Note
The information provided in this article is specific to a hub-based project, and doesn't apply for a Foundry project. For more information, see Types of projects.
An Azure AI Foundry hub defaults to use of a shared key to access its default Azure Storage account. With key-based authorization, anyone who has the key and access to the storage account can access data.
To reduce the risk of unauthorized access, you can disable key-based authorization, and instead use Microsoft Entra ID for authorization. This configuration uses a Microsoft Entra ID value to authorize access to the storage account. The identity used to access storage is either the user's identity or a managed identity. The user's identity is used to view data in the Azure Machine Learning studio, or to run a notebook while authenticated with the user's identity. The Azure Machine Learning service uses a managed identity to access the storage account - for example, when running a training job as the managed identity.
Use of your hub with a shared key disabled storage account is currently in preview.
Important
This feature is currently in public preview. This preview version is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.
For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Prerequisites
Install the SDK v2.
Important
The steps in this article require the azure-ai-ml Python package, version 1.17.0. To determine the installed package version, use the pip list command from your Python development environment.
Install azure-identity: pip install azure-identity. If you're working in a notebook cell, use %pip install azure-identity.
Provide your subscription details:
# Enter details of your subscription
subscription_id = "<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>"
resource_group = "<RESOURCE_GROUP>"
Get a handle to the subscription. All the Python code in this article uses ml_client:
# get a handle to the subscription
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
ml_client = MLClient(DefaultAzureCredential(), subscription_id, resource_group)
- (Optional) If you have multiple accounts, add the tenant ID of the Microsoft Entra ID you wish to use into the
DefaultAzureCredential. Find your tenant ID from the Azure portal, under Microsoft Entra ID, External Identities.
DefaultAzureCredential(interactive_browser_tenant_id="<TENANT_ID>")
- (Optional) If you're working in the Azure Government - US or Azure China 21Vianet regions, you must specify the cloud into which you want to authenticate. You can specify these regions in
DefaultAzureCredential.
from azure.identity import AzureAuthorityHosts
DefaultAzureCredential(authority=AzureAuthorityHosts.AZURE_GOVERNMENT))
To use the CLI commands in this document, you need the Azure CLI and the ml extension.
If you use the Azure Cloud Shell, the CLI is accessed through the browser, and it lives in the cloud.
Important
The steps in this article require the Azure CLI extension for machine learning, version 2.27.0 or greater. To determine the version of the extension you have installed, use the az version command from the Azure CLI. In the extensions collection that's returned, find the ml extension. This code sample shows an example return value:
{
"azure-cli": "2.61.0",
"azure-cli-core": "2.61.0",
"azure-cli-telemetry": "1.1.0",
"extensions": {
"ml": "2.27.0"
}
}
- An existing Azure Key Vault instance.
- The Azure Resource Manager ID for both the Azure Storage Account and Azure Key Vault to be used with the hub.
Create a new hub
When you create a new hub, the creation process can automatically disable shared key access. You can also create an Azure Storage account, disable shared key access, and use it during hub creation.
From the Azure portal, search for Azure AI Foundry. From the left menu, select AI Hubs, and then select + Create and Hub.
