Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Get started with Azure Arc-enabled servers to manage and govern your Linux machines hosted across on-premises, edge, and multicloud environments. Once your Linux machine is Arc-enabled, you can use Azure services on your on-premises machine, such as Azure Policy, Azure Monitor, Microsoft Defender, and Azure Update Manager.
In this quickstart, you deploy and configure the Azure Connected Machine agent on a Linux machine hosted outside of Azure. This quickstart provides a manual option to onboard to Arc-enabled servers with your package manager. If you prefer, you can use an Azure portal onboarding script to automate these steps. The onboarding script configures the Microsoft package repository on your machine, installs the agent using your package manager and onboards the server.
While you can repeat the steps in this article as needed to onboard additional machines, we also provide other options for deploying the agent, including several methods designed to onboard machines at scale. For more information, see Azure Connected Machine agent deployment options.
Tip
If you prefer to try out things in a sample/practice experience, get started quickly with Azure Arc Jumpstart.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- Root permissions on the Linux machine to install and configure the Connected Machine agent.
- Review the Connected Machine agent prerequisites and verify the following requirements:
- These resource providers are registered on your subscription:
- Microsoft.HybridCompute
- Microsoft.GuestConfiguration
- Microsoft.HybridConnectivity
- Microsoft.AzureArcData
- Your target machine is running a supported operating system.
- Your account has the required Azure built-in roles.
- The machine is in a supported region.
- The Linux hostname or Windows computer name doesn't use a reserved word or trademark.
- If the machine connects through a firewall or proxy server to communicate over the Internet, make sure the URLs listed aren't blocked. You can also use Azure Arc Gateway (preview) to reduce the number of required endpoints.
- These resource providers are registered on your subscription:
Deploy the Connected Machine agent using package manager
Follow these steps to install the Azure Connected Machine agent by using your distribution's package manager.
Configure the Microsoft package repository on your machine.
For example, for Ubuntu 24.04, perform the following steps:
- Download
packages-microsoft-prod.deb. This is the Debian package that configures your system to use the Microsoft package repository. - Install the package:
sudo dpkg -i packages-microsoft-prod.deb
- Download
Install the Connected Machine agent using your package manager:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install azcmagentRetrieve your Azure tenant ID and subscription ID by running the following Azure CLI command:
az account show --query "{tenantId: tenantId, subscriptionId: id}" --output tsvOnboard your Linux machine to Azure by using the
azcmagentconnect command, using the tenant ID and subscription ID you retrieved in the previous step. You also need to specify the Azure region and resource group in which to create the Arc-enabled server resource. If you need to create a new resource group, run this Azure CLI command:az group create --name <rg-name> --location <Azure-region>.sudo azcmagent connect --resource-group "<resource_group_name>" --tenant-id "<tenant_id>" --location "<azure_region>" --subscription-id "<subscription_id>" --cloud "AzureCloud" --tags 'ArcSQLServerExtensionDeployment=Disabled'Adjust the parameters as needed:
--tenant-id: an Azure globally unique identifier (GUID) assigned to your organization's Azure AD tenant.--subscription-id: an Azure unique identifier (GUID) assigned to each Azure subscription.--location: The Azure region in which to create your Arc-enabled server resource in Azure. The region should match or be near the actual machine location.--resource-group: The name for a resource group, an Azure logical container that holds related resources. Use a resource group created in the same region as the Arc-enabled server resource you're creating.--cloud: Keep the default value,AzureCloud, unless you're using a different Azure cloud environment.--tags: Used to organize your Azure resources. Keep the tag 'ArcSQLServerExtensionDeployment=Disabled' and add any other tags if desired.Tip
You can optionally use Azure Arc Gateway (preview) to reduce the number of required endpoints. If so, include
--gateway-idand provide the ID of your gateway resource. To find this ID, run this Azure CLI command:azcmagent gateway show.
Verify the connection with Azure Arc
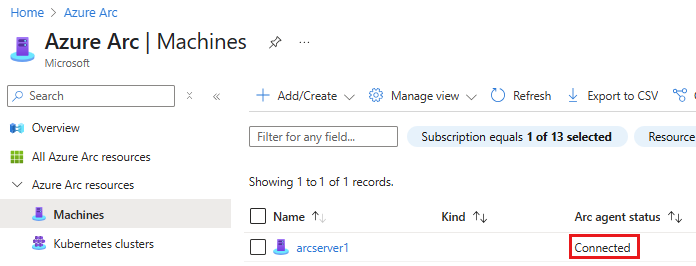
After you install the agent, verify that the server was successfully connected to Azure Arc. To do so, run azcmagent show and ensure the agent status is Connected.
This command also provides a link directly to the Azure Arc server resource in the Azure portal.
Alternately, you can go to the Azure portal page for hybrid machines and confirm that the machine has a connected status.
Next steps
Now that your Linux machine is Arc-enabled, you can enable Azure services, like Microsoft Defender, Azure Monitor, Azure Policy and Microsoft Sentinel, to manage and secure your Arc-enabled machines.
- Onboard Azure Arc-enabled servers to Microsoft Sentinel
- Deploy and configure Azure Monitor Agent using Azure Policy
- Connect your non-Azure machines to Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- Tutorial: Create a policy assignment to identify noncompliant resources
- Tutorial: Monitor a hybrid machine with VM insights