Prometheus isn't limited to monitoring Kubernetes clusters. Use Prometheus to monitor applications and services running on your servers, wherever they're running. For example, you can monitor applications running on virtual machines, virtual machine scale sets, or even on-premises servers. You can also send Prometheus metrics to an Azure Monitor workspace from your self-managed cluster and Prometheus server.
This article explains how to configure remote write to send data from a self-managed Prometheus instance to an Azure Monitor workspace.
Options for remote write
Self-managed Prometheus can run in Azure and non-Azure environments. The following are authentication options for remote write to an Azure Monitor workspace, based on the environment where Prometheus is running.
| Azure-managed virtual machines, virtual machine scale sets, and Kubernetes clusters |
Virtual machines and Kubernetes clusters running in non-Azure environments |
Use either system-assigned or user-assigned managed identity authentication for services running self-managed Prometheus in an Azure environment. Azure-managed services include:
- Azure Virtual Machines
- Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
To set up remote write for Azure-managed resources, see Remote write using managed identity authentication later in this article. |
If you have virtual machines or a Kubernetes cluster in non-Azure environments, or you onboarded to Azure Arc, install self-managed Prometheus and configure remote write by using Microsoft Entra application authentication. For more information, see Remote write using Microsoft Entra application authentication later in this article.
Onboarding to Azure Arc-enabled servers allows you to manage and configure non-Azure virtual machines in Azure. For more information, see Azure Arc-enabled servers and Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes. Azure Arc-enabled servers support only Microsoft Entra authentication. |
Prerequisites
Supported versions
- Prometheus versions 2.45 or later are required for user-assigned managed identity authentication.
- Prometheus versions 2.48 or later are required for Microsoft Entra application authentication.
- Prometheus versions 3.50 or later are required for system-assigned managed identity authentication.
Azure Monitor workspace
This article covers sending Prometheus metrics to an Azure Monitor workspace. To create an Azure monitor workspace, see Manage an Azure Monitor workspace.
Permissions
Administrator permissions for the cluster or resource are required to complete the steps in this article.
Set up authentication for remote write
Depending on the environment where Prometheus is running, you can configure remote write to use a user-assigned or system-assigned managed identity or Microsoft Entra application authentication to send data to an Azure Monitor workspace.
Use the Azure portal or the Azure CLI to create a user-assigned managed identity or Microsoft Entra application. A system-assigned managed identity, when enabled, is automatically setup for an Azure VM or AKS cluster. This identity can be used to authenticate Prometheus remote-write from an Azure VM/VMSS or an AKS cluster.
Remote write using system-assigned managed identity authentication
A system-assigned managed identity authentication can be used in case of Azure VM/VMSS or AKS. If your Prometheus service is running in a non-Azure environment, use Microsoft Entra application authentication.
A system-assigned managed identity, when enabled, is automatically setup for an Azure resource. In case your Prometheus service is running in an AKS cluster, you will need to use the system-assigned managed identity for the underlying VMSS of the cluster.
| Azure Kubernetes clusters |
Azure VMs and VMSS |
For Azure Kubernetes Service, the managed identity must be assigned to virtual machine scale sets. AKS creates a resource group that contains the virtual machine scale sets. The resource group name is in the format MC_<resource group name>_<AKS cluster name>_<region> and can be found in the Settings -> Properties -> Infrastructure Resource Group section of the AKS cluster.
For each virtual machine scale set in the resource group, enable system-assigned managed identity in the Security -> Identity section. |
For Azure VM/VMSS, enable system-assigned managed identity in the Security -> Identity section of the VM/VMSS page. See Configure system-assigned managed identity for more details. |
Follow the steps below to use the system-assigned managed identity for Prometheus remote-write.
Assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role to the application
On the workspace's data collection rule, assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role to the managed identity:
On the Azure Monitor workspace's overview pane, select the Data collection rule link.
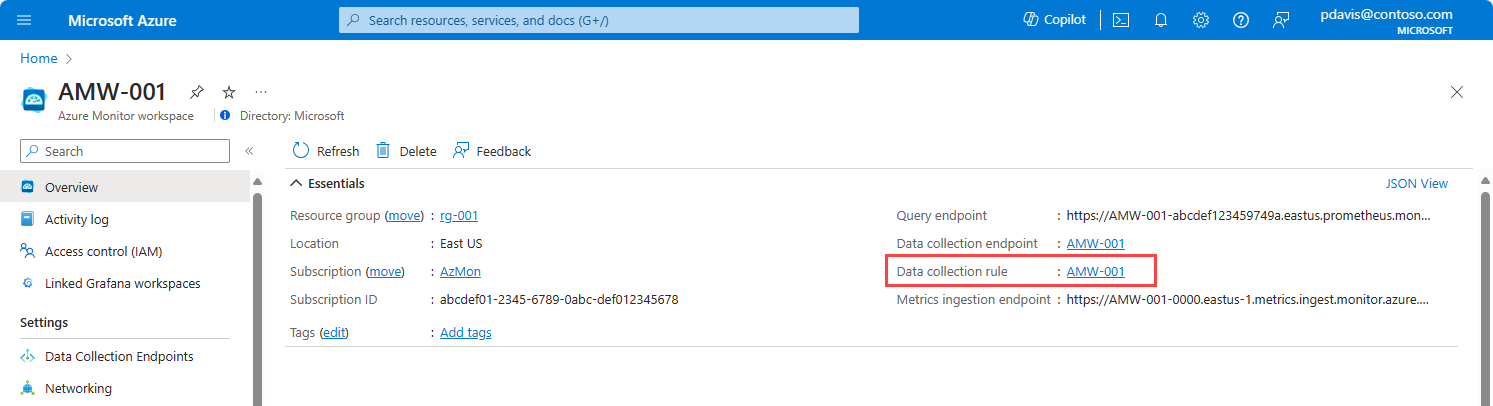
On the page for the data collection rule, select Access control (IAM).
