Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
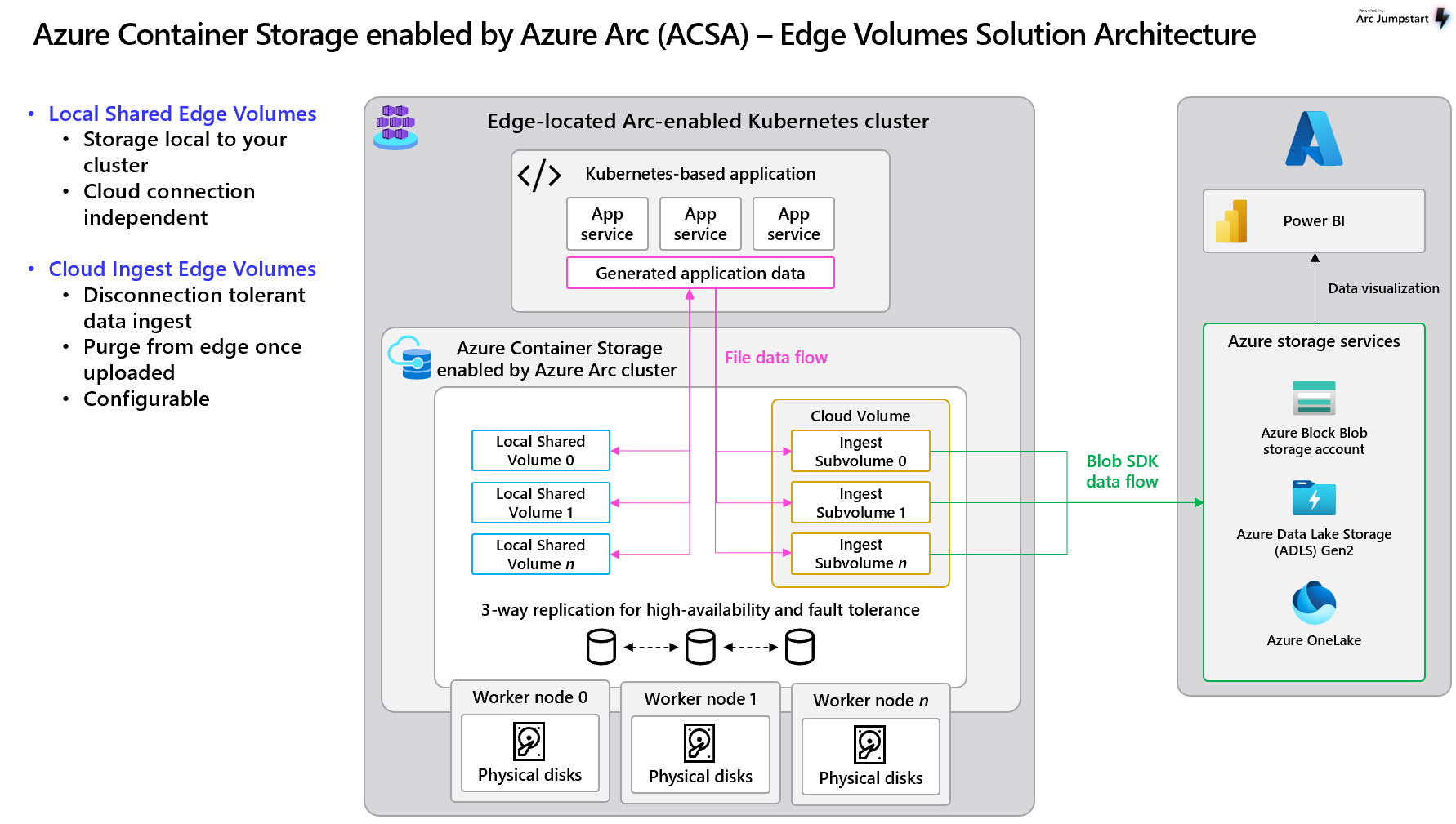
This article describes the Edge Volumes offering from Azure Container Storage enabled by Azure Arc.
What are the Edge Volumes offerings?
The first Edge Volumes offering is Local Shared Edge Volumes, providing highly available, failover-capable storage, local to your Kubernetes cluster. This shared storage type remains independent of cloud infrastructure, making it ideal for scratch space, temporary storage, and locally persistent data unsuitable for cloud destinations.
The second offering is Cloud Ingest Edge Volumes, which facilitates limitless data ingestion from edge to Blob, including Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 and OneLake. Files written to this storage type are seamlessly transferred to Blob storage and subsequently purged from the local cache once confirmed uploaded, ensuring space availability for new data. Configurable policies allow for flexibility in upload and purge behaviors. Moreover, this storage option supports data integrity in disconnected environments, enabling local storage and synchronization upon reconnection to the network.
Tailored for IoT applications, Edge Volumes not only eliminates local storage concerns and ingest limitations, but also optimizes local resource utilization and reduces storage requirements.
How do Edge Volumes work?
To download architecture diagrams in high resolution, visit Jumpstart Gems.
You write to Edge Volumes as if they were your local file system. For a Local Shared Edge Volume, your data is stored and left untouched. For a Cloud Ingest Edge Volume, the volume follows your specified ingest policy for delays and ingestion times, and uploads your data. It will then purge the local copy, also in accord with your specified ingest policy parameter, allowing you to keep your local volume clear of old data and continue to receive new data.