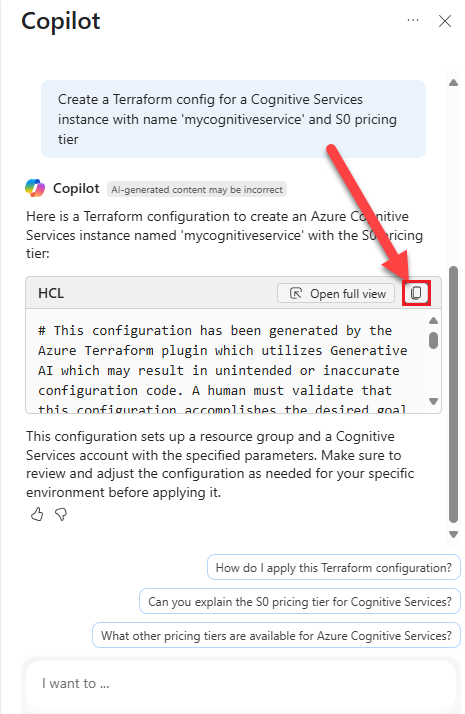
Select the Copy icon to copy the new configuration to the clipboard.
Paste the code into your editor.
Use GitHub Copilot for Azure from Visual Studio Code
Open Visual Studio Code.
From the Activity Bar, select Extensions, and search for
copilot.
Ensure that the GitHub Copilot extension is installed. If it isn't, install it.
Ensure that the GitHub Copilot Chat extension is installed. If it isn't, install it.
Select Toggle Chat.
Enter a prompt for a Terraform Configuration that begins with
@azure. For example, the following prompt creates a Content Delivery Network (CDN) resource with various settings.@azure Use Terraform to create an Azure CDN Front Door profile named "myCDN profile" with a custom domain association for "example.com". Configure a CDN Front Door route that links to the default domain, and create a CDN endpoint named "myEndpoint" associated with the custom domain. Ensure that a security policy is applied for enhanced protection in production, and verify that the route is correctly configured with the appropriate origin group.Press <Enter>.
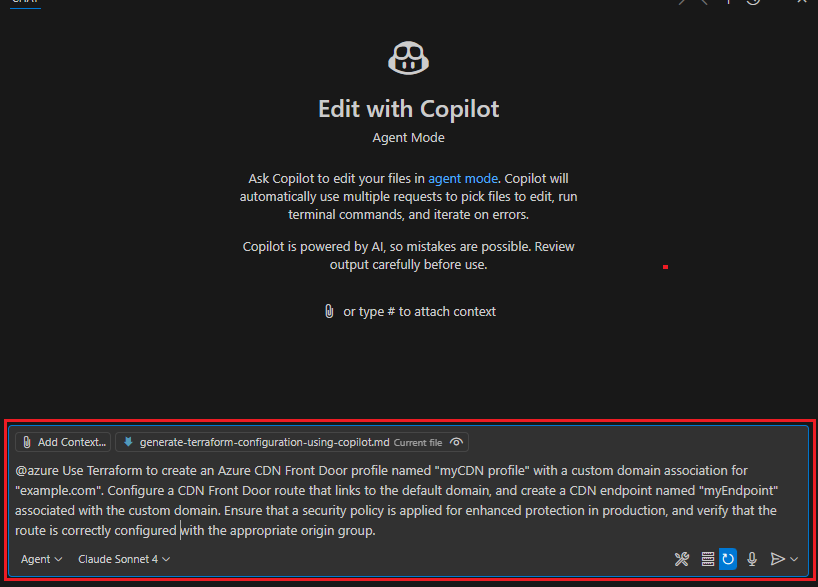
GitHub Copilot for Azure interactively guides you through the process and creates the required files for your configuration.