Select Add > Add role assignment.
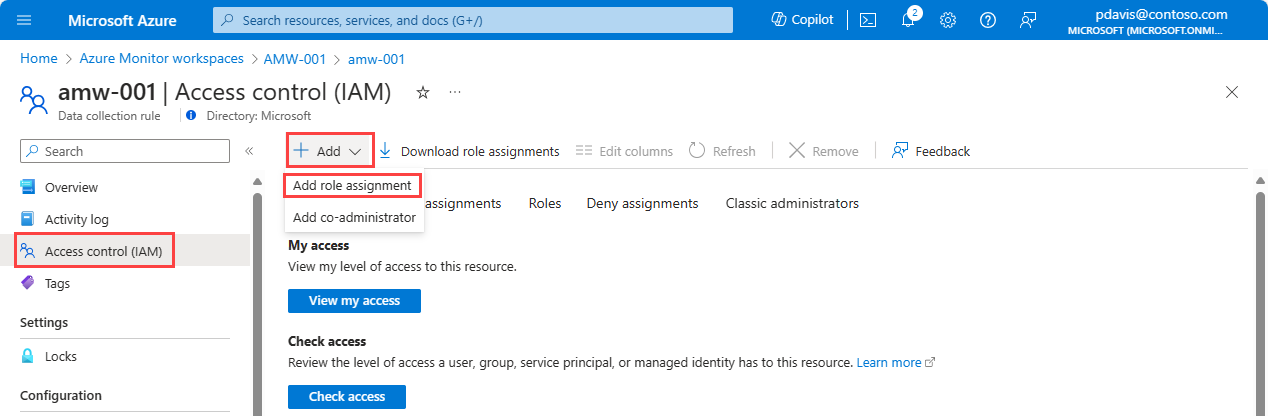
Search for and select Monitoring Metrics Publisher, and then select Next.
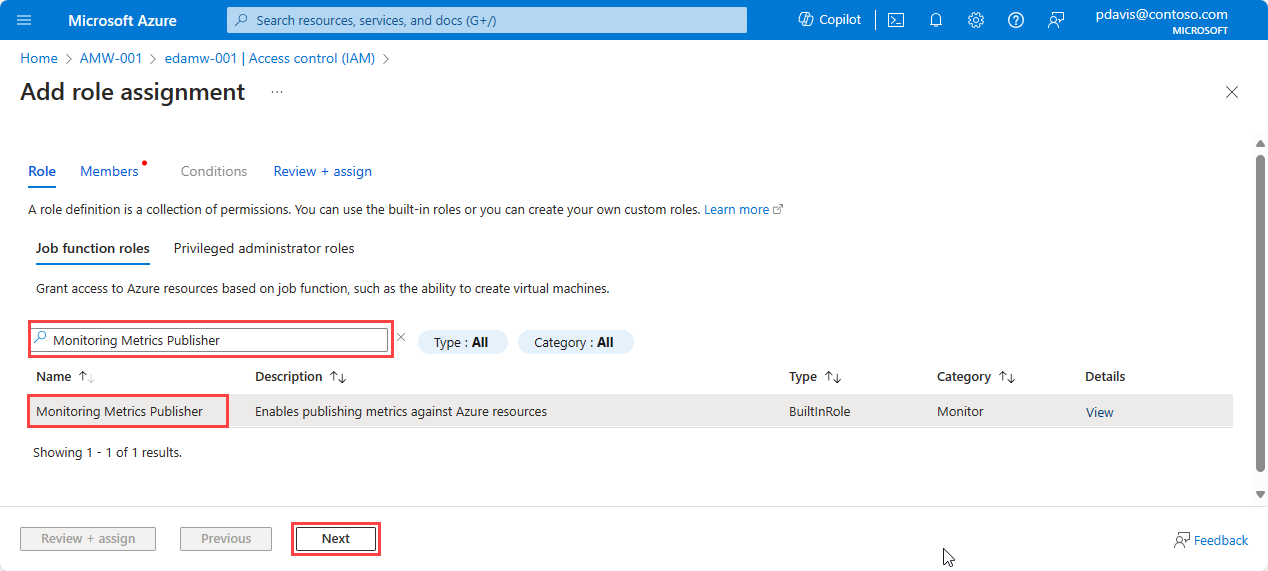
Select Managed Identity.
Choose Select members.
In the Managed identity dropdown list, select System-assigned managed identity, and then choose the VM/VMSS or the VMSS that hosts the AKS cluster.
