Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Generative AI, powered by large language models (LLMs), brings new opportunities for developers and organizations. Services like Azure OpenAI make AI easy to use with simple APIs. Developers of all skill levels can add advanced AI features to their apps without needing special knowledge or hardware.
As a developer, you might wonder what your role is and where you fit in. Maybe you want to know which part of the "AI stack" to focus on, or what you can build with today's technology.
To answer these questions, start by building a mental model that connects new terms and technologies to what you already know. This approach helps you design and add generative AI features to your apps.
In this series, we show how your current software skills apply to generative AI. We also introduce key terms and concepts to help you start building your first generative AI solutions.
How businesses benefit from using generative AI
To see how your software skills fit with generative AI, first look at how businesses use it.
Businesses use generative AI to boost customer engagement, work more efficiently, and solve problems in creative ways. Adding generative AI to existing systems lets businesses improve their software. It can add features like personalized recommendations or smart agents that answer questions about a company or its products.
Common ways that generative AI helps businesses:
Content generation:
- Create text, code, images, and sound for marketing, sales, IT, and internal communications.
Natural language processing:
- Write or improve business messages.
- Let users chat with their data by asking questions based on company documents.
- Summarize, organize, and simplify large amounts of content.
- Use semantic search to find information without exact keywords.
- Translate content to reach more people.
Data analysis:
- Find trends in data and analyze markets.
- Model "what if" scenarios to help plan for changes.
- Review code to suggest improvements, fix bugs, and create documentation.
As a developer, you can make significant improvements by adding generative AI features to the software your organization uses.
How to build generative AI applications
Although the LLM does the heavy lifting, you build systems that integrate, orchestrate, and monitor the results. There's much to learn, but you can apply the skills you already have, including how to:
- Make calls to APIs by using REST, JSON, or language-specific software development kits (SDKs)
- Orchestrate calls to APIs and perform business logic
- Store to and retrieve from data stores
- Integrate input and results into the user experience
- Create APIs that can be called from LLMs
Developing generative AI solutions build on your existing skills.
Developer tools and services
Microsoft builds tools, services, APIs, samples, and learning resources to help you start with generative AI. Each one covers a key part of building a generative AI solution. To use these resources well, make sure you:
- Know the main functions, roles, and responsibilities for each type of generative AI feature. For example, in RAG-based chat systems, you need to understand the problem and its limits before you design a solution.
- Learn about the APIs, services, and tools for each function or role. Once you know the problem, you can build it yourself with code, use low-code/no-code tools, or call existing services.
- Explore your options, including code, low-code, and no-code solutions. You can build everything yourself, but sometimes it's faster and easier to combine different tools and approaches.
There’s no single right way to add generative AI features to your apps. You can choose from many tools and methods. Always weigh the pros and cons of each.
Start with the application layer
You don’t need to know everything about generative AI to get started. You likely already have the skills you need. Use APIs and your current knowledge to begin.
You don’t need to train your own LLM. Training an LLM takes too much time and money for most companies. Instead, use existing pretrained models like GPT-4o by making API calls to hosted services such as Azure OpenAI API. Adding generative AI features to your app is just like adding any other feature that uses an API.
You might want to learn how LLMs are trained or how they work. But fully understanding LLMs requires deep knowledge of data science and math, often at a graduate level.
If you have a computer science background, you know most app development happens at a higher layer in the technology stack. You might know a bit about each layer, but you probably focus on app development, using a specific language, platform, APIs, and tools.
The same idea applies to AI. You can learn the theory behind LLMs, but you should focus on building apps or creating patterns and processes for generative AI in your company.
Here’s a simple view of the knowledge layers needed to add generative AI features to an app:
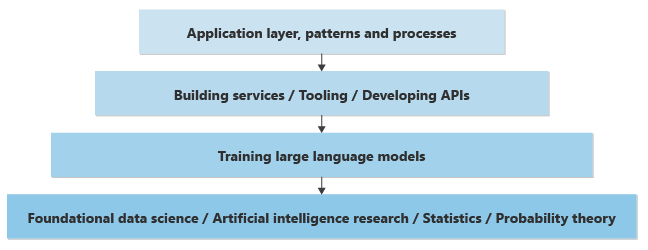
At the lowest level, data scientists do research to improve AI using advanced math like statistics and probability.
One layer up, data scientists use theory to build LLMs. They create neural networks and train them to accept prompts and generate results (completions). The process of generating results from prompts is called inference. Data scientists decide how the neural network predicts the next word or pixel.
Because training and running models takes significant computing power, most models are trained and hosted in large datacenters. You can train or host a model on your own computer, but it’s slow. Dedicated GPUs make this training faster and more efficient.
When models run in datacenters, you access them through REST APIs. SDKs often wrap these APIs to make them easier for developers. Other tools help with monitoring and other tasks.
App developers use these APIs to build business features.
Beyond calling models, new patterns and processes help organizations build reliable generative AI features. For example, some patterns help make sure generated content meets ethical, safety, and privacy standards.
If you’re an app developer, consider focusing on these app layer topics:
- APIs and SDKs: Learn what’s available and what each endpoint does.
- Tools and services: Learn how to build the features needed for a production-ready generative AI solution.
- Prompt engineering: Learn how to get the best results by asking or rephrasing questions.
- Bottlenecks and scaling: Find where slowdowns happen and how to scale. Learn how to log and get application data without violating privacy.
- LLM characteristics: Know the strengths, use cases, benchmarks, and differences between models and vendors. This knowledge helps you pick the right model for your needs.
