Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Hi ,in this article i am trying to explain the SCCM 2012 DATA Replication Concept with neccessay points.So you can understand the concept in 2-3 mints.
In a SCCM hierarchy, each site communicates with its parent site and its direct child sites by using two different data transfer methods: File-based replication and Database replication.
**File-Based Replication:
**
- Includes content such as applications and packages that you want to deploy to distribution points.
- File-based communication between sites uses the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol by using TCP/IP port 445
**Database Replication:
**
- Database replication uses SQL Server to transfer data and merge changes that are made in a site database with the information stored in the database at other sites in the hierarchy.
- Database replication is automatically configured by all Configuration Manager sites.
- The database replication service uses SQL Server change tracking to monitor the local site database for changes, and then replicates those changes to other sites by using a SQL Server Service Broker.
- This process uses the TCP/IP port 4022.
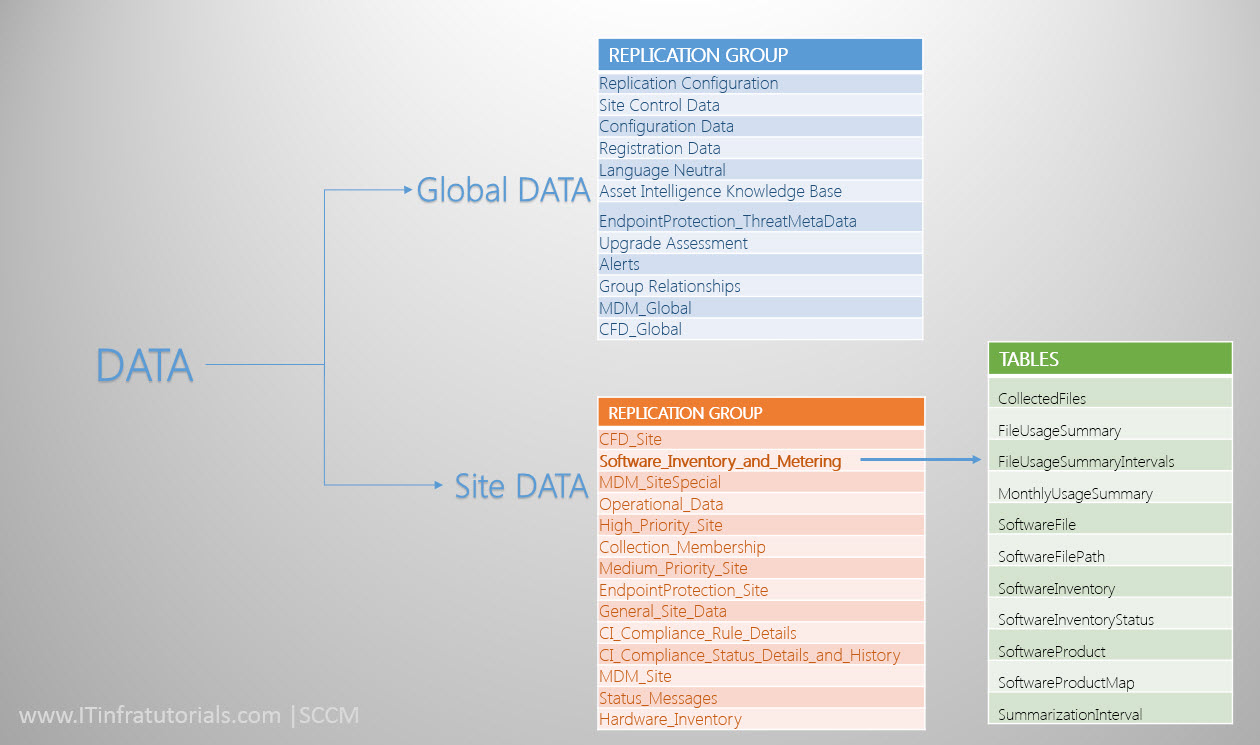
- Configuration Manager classifies the Data that it replicates by database replication as either Global data or Site data.
- Global Data**:** Global data refers to administrator-created objects that replicate to all sites throughout the hierarchy.Examples of global data include software deployments, software updates, collection definitions, and role-based administration security scopes.
- Site Data: Site data refers to operational information's.Examples of site data include hardware inventory data, status messages, alerts, and the results from query-based collections.
- Configuration Manager groups data that replicates by database replication into different Replication groups.
- Each replication group has a separate, fixed replication schedule that determines how frequently changes to the data in the group is replicated to other sites. For example, a configuration change to a role-based administration configuration replicates quickly to other sites to ensure that these changes are enforced as soon as possible. Meanwhile a lower priority configuration change, such as a request to install a new secondary site, replicates with less urgency and takes several minutes for the new site request to reach the destination primary site.
In the next article i will explain this concept with example .Thanks.