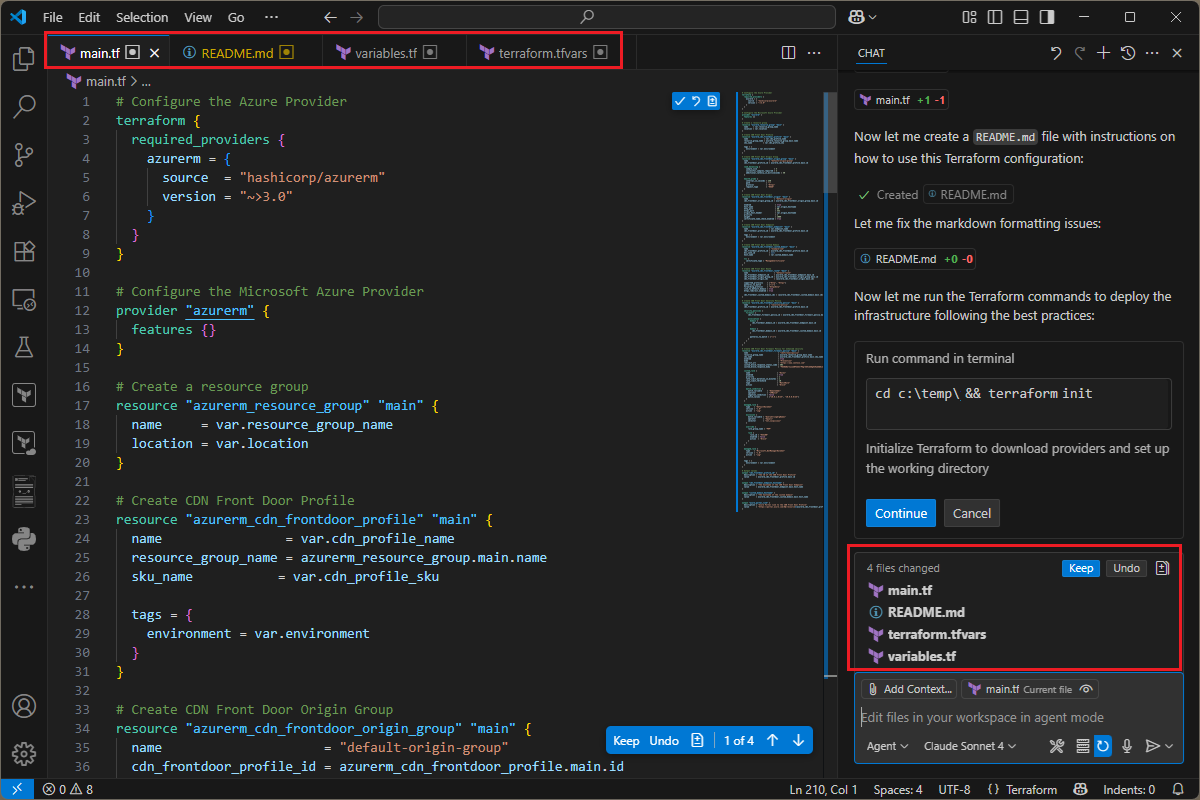
Once the files are created or updated, GitHub Copilot for Azure offers to run the
terraform initandterraform validatecommands against the generated configuration.
Review and use sample Terraform prompts
This section contains several example prompts you can use to generate Terraform configurations. Modify these prompts based on your scenarios, or try other prompts to create different kinds of queries.
Create a Terraform configuration for a Cognitive Services instance with
name "mycognitiveservice" and S0 pricing tier.
Create a Terraform configuration that deploys a Linux virtual machine
running Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, with 8 GB of RAM. The virtual machine should
be located in the West US region and assigned a public IP address.
It must be connected to a virtual network that includes a subnet and is
secured by a network security group.
Create a Terraform configuration for a Container App resource named
"myApp" using the quick start image. Set the container app environment name
to "awesomeAzureEnv" and the container name to "myQuickStartContainer".
Create a Terraform configuration for an Azure Databricks workspace named
"myworkspace" with the premium SKU. The workspace should be deployed in
the West US region.
Create a Terraform configuration for an Azure OpenAI deployment that uses
the "gpt-4" model. Specify the model version as "2024-05-01-preview" and
set the deployment name to "myOpenAIModel".
Tip
For more example prompts, see Generate Terraform and Bicep configurations using Microsoft Copilot in Azure.