Remote write using user-assigned managed identity authentication
User-assigned managed identity authentication can be used in any Azure-managed environment. If your Prometheus service is running in a non-Azure environment, you can use Microsoft Entra application authentication.
To configure a user-assigned managed identity for remote write to an Azure Monitor workspace, complete the following steps.
Create a user-assigned managed identity
To create a user-managed identity to use in your remote write configuration, see Manage user-assigned managed identities.
Note the value of clientId for the managed identity that you created. This ID is used in the Prometheus remote write configuration.
Assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role to the application
On the workspace's data collection rule, assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role to the managed identity:
On the Azure Monitor workspace's overview pane, select the Data collection rule link.

On the page for the data collection rule, select Access control (IAM).
Select Add > Add role assignment.

Search for and select Monitoring Metrics Publisher, and then select Next.

Select Managed Identity.
Choose Select members.
In the Managed identity dropdown list, select User-assigned managed identity.
Select the user-assigned identity that you want to use, and then choose Select.
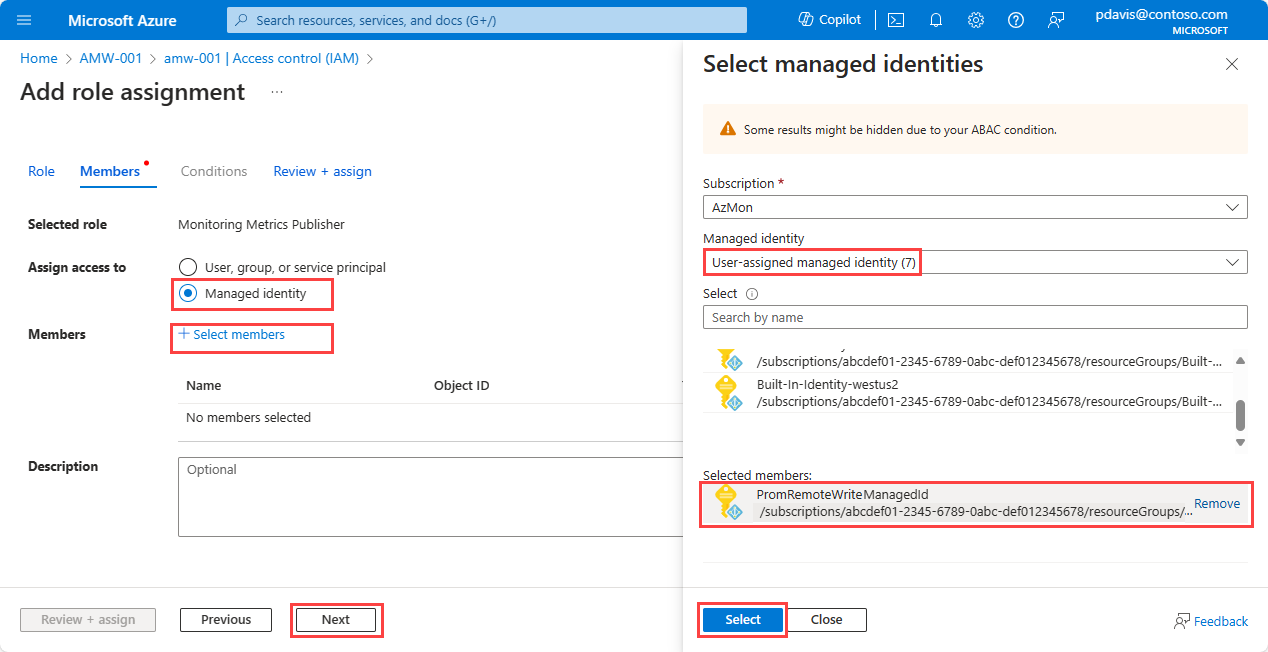
Select Review + assign to complete the role assignment.
Assign the managed identity to a virtual machine or a virtual machine scale set
Important
To complete the steps in this section, you must have Owner or User Access Administrator permissions for the virtual machine or the virtual machine scale set.
In the Azure portal, go to the page for the cluster, virtual machine, or virtual machine scale set.
Select Identity.
Select User assigned.
Select Add.
Select the user-assigned managed identity that you created, and then select Add.