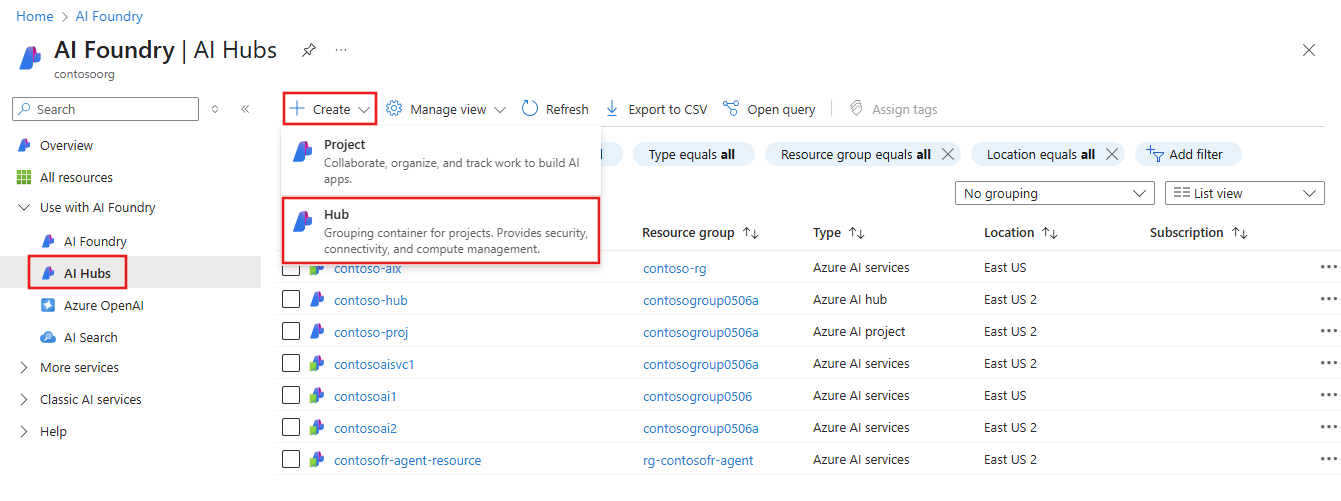
From the Basics tab, enter the hub details and then select the Storage tab. Select the Azure Storage account that you previously created.
From the Identity tab, set the Storage account access type to identity-based and then enable the Disable shared key access option.
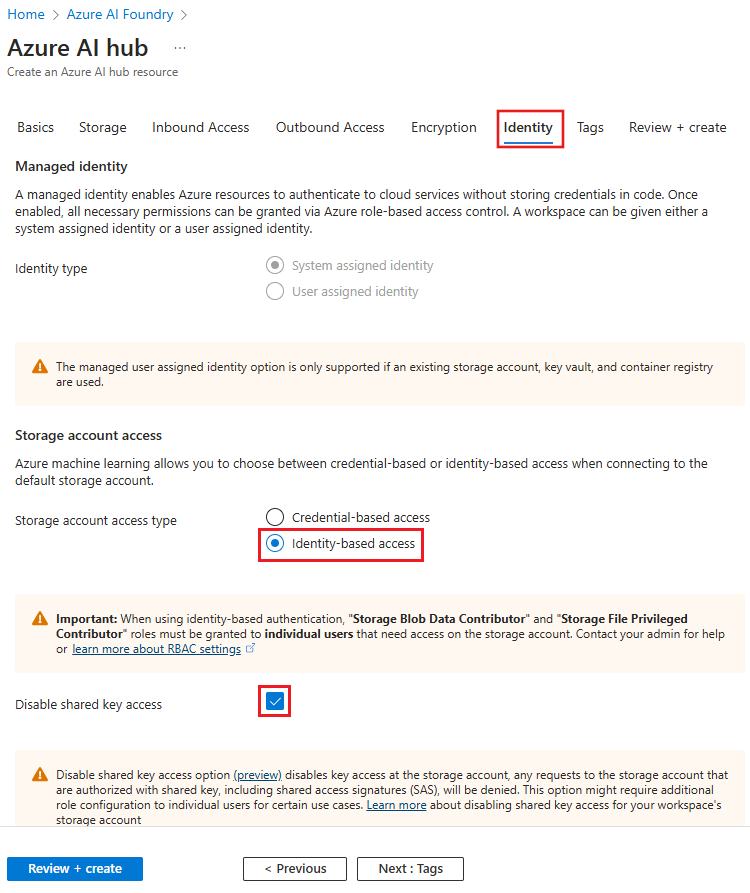
Continue the hub creation process. As the hub is created, the managed identity is automatically assigned the permissions it needs to access the storage account.
