Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to expose a Spring Boot web app's functionality through OpenAPI, add it as a tool to Azure AI Foundry Agent Service, and interact with your app using natural language in the agents playground.
If your web application already has useful features, like shopping, hotel booking, or data management, it's easy to make those capabilities available to an AI agent in Azure AI Foundry Agent Service. By simply adding an OpenAPI schema to your app, you enable the agent to understand and use your app's capabilities when it responds to users' prompts. This means anything your app can do, your AI agent can do too, with minimal effort beyond creating an OpenAPI endpoint for your app. In this tutorial, you start with a simple to-do list app. By the end, you'll be able to create, update, and manage tasks with an agent through conversational AI.
- Add OpenAPI functionality to your web app.
- Make sure OpenAPI schema compatible with Azure AI Foundry Agent Service.
- Register your app as an OpenAPI tool in Azure AI Foundry Agent Service.
- Test your agent in the the agents playground.
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes you're working with the sample used in Tutorial: Build a Java Spring Boot web app with Azure App Service on Linux and Azure Cosmos DB.
At a minimum, open the sample application in GitHub Codespaces and deploy the app by running azd up.
Add OpenAPI functionality to your web app
Tip
You can make all the following changes by telling GitHub Copilot in Agent mode:
I'd like to generate OpenAPI functionality using Spring Boot OpenAPI. Please also generate the server URL and operation ID in the schema.
In the codespace, open pom.xml and add the following dependency:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springdoc</groupId> <artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId> <version>2.6.0</version> </dependency>Open src/main/java/com/microsoft/azure/appservice/examples/springbootmongodb/controller/TodoListController.java and add the following imports.
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation; import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;The
TodoListControllerclass implements@RestController, so you only need to add a few annotations to make it compatible with OpenAPI. Additionally, to make the APIs compatible with the Azure AI Foundry Agent Service, you must specify theoperationIdproperty in the@Operationannotation (see How to use Azure AI Foundry Agent Service with OpenAPI Specified Tools: Prerequisites).Find the class declaration and add the
@Tagannotation as shown in the following snippet:@RestController @Tag(name = "Todo List", description = "Todo List management APIs") public class TodoListController {Find the
getTodoItemmethod declaration and add the@Operationannotation withdescriptionandoperationId, as shown in the following snippet:@Operation(description = "Returns a single todo item", operationId = "getTodoItem") @GetMapping(path = "/api/todolist/{index}", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE}) public TodoItem getTodoItem(@PathVariable("index") String index) {Find the
getAllTodoItemsmethod declaration and add the@Operationannotation withdescriptionandoperationId, as shown in the following snippet:@Operation(description = "Returns a list of all todo items", operationId = "getAllTodoItems") @GetMapping(path = "/api/todolist", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE}) public List<TodoItem> getAllTodoItems() {Find the
addNewTodoItemmethod declaration and add the@Operationannotation withdescriptionandoperationId, as shown in the following snippet:@Operation(description = "Creates a new todo item", operationId = "addNewTodoItem") @PostMapping(path = "/api/todolist", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) public String addNewTodoItem(@RequestBody TodoItem item) {Find the
updateTodoItemmethod declaration and add the@Operationannotation withdescriptionandoperationId, as shown in the following snippet:@Operation(description = "Updates an existing todo item", operationId = "updateTodoItem") @PutMapping(path = "/api/todolist", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) public String updateTodoItem(@RequestBody TodoItem item) {Find the
deleteTodoItemmethod declaration and add the@Operationannotation withdescriptionandoperationId, as shown in the following snippet:@Operation(description = "Deletes a todo item by ID", operationId = "deleteTodoItem") @DeleteMapping("/api/todolist/{id}") public String deleteTodoItem(@PathVariable("id") String id) {This minimal configuration gives you the following settings, as documented in springdoc-openapi:
- Swagger UI at
/swagger-ui.html. - OpenAPI specification at
/v3/api-docs.
- Swagger UI at
In the codespace terminal, run the application with
mvn spring-boot:run.Select Open in Browser.
Navigate to the Swagger UI by adding
/swagger-ui.htmlto the URL.Confirm that the API operations work by trying them out in the Swagger UI.
Back in the codespace terminal, deploy your changes by committing your changes (GitHub Actions method) or run
azd up(Azure Developer CLI method).Once your changes are deployed, navigate to
https://<your-app's-url>/v3/api-docsand copy the schema for later.
Create an agent in Azure AI Foundry
Create an agent in the Azure AI Foundry portal by following the steps at: Quickstart: Create a new agent.
Select the new agent and add an action with the OpenAPI 3.0 specified tool by following the steps at How to use the OpenAPI spec tool.
In the Define schema page, paste the schema that you copied earlier. Review and save the action.