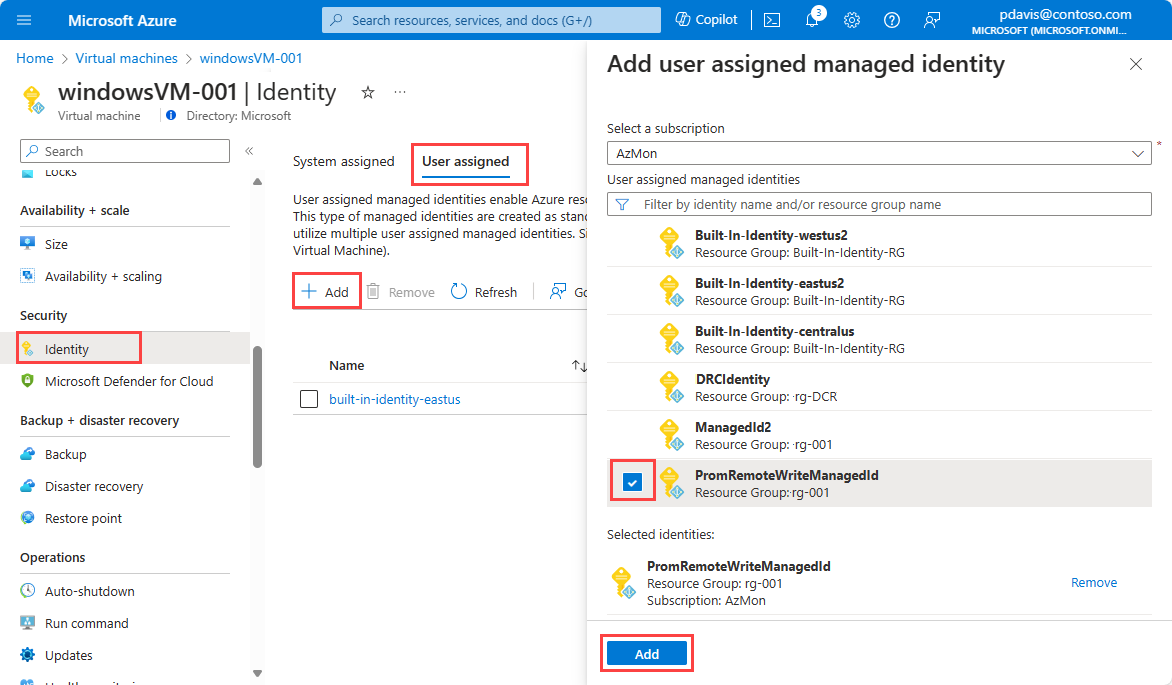
Assign the managed identity for Azure Kubernetes Service
For Azure Kubernetes Service, the managed identity must be assigned to virtual machine scale sets.
AKS creates a resource group that contains the virtual machine scale sets. The resource group name is in the format MC_<resource group name>_<AKS cluster name>_<region>.
For each virtual machine scale set in the resource group, assign the managed identity according to the steps in the previous section, Assign the managed identity to a virtual machine or a virtual machine scale set.
Remote write using Microsoft Entra application authentication
You can use Microsoft Entra application authentication in any environment. If your Prometheus service is running in an Azure-managed environment, consider using user-assigned managed identity authentication.
To configure remote write to an Azure Monitor workspace by using a Microsoft Entra application, create a Microsoft Entra application. On the Azure Monitor workspace's data collection rule, assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role to the Microsoft Entra application.
Note
Your Microsoft Entra application uses a client secret or password. Client secrets have an expiration date. Make sure to create a new client secret before it expires so you don't lose authenticated access.
Create a Microsoft Entra ID application
To create a Microsoft Entra ID application by using the portal, see Register an application with Microsoft Entra ID and create a service principal.
After you create your Microsoft Entra application, get the client ID and generate a client secret:
In the list of applications, copy the Client ID value for the registered application. This value is used in the Prometheus remote write configuration as the value for client_id.
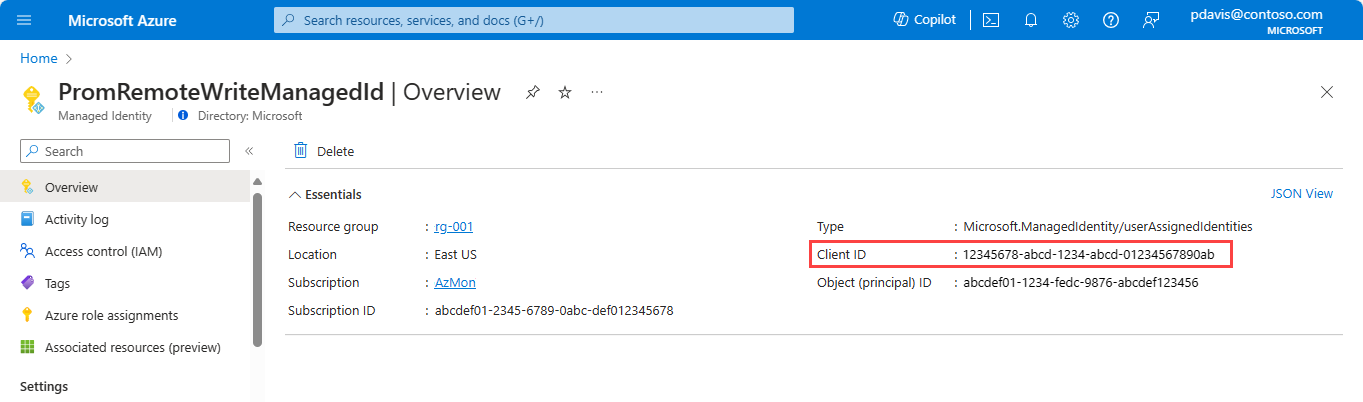
Select Certificates & secrets.