When you create your hub with the SDK, set system_datastores_auth_mode="identity". To use a preexisting storage account, use the storage_account parameter to specify the Azure Resource Manager ID of an existing storage account:
# Creating a unique hub name with current datetime to avoid conflicts
from azure.ai.ml.entities import Hub
import datetime
hub_name = "mlw-hub-prod-" + datetime.datetime.now().strftime(
"%Y%m%d%H%M"
)
ws_hub = Hub(
name=hub_name,
location="eastus",
display_name="Hub-example",
description="This example shows how to create a Hub",
hbi_workspace=False,
tags=dict(purpose="demo"),
storage_account= {existing_storage_account with AllowSharedKeyAccess=false},
system_datastores_auth_mode="identity",
)
created_hub = ml_client.workspaces.begin_create(ws_hub).result()
print(created_hub)
To create a new hub with Microsoft Entra ID authorization for the storage account, use a YAML configuration file that sets system_datastores_auth_mode to identity. You can also specify the Azure Resource ID value of an existing storage account with the storage_account entry.
This example YAML file shows how to set the hub to use a managed identity and an existing storage account:
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/workspace.schema.json
name: mlw-basicex-prod
location: eastus
display_name: Bring your own dependent resources-example
description: This configuration specifies a workspace configuration with existing dependent resources
storage_account: {your storage account resource id}
system_datastores_auth_mode: identity
tags:
purpose: demonstration
This YAML file can be used with the az ml workspace create command, with the --file parameter:
az ml workspace create -g <resource-group-name> --kind hub --file workspace.yml
In the following JSON template example, substitute your own values for the following placeholders:
- [workspace name]
- [workspace friendly name]
- [Storage Account ARM resource ID]
- [Key Vault ARM resource ID]
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources":
[
{
"type": "Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces",
"apiVersion": "2024-04-01",
"name": "[workspace name]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"sku":
{
"name": "Basic",
"tier": "Basic"
},
"kind": "Hub",
"identity":
{
"type": "SystemAssigned"
},
"properties":
{
"friendlyName": "[workspace friendly name]",
"storageAccount": "[Storage Account ARM resource ID]",
"keyVault": "[Key Vault ARM resource ID]",
"systemDatastoresAuthMode": "identity",
"managedNetwork":
{
"isolationMode": "Disabled"
},
"publicNetworkAccess": "Enabled"
}
}
]
}
For information on deploying an ARM template, use one of the following articles:
After you create the hub, identify all the users that will use it - for example, Data Scientists. These users must be assigned the Storage Blob Data Contributor and Storage File Data Privileged Contributor roles in Azure role-based access control for the storage account. If these users only need read access, use the Storage Blob Data Reader and Storage File Data Privileged Reader roles instead. For more information, visit the role assignments section.
Update an existing hub
If you have an existing Azure AI Foundry hub, use the steps in this section to update the hub to use Microsoft Entra ID, to authorize access to the storage account. Then, disable shared key access on the storage account.
Go to the Azure portal and select the Azure AI Foundry hub.
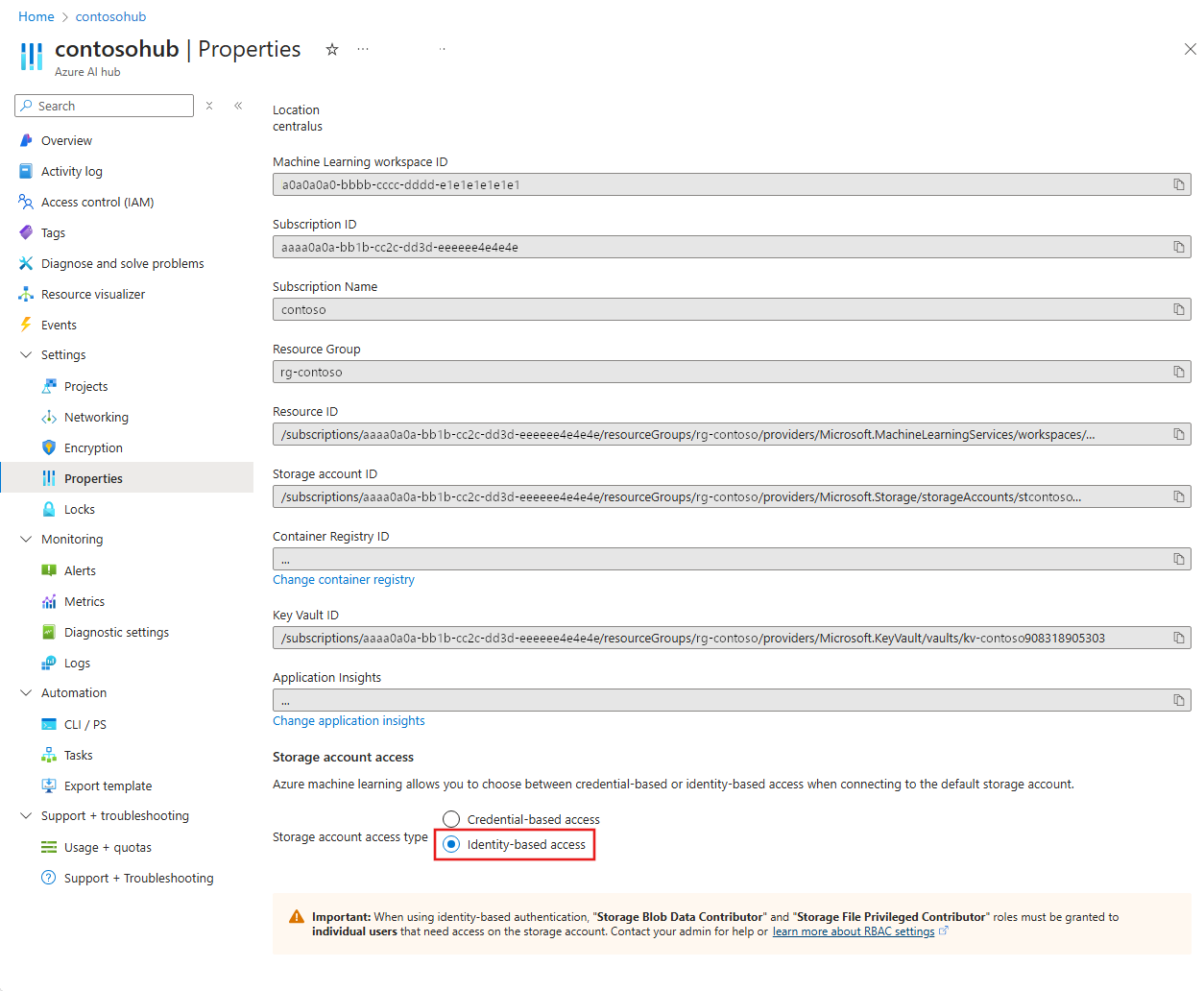
From the left menu, select Properties. From the bottom of the page, set Storage account access type to Identity-based. Select Save from the top of the page to save the configuration.
To update an existing hub, set the system_datastores_auth_mode = "identity" for the hub. This code sample shows an update of a hub named test-ws1:
ml_client = MLClient(DefaultAzureCredential(), subscription_id, resource_group)
ws = ml_client.workspaces.get(name="test-ws1")
ws.system_datastores_auth_mode = "identity"
ws = ml_client.workspaces.begin_update(workspace=ws).result()
To update an existing hub, use the az ml workspace update command, and specify --system-datastores-auth-mode identity. This example shows an update of a hub named myhub:
az ml workspace update --name myhub --system-datastores-auth-mode identity
In the following JSON template example, substitute your own values for the following placeholders:
- [workspace name]
- [workspace friendly name]
- [Storage Account ARM resource ID]
- [Key Vault ARM resource ID]
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources":
[
{
"type": "Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces",
"apiVersion": "2024-04-01",
"name": "[workspace name]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"sku":
{
"name": "Basic",
"tier": "Basic"
},
"kind": "Hub",
"identity":
{
"type": "SystemAssigned"
},
"properties":
{
"friendlyName": "[workspace friendly name]",
"storageAccount": "[Storage Account ARM resource ID]",
"keyVault": "[Key Vault ARM resource ID]",
"systemDatastoresAuthMode": "identity",
"managedNetwork":
{
"isolationMode": "Disabled"
},
"publicNetworkAccess": "Enabled"
}
}
]
}
For information on deploying an ARM template, use one of the following articles:
Assign roles to users
After you update the hub, update the storage account to disable shared key access. For more information about disabling shared key access, visit the Prevent shared key authorization for an Azure Storage account article resource.