Test the agent
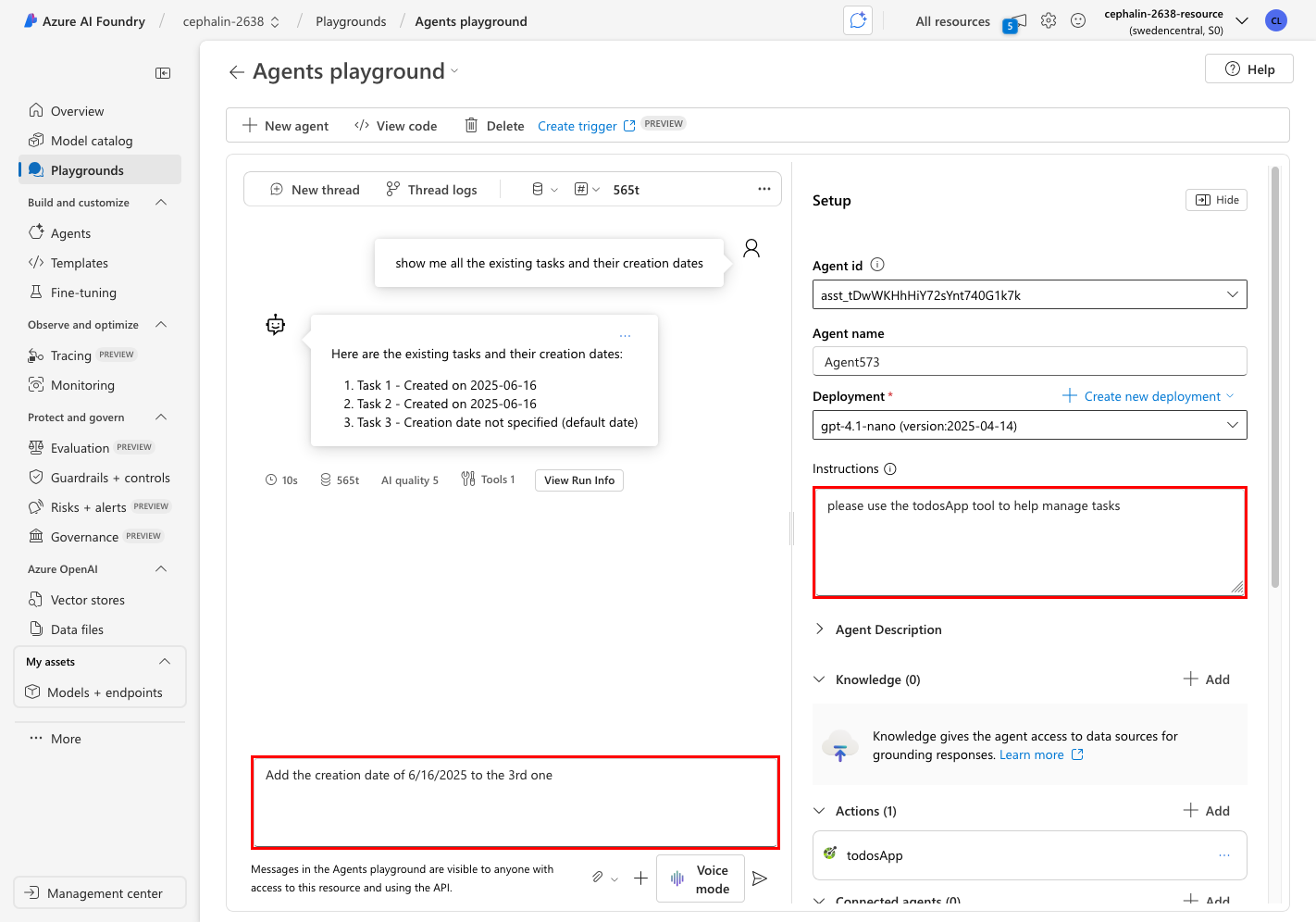
If the agents playground isn't already opened in the foundry portal, select the agent and select Try in playground.
In Instructions, give some simple instructions, like "Please use the todosApp tool to help manage tasks."
Chat with the agent with the following prompt suggestions:
- Show me all the tasks.
- Create a task called "Come up with three lettuce jokes."
- Change that to "Come up with three knock-knock jokes."

Security best practices
When exposing APIs via OpenAPI in Azure App Service, follow these security best practices:
- Authentication and Authorization: Protect your OpenAPI endpoints in App Service behind Azure API Management with Microsoft Entra ID and ensure only authorized users or agents can access the tools.
- Validate and sanitize input data: The example code in this tutorial omits input validation and sanitization for simplicity and clarity. In production scenarios, always implement proper validation and sanitization to protect your application. For Spring, see Spring: Validating Form Input.
- Use HTTPS: The sample relies on Azure App Service, which enforces HTTPS by default and provides free TLS/SSL certificates to encrypt data in transit.
- Limit CORS: Restrict Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) to trusted domains only. For more information, see Enable CORS.
- Apply rate limiting: Use API Management or custom middleware to prevent abuse and denial-of-service attacks.
- Hide sensitive endpoints: Avoid exposing internal or admin APIs in your OpenAPI schema.
- Review OpenAPI schema: Ensure your OpenAPI schema doesn't leak sensitive information (such as internal URLs, secrets, or implementation details).
- Keep dependencies updated: Regularly update NuGet packages and monitor for security advisories.
- Monitor and log activity: Enable logging and monitor access to detect suspicious activity.
- Use managed identities: When calling other Azure services, use managed identities instead of hardcoded credentials.
For more information, see Secure your App Service app and Best practices for REST API security.
Next step
You've now enabled your App Service app to be used as a tool by Azure AI Foundry Agent Service and interact with your app's APIs through natural language in the agents playground. From here, you can continue add features to your agent in the Foundry portal, integrate it into your own applications using the Azure AI Foundry SDK or REST API, or deploy it as part of a larger solution. Agents created in Azure AI Foundry can be run in the cloud, integrated into chatbots, or embedded in web and mobile apps.
Note
Azure AI Foundry Agent Service doesn't have a Java SDK currently. To see how you can use the agent you created, see Tutorial: Build an agentic web app in Azure App Service with Microsoft Semantic Kernel or Azure AI Foundry Agent Service (.NET).