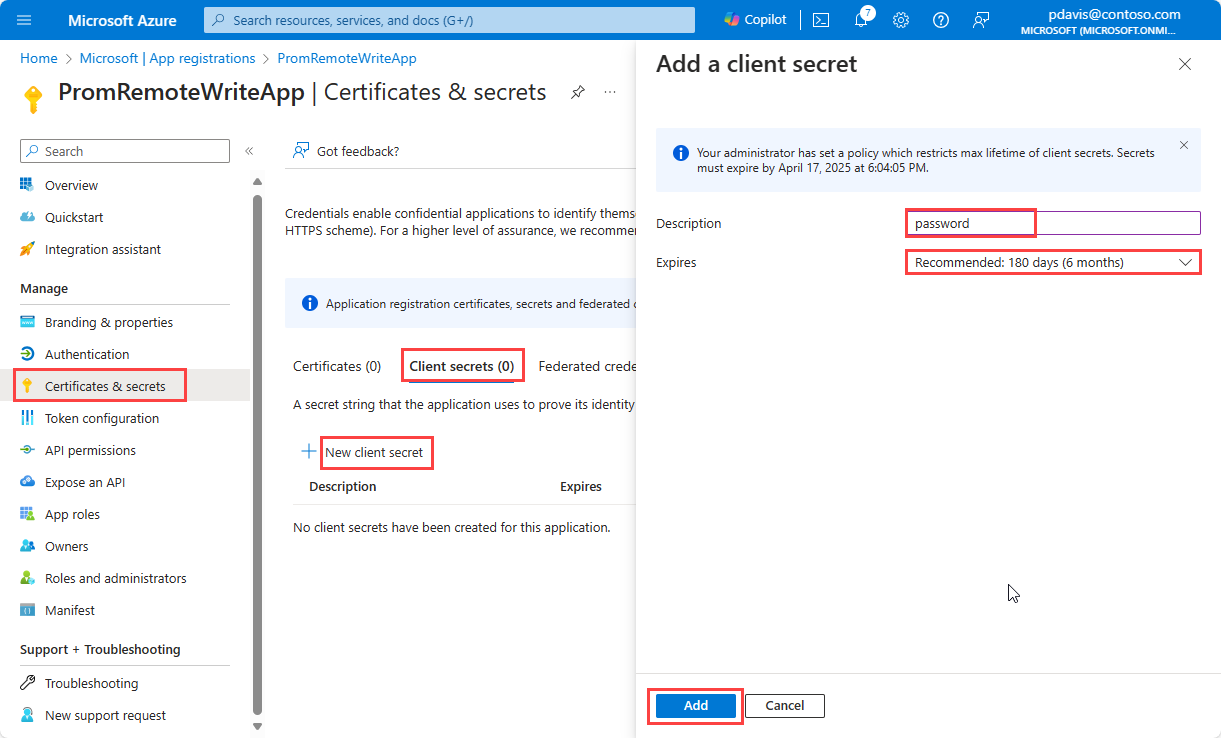
Select Client secrets, and then select New client secret to create a secret.
Enter a description, set the expiration date, and then select Add.
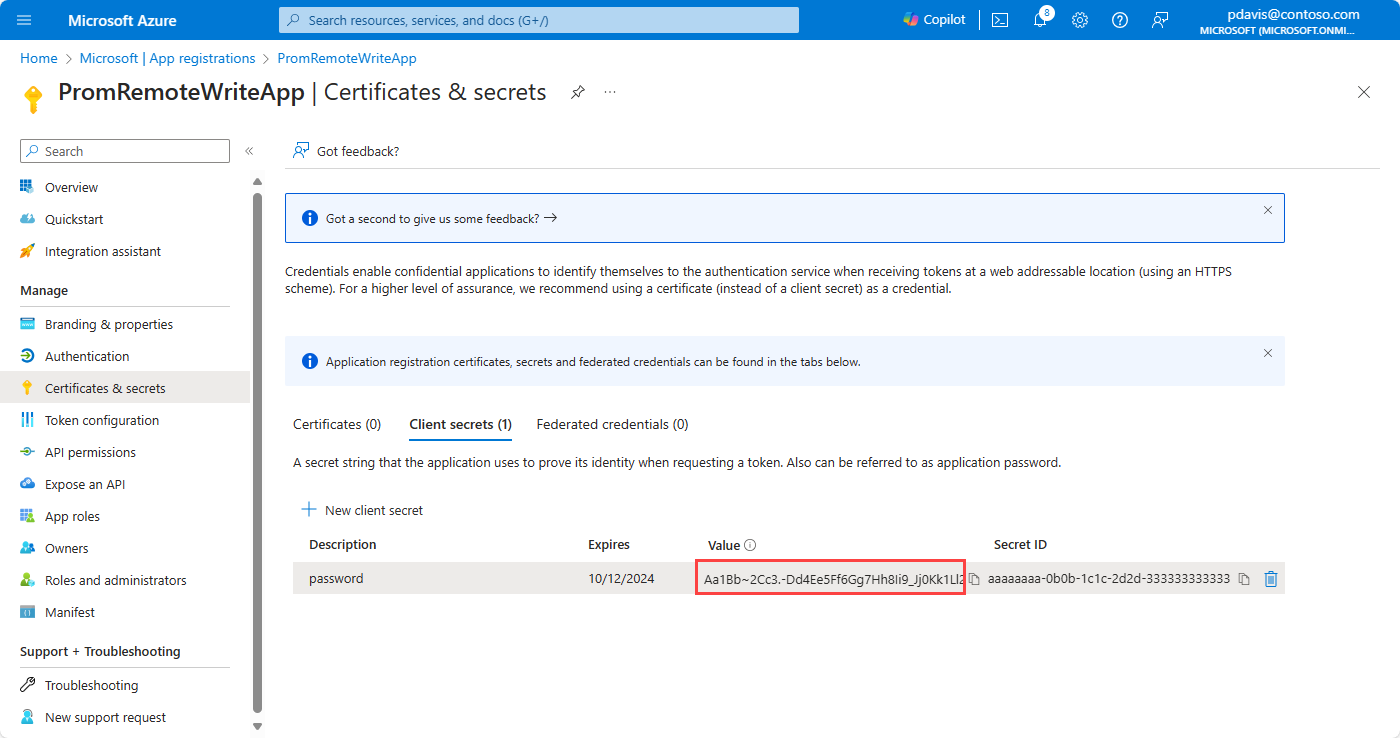
Copy the value of the secret securely. The value is used in the Prometheus remote write configuration as the value for client_secret. The client secret value is visible only when it's created, and you can't retrieve it later. If you lose it, you must create a new one.
Assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role to the application
Assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role on the workspace's data collection rule to the application:
On the Azure Monitor workspace's overview pane, select the Data collection rule link.

On the page for the data collection rule, select Access control (IAM).
Select Add, and then select Add role assignment.

Select the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role, and then select Next.

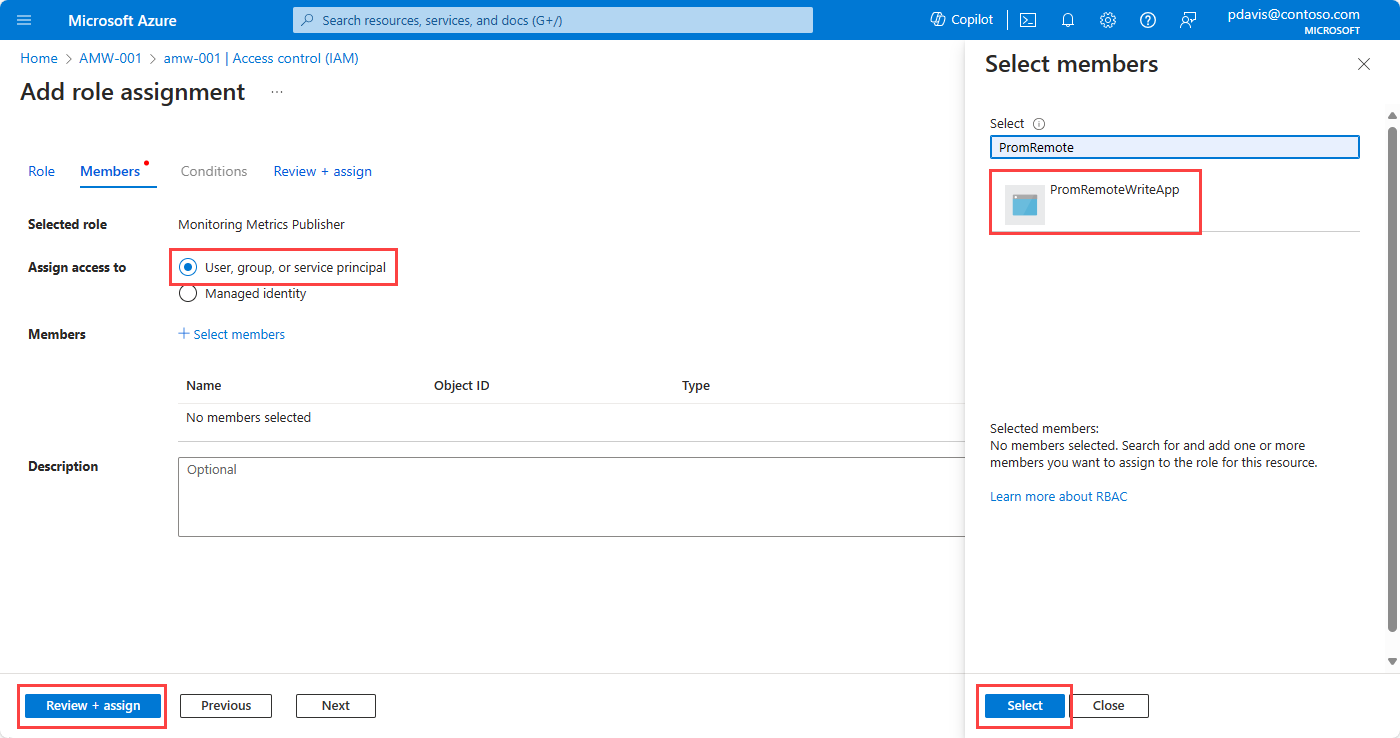
Select User, group, or service principal, and then choose Select members. Select the application that you created, and then choose Select.
To complete the role assignment, select Review + assign.
Creation of user-assigned identities and Microsoft Entra ID apps via the Azure CLI
Create a user-assigned managed identity
Create a user-assigned managed identity for remote write by using the following steps.
Note the value of clientId for the managed identity that you create. This ID is used in the Prometheus remote write configuration.
