Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Introduction
This article introduces how to export data to an Excel file. Most of the back-end applications have report functionality that shows the data in the grid. So, we are required to export this grid data into an Excel file. The export to Excel functionality is implemented using the EPPlus NuGet package, as shown in this example.
Configuration and Process
We install EPPlus NuGet package in the application. The EPPlus is a library to manage Excel spreadsheets using OOXML. The OOXML stands for Office Open Extended Markup Language and is also called Open XML. The OOXML is developed by Microsoft. It has by default target file formats for Microsoft office.
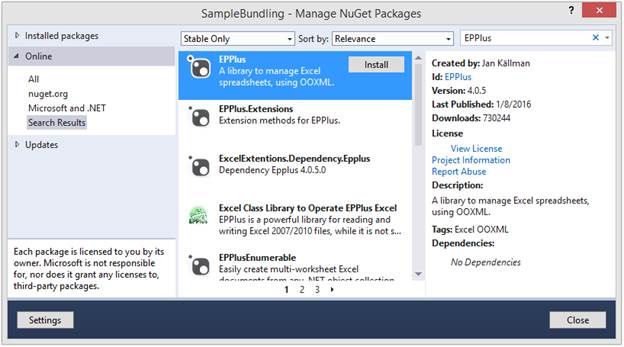
The EPPlus is a NuGet package and can be installed from Manage NuGet Packages window, as shown in figure 1. The package is available here also.
Figure 1: Install EPPlus NuGet
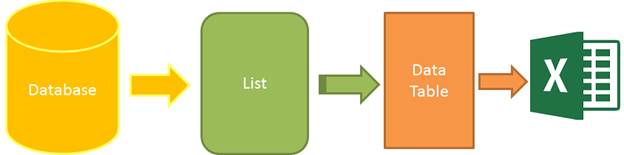
When we use ORM in our application, we keep most of the data in the collection which easily converts it into a list. The list can't be exported to the Excel directly. That's why we need to convert this list into a data table first. After that, this data table can be exported in the Excel file as shown in figure 2.
Figure 2: Process Export to Excel
Using the Code
As per the above process, we need four operations here. These are as follows,
- Data: We use static data to keep this example simple.
- List: Static data store in a List.
- Data Table : Convert List in to DataTable.
- Export: DataTable exports to excel file.
First of all, we create a class, so that we can have a collection of similar data. The following code snippet is for Technology class.
namespace ExportExcel.Code
{
public class Technology
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Project { get; set; }
public int Developer { get; set; }
public int TeamLeader { get; set; }
}
}
Now, we create a static data list of Technology types in that StaticData class, as per the following code snippet.
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ExportExcel.Code
{
public class StaticData
{
public static List<Technology> Technologies
{
get
{
return new List<Technology>{
new Technology{Name="ASP.NET", Project=12,Developer=50, TeamLeader=6},
new Technology{Name="Php", Project=40,Developer=60, TeamLeader=9},
new Technology{Name="iOS", Project=11,Developer=5, TeamLeader=1},
new Technology{Name="Android", Project=20,Developer=26, TeamLeader=2}
};
}
}
}
}
This data will be used to export to Excel. After that, we create export to excel functionality helper class which has the following features.
- Convert List to DataTable method
- Customize the columns which need to export means dynamically choose columns which will be export from list to Excel.
- Serial number in Excel sheet.
- Add and Remove functionality for the custom heading in Excel sheet.
- Excel sheet heading with colors.
- Dynamic name for worksheet.
