Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Introduction
By default when setting up a connection string using Entity Framework Core the connection string is setup in OnConfiguring method of a DbContext. Information provided here will provide an easy way to setup a connection string for windows form projects.
EF Core 5 connections
See the following article which moves away from app.config and uses appsettings.json. Full source is located in the following repository.
{
"database": {
"DatabaseServer": ".\\SQLEXPRESS",
"Catalog": "School",
"IntegratedSecurity": "true",
"UsingLogging": "true"
}
}
Out of the box connection
The following shows how a connection string is setup for, in this case SQL-Server. This is fine for applications where the server is always the same in development, test and production environments while when the server name changes in a fluid environment this will not work without changing the server name, build then deploy each time the environment changes.
For those applications that require a user name and password the best option is not to store user name and password in the connection string, instead setup users and roles in the database. See the following for SQL-Server for creating a login.
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
if (!optionsBuilder.IsConfigured)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(
"Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;" +
"Database=NorthWindAzureForInserts;Trusted_Connection=True;");
}
}
Using an application configuration file
A flexible solution is to store the server and database properties for a connection in the project application configuration file and not storing these properties under project properties setting, instead using the following.
First add a reference for System.Configuration. Next add the following to the project's application configuration file. Change both setting to the correct database and catalog. When the environment changes edit the configuration file with note pad and save.
See this in app.config in the source code.
<appSettings>
<add key="DatabaseServer" value = ".\SQLEXPRESS" />
<add key="DefaultCatalog" value = "NorthWindAzureForInserts" />
</appSettings>
Add the following using statement to the project's DbContext class.
using static System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager;
Update OnConfiguring method in the DbContext class.
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
if (!optionsBuilder.IsConfigured)
{
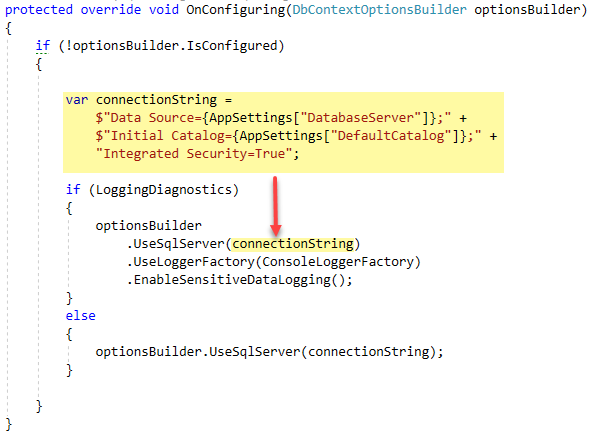
var connectionString =
$"Data Source={AppSettings["DatabaseServer"]};" +
$"Initial Catalog={AppSettings["DefaultCatalog"]};" +
"Integrated Security=True";
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(connectionString);
}
}
One more thing should be done to ensure both properties are set and exists. In the default constructor of the DbContext assert the two properties exists.
public NorthWindContext()
{
if (AppSettings["DatabaseServer"] == null || AppSettings["DefaultCatalog"] == null)
{
throw new Exception("Missing connection string properties in app.config");
}
}
Summary
Storing a DbContext connection string for a Windows Form project in app.config provide more flexibility then hard coding a connection string in the DbContext code.
See also
.NET Core desktop application configurations
Entity Framework Core shadow properties (C#)
Entity Framework Core 3.x Global Query Filters (C#)
Windows Forms: Entity Framework Core Reverse Engineering databases
Source code
Clone or download the following GitHub repository which contains more than focus on a dynamic connection string. There are two project in the repository, the project ConsoleLoggingExample is the one to work from.
Note the following code is for another article on how to log with Entity Framework .