You must also identify all the users that need access to the default datastores - for example, Data Scientists. These users must be assigned the Storage Blob Data Contributor and Storage File Data Privileged Contributor roles in Azure role-based access control for the storage account. If these users only need read access, use the Storage Blob Data Reader and Storage File Data Privileged Reader roles instead. For more information, visit the role assignments resource in this document.
Revert to use shared keys
To revert a hub back to use of shared keys to access the storage account, use this information:
To update an existing workspace, go to Properties and select Credential-based access.
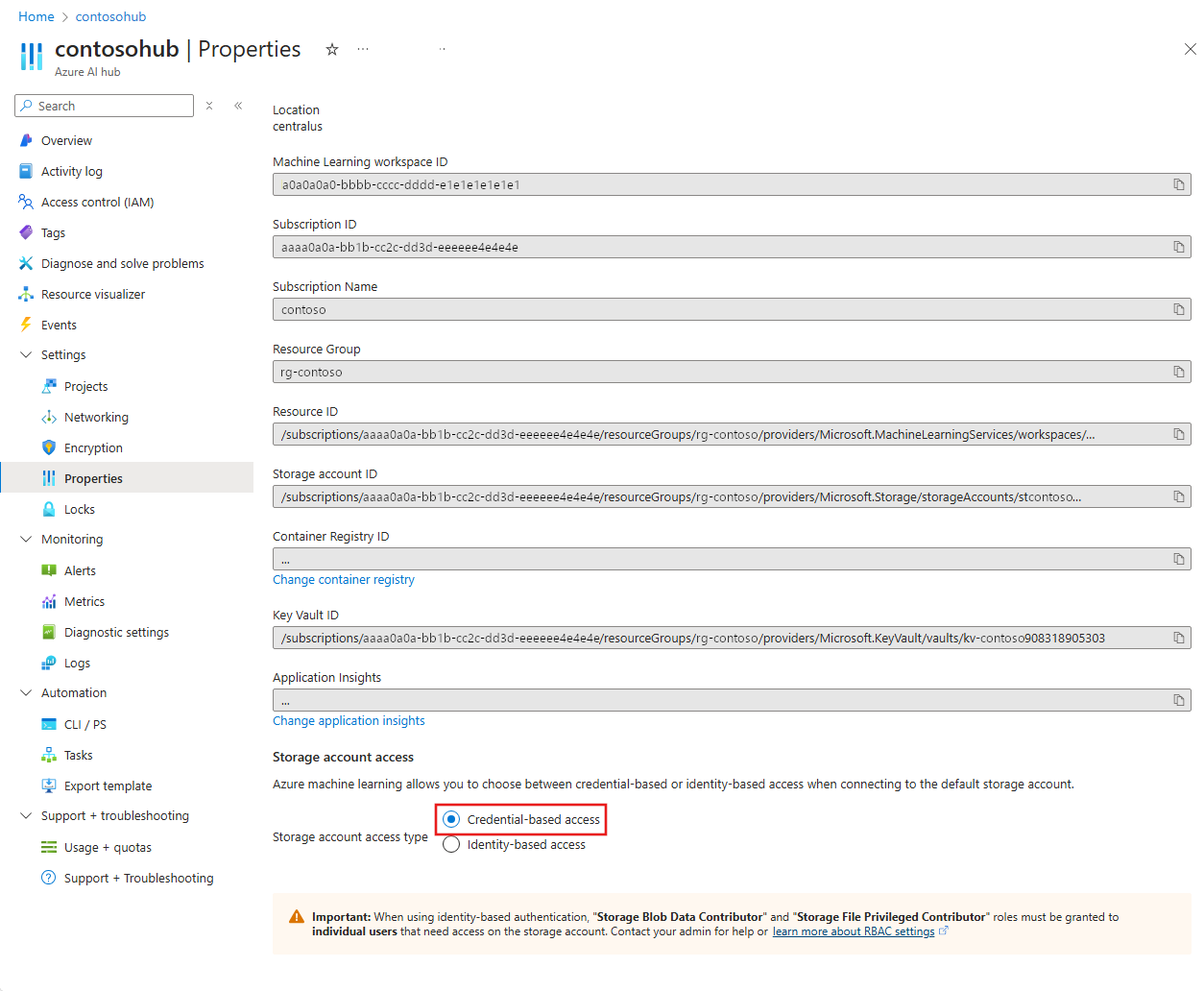
Select Save to save this choice.