Create a user-assigned managed identity by using the following Azure CLI command:
az account set \
--subscription <subscription id>
az identity create \
--name <identity name> \
--resource-group <resource group name>
The following code is an example of the displayed output:
{
"clientId": "00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444",
"id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourcegroups/rg-001/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/PromRemoteWriteIdentity",
"location": "eastus",
"name": "PromRemoteWriteIdentity",
"principalId": "aaaaaaaa-bbbb-cccc-1111-222222222222",
"resourceGroup": "rg-001",
"systemData": null,
"tags": {},
"tenantId": "aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee",
"type": "Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities"
}
Assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role on the workspace's data collection rule to the managed identity:
az role assignment create \
--role "Monitoring Metrics Publisher" \
--assignee <managed identity client ID> \
--scope <data collection rule resource ID>
For example:
az role assignment create \
--role "Monitoring Metrics Publisher" \
--assignee 00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444 \
--scope /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/MA_amw-001_eastus_managed/providers/Microsoft.Insights/dataCollectionRules/amw-001
Assign the managed identity to a virtual machine or a virtual machine scale set.
Here are the commands for a virtual machine:
az vm identity assign \
-g <resource group name> \
-n <virtual machine name> \
--identities <user assigned identity resource ID>
Here are the commands for a virtual machine scale set:
az vmss identity assign \
-g <resource group name> \
-n <scale set name> \
--identities <user assigned identity resource ID>
The following example shows the commands for a virtual machine scale set:
az vm identity assign \
-g rg-prom-on-vm \
-n win-vm-prom \
--identities /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourcegroups/rg-001/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/PromRemoteWriteIdentity
For more information, see az identity create and az role assignment create.
Create a Microsoft Entra application
To create a Microsoft Entra application by using the Azure CLI, and assign the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role, run the following command:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --name <application name> \
--role "Monitoring Metrics Publisher" \
--scopes <azure monitor workspace data collection rule Id>
For example:
az ad sp create-for-rbac \
--name PromRemoteWriteApp \
--role "Monitoring Metrics Publisher" \
--scopes /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/MA_amw-001_eastus_managed/providers/Microsoft.nsights/dataCollectionRules/amw-001
The following code is an example of the displayed output:
{
"appId": "66667777-aaaa-8888-bbbb-9999cccc0000",
"displayName": "PromRemoteWriteApp",
"password": "Aa1Bb~2Cc3.-Dd4Ee5Ff6Gg7Hh8Ii9_Jj0Kk1Ll2",
"tenant": "ffff5f5f-aa6a-bb7b-cc8c-dddddd9d9d9d"
}
The output contains the appId and password values. Save these values to use in the Prometheus remote write configuration as values for client_id and client_secret. The password or client secret value is visible only when it's created, and you can't retrieve it later. If you lose it, you must create a new one.
For more information, see az ad app create and az ad sp create-for-rbac.
Remote write is configured in the Prometheus configuration file prometheus.yml or in Prometheus Operator.
For more information on configuring remote write, see this Prometheus.io article: Configuration. For information on tuning the remote write configuration, see Remote write tuning.
To send data to your Azure Monitor workspace, add the following section to the configuration file (prometheus.yml) of your self-managed Prometheus instance:
remote_write:
- url: "<metrics ingestion endpoint for your Azure Monitor workspace>"
# Microsoft Entra ID configuration.
# The Azure cloud. Options are 'AzurePublic', 'AzureChina', or 'AzureGovernment'.
azuread:
cloud: 'AzurePublic'
managed_identity:
client_id: "<client-id of the managed identity>"
oauth:
client_id: "<client-id from the Entra app>"
client_secret: "<client secret from the Entra app>"
tenant_id: "<Azure subscription tenant Id>"
Prometheus Operator
If you're on a Kubernetes cluster that's running Prometheus Operator, use the following steps to send data to your Azure Monitor workspace:
If you're using Microsoft Entra authentication, convert the secret by using Base64 encoding, and then apply the secret in your Kubernetes cluster. Save the following code into a YAML file. Skip this step if you're using managed identity authentication.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: remote-write-secret
namespace: monitoring # Replace with the namespace where Prometheus Operator is deployed.
type: Opaque
data:
password: <base64-encoded-secret>
Apply the secret:
# Set context to your cluster
az aks get-credentials -g <aks-rg-name> -n <aks-cluster-name>
kubectl apply -f <remote-write-secret.yaml>
Update the values for the remote write section in Prometheus Operator. Copy the following YAML and save it as a file. For more information on the Azure Monitor workspace specification for remote write in Prometheus Operator, see the Prometheus Operator documentation.
prometheus:
prometheusSpec:
remoteWrite:
- url: "<metrics ingestion endpoint for your Azure Monitor workspace>"
azureAd:
