Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Feature flags can use feature filters to enable features conditionally. To learn more about feature filters, see Enable conditional features with feature filters.
The example used in this guide is based on the Go Gin web application introduced in the feature management quickstart. Before proceeding further, complete the quickstart to create a Go Gin web application with a Beta feature flag. Once completed, you must add a custom feature filter to the Beta feature flag in your App Configuration store.
In this guide, you learn how to implement a custom feature filter and use the feature filter to enable features conditionally.
Prerequisites
- Create a Go Gin web application with a feature flag.
- Add a custom feature filter to the feature flag
Implement a custom feature filter
You added a custom feature filter named Random with a Percentage parameter for your Beta feature flag in the prerequisites. Next, you'll implement the feature filter to enable the Beta feature flag based on the chance defined by the Percentage parameter.
Create a
random_filter.gofile with the following code:package main import ( "fmt" "math/rand" "time" "github.com/microsoft/Featuremanagement-Go/featuremanagement" ) type RandomFilter struct{} func (f *RandomFilter) Name() string { return "Random" } func (f *RandomFilter) Evaluate(evalCtx featuremanagement.FeatureFilterEvaluationContext, appCtx any) (bool, error) { percentage, ok := evalCtx.Parameters["Percentage"].(float64) if !ok { return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid parameter type for Percentage: expected float64, got %T", evalCtx.Parameters["Percentage"]) } rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano()) randomValue := rand.Intn(100) return randomValue <= int(percentage), nil }You added a
RandomFilterstruct that implements theFeatureFilterinterface from thefeaturemanagementlibrary. TheFeatureFilterinterface has two methods:Name()returns the filter name Random, which matches the filter name you set in the Beta feature flag in Azure App Configuration.Evaluate()is called whenever a feature flag is evaluated. A feature filter enables a feature flag by returningtrue.
Update your
main.gofile to register theRandomFilterwhen creating the feature manager:// ...existing code... func main() { ctx := context.Background() // Load Azure App Configuration appConfig, err := loadAzureAppConfiguration(ctx) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Error loading Azure App Configuration: %v", err) } // Create feature flag provider featureFlagProvider, err := azappconfig.NewFeatureFlagProvider(appConfig) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Error creating feature flag provider: %v", err) } // Register custom filters options := &featuremanagement.Options{ Filters: []featuremanagement.FeatureFilter{ &RandomFilter{}, }, } // Create feature manager with custom filters featureManager, err := featuremanagement.NewFeatureManager(featureFlagProvider, options) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Error creating feature manager: %v", err) } // ...existing code... }
Feature filter in action
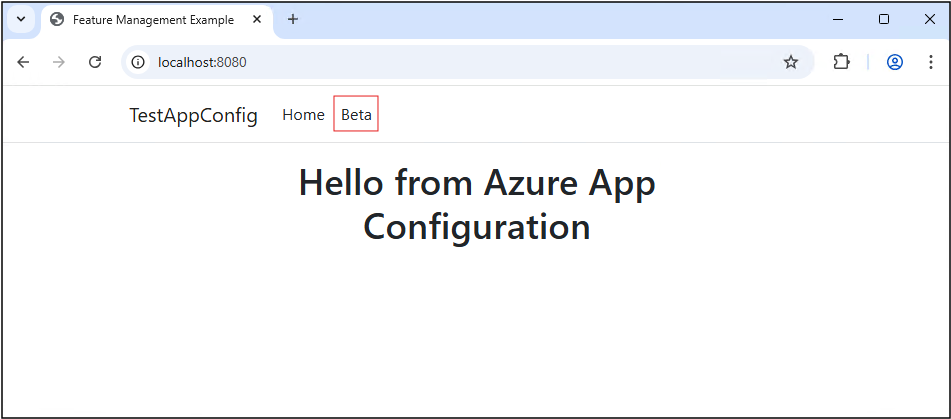
Relaunch the application and refresh the browser a few times. Without manually toggling the feature flag, the Beta menu appears randomly based on the percentage you set.
Next steps
To learn more about the built-in feature filters, continue to the following documents.
For the full feature rundown of the Go feature management library, continue to the following document.