- Patterns and workflows: Stay up to date on the latest ways to build effective and reliable generative AI features in your apps.
Tools and services from Microsoft
You can use low-code and no-code generative AI tools and services from Microsoft to help you build some or all of your solution. Various Azure services can play pivotal roles. Each contributes to the efficiency, scalability, and robustness of the solution.
API and SDKs for a code-centric approach
Every generative AI solution uses an LLM. Azure OpenAI gives you all the features in models like GPT-4.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure OpenAI | A hosted service that gives you access to powerful language models like GPT-4. Use APIs to create embeddings, build chat features, and customize results to fit your needs. |
Execution environments
You need a service to run your business logic, presentation logic, or APIs for generative AI in your apps.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure App Service (or other container-based cloud services) | Host web interfaces or APIs for users to interact with your RAG chat system. Quickly develop, deploy, and scale web apps. Easily manage the front end of your system. |
| Azure Functions | Use serverless compute for event-driven tasks in your RAG chat system. Trigger data retrieval, process user queries, or handle background tasks like syncing and cleanup. Build a modular, scalable back end. |
Low-code and no-code solutions
Some of the logic that you need to implement your generative AI vision can be built quickly and be hosted reliably by using a low-code or no-code solution.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure AI Foundry | You can use Azure AI Foundry to train, test, and deploy custom machine learning models to enhance a RAG chat system. For example, use Azure AI Foundry to customize response generation or to improve the relevance of retrieved information. |
For guidance on building low-code solutions, see Low-code application development on Azure.
Vector database
Some generative AI solutions need to store and retrieve data to improve results. For example, a RAG-based chat system lets users chat with your company’s data. In this case, you need a vector database.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure AI Search | Search large datasets to find information for the language model. Use it for the retrieval part of a RAG system to make responses more relevant and useful. |
| Azure Cosmos DB | Store large amounts of structured and unstructured data for the RAG chat system. Fast read and write speeds help serve real-time data and store user interactions. |
| Azure Cache for Redis | Cache frequently used information to reduce delays and speed up the RAG chat system. Store session data, user preferences, and common queries. |
| Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server | Store app data like logs, user profiles, and chat history. Its flexibility and scalability keep your data available and secure. |
Each of these Azure services helps you build a scalable, efficient generative AI solution. They let you use the best of Azure’s cloud and AI features. For more information, see Choosing a Vector Database.
Code-centric generative AI development by using the Azure OpenAI API
This section covers the Azure OpenAI API. You use a REST API to access LLM features. You can call these APIs from any modern programming language. Many languages have SDKs that make calling the API easier.
Here's the list of Azure OpenAI REST API wrappers:
- Azure OpenAI client library for .NET
- Azure OpenAI client library for Java
- Azure OpenAI client library for JavaScript
- Azure OpenAI client module for Go
- Use the OpenAI Python package and change several options. Python doesn't offer an Azure-specific client library.
If there’s no SDK for your language or platform, make REST calls directly to the web APIs:
Most developers know how to call web APIs.
Azure OpenAI has several APIs for different AI tasks. Here’s an overview of the main APIs:
- Chat Completions API: Generate text, chat, and answer questions. Use it for chatbots, virtual assistants, summarization, writing, and translation. It also supports vision features (like uploading an image and asking questions).
- Content Moderation API: Find and filter harmful or unsafe content in text. Use it to keep user interactions safe.
- Embeddings API: Turn text into vectors for search, clustering, and finding similar content. Use it to capture the meaning and relationships in text.
- Image Generation API: Create images and art from text prompts. Based on the DALL·E model.
- Speech to text REST API: Convert speech to text or text to speech in many languages. Use it for voice commands and audio transcription.
This article focuses on text-based generative AI, like chat and summarization, but you can use these APIs for many types of media.
Get started developing with generative AI
When you learn a new language, API, or technology, start with tutorials or training that show how to build small apps. Some developers prefer to learn by building their own small projects. Both ways work well.
Start small, set simple goals, and build your skills step by step. Generative AI development is different from traditional software. In regular software, you get the same output for the same input every time. With generative AI, you get different answers for the same prompt, which brings new challenges.
As you begin, keep these tips in mind.
Tip 1: Be clear about your goal
- Define the problem you want to solve. Generative AI can do many things, but you get better results if you know exactly what you want—like generating text, images, or code.
- Know your audience. Tailor the AI’s output to match who uses it, whether they’re casual users or experts.
Tip 2: Use LLM strengths
- Know the limits and biases of LLMs. They’re powerful but not perfect. Plan for their weaknesses.
- Use LLMs for what they do best, like creating content, summarizing, or translating. Sometimes, another type of AI might be better for your needs.
Tip 3: Write good prompts
- Learn prompt engineering. Try different prompts to see what works best. Be clear and specific.
- Refine your prompts. The first iteration might not work. Use the results to improve your next prompt.
Build your first generative AI solution
To try building a generative AI solution, start with Get started with chat by using your own data sample for Python. You can also find tutorials for .NET, Java, and JavaScript.
Final considerations for application design
Here's a short list of things to consider and other takeaways from this article that might affect your application design decisions:
- Define the problem space and audience clearly to align AI's capabilities with user expectations. Optimize the solution's effectiveness for the intended use case.
- Use low-code/no-code platforms for rapid prototyping and development if they meet your project's requirements. Evaluate the trade-off between development speed and customizability. Try low-code and no-code tools for parts of your app to speed up development and let nontechnical team members help.