Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In Azure Container Storage enabled by Azure Arc, a volume refers to a Persistent Volume, the Kubernetes resource object.
Edge Volumes
An Edge Volume is a mountable filesystem, consisting of the Edge Volume service, a local storage volume, and other components needed to present a filesystem to applications.
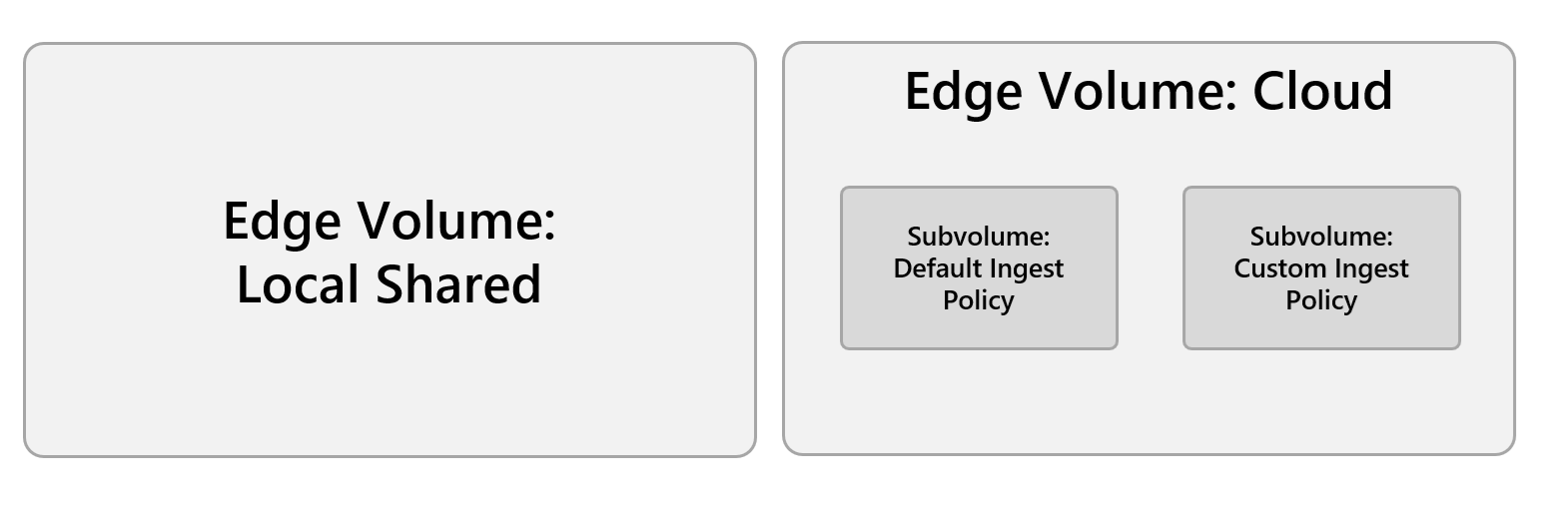
Edge Volumes run in one of two volume modes: a Local Shared mode, in which the underlying local storage isn't backed by the cloud, and a Cloud mode in which the local storage is synchronized to Azure Blob Storage.
Local Shared mode
For Edge Volumes in Local Shared mode, there's no corresponding cloud container. Data is stored only on the edge cluster in a corresponding persistent volume. This mode is intended for applications that keep local databases or have their own logic for uploading data to the cloud.
Cloud mode
An Edge Volume in Cloud mode consists of a read-only pseudo-filesystem containing subdirectories that are mapped to containers in Azure storage accounts. These subdirectories are called subvolumes. Each subvolume of a Cloud Edge Volume has a synchronization policy assigned to it upon creation. These policies specify how and when local files are synchronized with corresponding storage destinations in the cloud.
Synchronization policies
Currently, the only available synchronization policy is an Ingest policy. Under this policy, files are automatically uploaded to a corresponding cloud container, and then the local copy of that file is evicted. This process makes this policy well-suited for applications that create file-based data at the edge, but don't need to read that data back at the edge--only in the cloud. This mode continues to allow writes when the cluster is disconnected from the cloud, resuming uploads after connectivity is reestablished. Files that are successfully uploaded to the cloud are removed from the local namespace after a user-specified time, after which the cluster can no longer read them. For more information about ingest policies, see Set ingest policy.
All the subvolumes within an Edge Volume share the same local storage capacity, provisioned at the time the PVC is created. There's also a feature to limit the concurrency of data upload, and that is done at the Edge Volume level, not at the subvolume level. However, the synchronization policy is applied at the subvolume level, and controls some upload behavior, such as the upload order. For more information, see Ingest data flow.
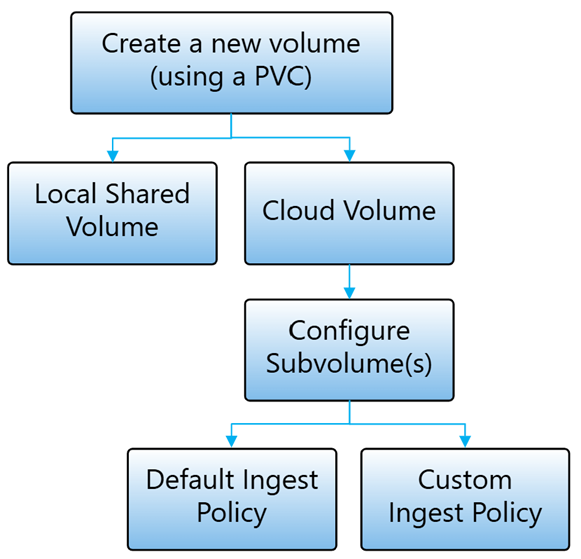
When the cluster is disconnected from the cloud, writes to the Ingest subvolume continue to be allowed, as long as you allocated sufficient storage space to fit the data that your use case generates. Once connectivity is restored, all data and any potential backlog are synchronized based on the predefined synchronization policy of the subvolume.