To configure the hub to use a shared key again, set the system_datastores_auth_mode = "accesskey" for the hub. This code demonstrates an update of a hub named test-ws1:
ml_client = MLClient(DefaultAzureCredential(), subscription_id, resource_group)
ws = ml_client.workspaces.get(name="test-ws1")
ws.system_datastores_auth_mode = "accesskey"
ws = ml_client.workspaces.begin_update(workspace=ws).result()
To configure the hub to once again use a shared key, use the az ml workspace update command, and specify --system-datastores-auth-mode accesskey. This example demonstrates an update of a hub named myhub:
az ml workspace update --name myhub --system-datastores-auth-mode accesskey
If you have an existing Azure AI Foundry hub, use the steps in this section to update the hub to use Microsoft Entra ID, to authorize access to the storage account. Then, disable shared key access on the storage account.
In the following JSON template example, substitute your own values for the following placeholders:
- [workspace name]
- [workspace friendly name]
- [Storage Account ARM resource ID]
- [Key Vault ARM resource ID]
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources":
[
{
"type": "Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces",
"apiVersion": "2024-04-01",
"name": "[workspace name]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"sku":
{
"name": "Basic",
"tier": "Basic"
},
"kind": "Hub",
"identity":
{
"type": "SystemAssigned"
},
"properties":
{
"friendlyName": "[workspace friendly name]",
"storageAccount": "[Storage Account ARM resource ID]",
"keyVault": "[Key Vault ARM resource ID]",
"systemDatastoresAuthMode": "accesskey",
"managedNetwork":
{
"isolationMode": "Disabled"
},
"publicNetworkAccess": "Enabled"
}
}
]
}
For information on deploying an ARM template, use one of the following articles:
After you create the hub, identify all the users that will use it - for example, Data Scientists. These users must be assigned the Storage Blob Data Contributor and Storage File Data Privileged Contributor roles in Azure role-based access control for the storage account. If these users only need read access, use the Storage Blob Data Reader and Storage File Data Privileged Reader roles instead. For more information, visit the role assignments resource in this document.
After you revert the hub, update the storage account to enable shared key access. For more information, visit the Prevent shared key authorization for an Azure Storage account article.
Scenarios for hub storage account role assignments
To work with a storage account with disabled shared key access, you might need to grant more roles to either your users or the managed identity for your hub. Hubs have a system-assigned managed identity by default. However, some scenarios require a user-assigned managed identity. This table summarizes the scenarios that require extra role assignments:
| Scenario |
Microsoft Entra ID |
Required roles |
Notes |
| AI Speech |
Storage Blob Data Contributor
Storage File Data Privileged Contributor |
|
|
| Model-as-a-Service |
system-assigned managed identity |
Storage Blob Data Contributor |
The hub's managed identity.
Automatically assigned the role when provisioned.
Don't manually change this role assignment. |
| Azure Search |
system-assigned managed identity |
Storage Blob Data Contributor |
The hub's managed identity.
Automatically assigned the role when provisioned.
Don't manually change this role assignment. |
| Fine tuning of OSS models |
User-assigned managed identity |
Storage Blob Data Contributor |
|
| PromptFlow |
User's identity |
Storage Blob Data Contributor
Storage File Data Privileged Contributor |
|
| Add and manage your own data |
User's identity |
Storage Blob Data Contributor |
|
Related content