# Microsoft Entra ID configuration.
# The Azure cloud. Options are 'AzurePublic', 'AzureChina', or 'AzureGovernment'.
cloud: 'AzurePublic'
managedIdentity:
clientId: "<clientId of the managed identity>"
oauth:
clientId: "<clientId of the Entra app>"
clientSecret:
name: remote-write-secret
key: password
tenantId: "<Azure subscription tenant Id>"
Use Helm to update your remote write configuration by using the preceding YAML file:
helm upgrade -f <YAML-FILENAME>.yml prometheus prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack --namespace <namespace where Prometheus Operator is deployed>
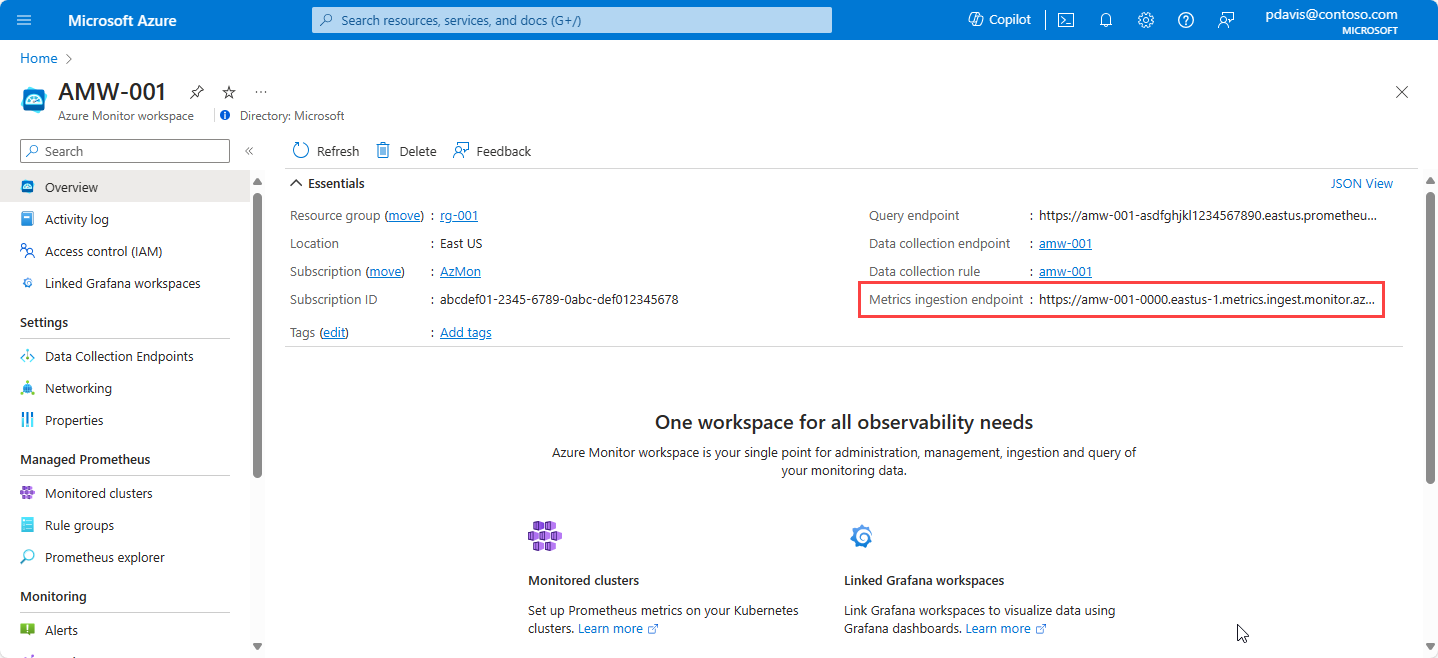
The url parameter specifies the metrics ingestion endpoint of the Azure Monitor workspace. You can find it on the overview pane for your Azure Monitor workspace in the Azure portal.
Use either managed_identity or oauth for Microsoft Entra application authentication, depending on your implementation. Remove the object that you're not using.
Note
For system-assigned managed identity, leave the client ID field blank (client_id: "" or clientId: "").
For user-assigned managed identity, find the client ID by using the following Azure CLI command:
az identity list --resource-group <resource group name>
For more information, see az identity list.
To find your client ID for managed identity authentication in the portal, go to Managed Identities in the Azure portal and select the relevant identity name. Copy the value of Client ID from the managed identity's Overview pane.

To find the client ID for the Microsoft Entra ID application, use the following Azure CLI command (or see the first step in the earlier Remote write using Microsoft Entra application authentication section):
$ az ad app list --display-name < application name>
For more information, see az ad app list.
Note
After you edit the configuration file, restart Prometheus to apply the changes.
Verify that remote write data is flowing
Use the following methods to verify that Prometheus data is being sent to your Azure Monitor workspace.
Azure Monitor metrics explorer with PromQL
To check if the metrics are flowing to the Azure Monitor workspace, from your Azure Monitor workspace in the Azure portal, select Metrics. Use metrics explorer with Prometheus Query Language (PromQL) to query the metrics that you're expecting from the self-managed Prometheus environment. For more information, see Azure Monitor metrics explorer with PromQL.
Prometheus explorer in the Azure Monitor workspace
Prometheus explorer provides a convenient way to interact with Prometheus metrics within your Azure environment, so that monitoring and troubleshooting are more efficient. To use Prometheus explorer, go to your Azure Monitor workspace in the Azure portal and select Prometheus Explorer. You can then query the metrics that you're expecting from the self-managed Prometheus environment.
For more information, see Query Prometheus metrics using Azure workbooks.
Grafana
Use PromQL queries in Grafana to verify that the results return the expected data. To configure Grafana, see the article about getting Grafana set up with managed Prometheus.
Troubleshoot remote write
If remote data isn't appearing in your Azure Monitor workspace, see Troubleshoot remote write for common problems and solutions.
Related content