The following code snippet is used for the class ExcelExportHelper
using OfficeOpenXml;
using OfficeOpenXml.Style;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
namespace ExportExcel.Code
{
public class ExcelExportHelper
{
public static string ExcelContentType
{
get
{ return "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet"; }
}
public static DataTable ListToDataTable<T>(List<T> data)
{
PropertyDescriptorCollection properties = TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(typeof(T));
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
for (int i = 0; i < properties.Count; i++)
{
PropertyDescriptor property = properties[i];
dataTable.Columns.Add(property.Name, Nullable.GetUnderlyingType(property.PropertyType) ?? property.PropertyType);
}
object[] values = new object[properties.Count];
foreach (T item in data)
{
for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++)
{
values[i] = properties[i].GetValue(item);
}
dataTable.Rows.Add(values);
}
return dataTable;
}
public static byte[] ExportExcel(DataTable dataTable, string heading = "", bool showSrNo = false, params string[] columnsToTake)
{
byte[] result = null;
using (ExcelPackage package = new ExcelPackage())
{
ExcelWorksheet workSheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets.Add(String.Format("{0} Data",heading));
int startRowFrom = String.IsNullOrEmpty(heading) ? 1 : 3;
if (showSrNo)
{
DataColumn dataColumn = dataTable.Columns.Add("#", typeof(int));
dataColumn.SetOrdinal(0);
int index = 1;
foreach (DataRow item in dataTable.Rows)
{
item[0] = index;
index++;
}
}
// add the content into the Excel file
workSheet.Cells["A" + startRowFrom].LoadFromDataTable(dataTable, true);
// autofit width of cells with small content
int columnIndex = 1;
foreach (DataColumn column in dataTable.Columns)
{
ExcelRange columnCells = workSheet.Cells[workSheet.Dimension.Start.Row, columnIndex, workSheet.Dimension.End.Row, columnIndex];
int maxLength = columnCells.DefaultIfEmpty().Max(cell => cell.Value == null ? 0 : cell.Value.ToString().Count());
if (maxLength < 150)
{
workSheet.Column(columnIndex).AutoFit();
}
columnIndex++;
}
// format header - bold, yellow on black
using (ExcelRange r = workSheet.Cells[startRowFrom, 1, startRowFrom, dataTable.Columns.Count])
{
r.Style.Font.Color.SetColor(System.Drawing.Color.White);
r.Style.Font.Bold = true;
r.Style.Fill.PatternType = OfficeOpenXml.Style.ExcelFillStyle.Solid;
r.Style.Fill.BackgroundColor.SetColor(System.Drawing.ColorTranslator.FromHtml("#1fb5ad"));
}
// format cells - add borders
using (ExcelRange r = workSheet.Cells[startRowFrom + 1, 1, startRowFrom + dataTable.Rows.Count, dataTable.Columns.Count])
{
r.Style.Border.Top.Style = ExcelBorderStyle.Thin;
r.Style.Border.Bottom.Style = ExcelBorderStyle.Thin;
r.Style.Border.Left.Style = ExcelBorderStyle.Thin;
r.Style.Border.Right.Style = ExcelBorderStyle.Thin;
r.Style.Border.Top.Color.SetColor(System.Drawing.Color.Black);
r.Style.Border.Bottom.Color.SetColor(System.Drawing.Color.Black);
r.Style.Border.Left.Color.SetColor(System.Drawing.Color.Black);
r.Style.Border.Right.Color.SetColor(System.Drawing.Color.Black);
}
// removed ignored columns
for (int i = dataTable.Columns.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (i == 0 && showSrNo)
{
continue;
}
if (!columnsToTake.Contains(dataTable.Columns[i].ColumnName))
{
workSheet.DeleteColumn(i + 1);
}
}
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(heading))
{
workSheet.Cells["A1"].Value = heading;
workSheet.Cells["A1"].Style.Font.Size = 20;
workSheet.InsertColumn(1, 1);
workSheet.InsertRow(1, 1);
workSheet.Column(1).Width = 5;
}
result = package.GetAsByteArray();
}
return result;
}
public static byte[] ExportExcel<T>(List<T> data, string Heading = "", bool showSlno = false, params string[] ColumnsToTake)
{
return ExportExcel(ListToDataTable<T>(data), Heading, showSlno, ColumnsToTake);
}
}
}
Now, we do front-end development and create Model, View, and Controller. We create TechnologyViewModel view model that binds to the View, as per the following code snippet.
using ExportExcel.Code;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ExportExcel.Models
{
public class TechnologyViewModel
{
public List<Technology> Technologies
{
get
{
return StaticData.Technologies;
}
}
}
}
After this, we create a controller, HomeController, which has an Index action method. It returns View with Model in the browser.
using ExportExcel.Code;
using ExportExcel.Models;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace ExportExcel.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Index()
{
TechnologyViewModel model = new TechnologyViewModel();
return View(model);
}
}
}
Now, we create a view that shows the data in the listing and has a button linked to export to Excel functionality. The following code snippet is for the Index view.
@model ExportExcel.Models.TechnologyViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Export To Excel";
}
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<a href="@Url.Action("ExportToExcel")" class="btn btn-primary">Export</a>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<table class="table table-striped table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Project</th>
<th>Team Leader</th>
<th>Developer</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Technologies)
{
<tr>
<td>@item.Name</td>
<td>@item.Project</td>
<td>@item.TeamLeader</td>
<td>@item.Developer</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
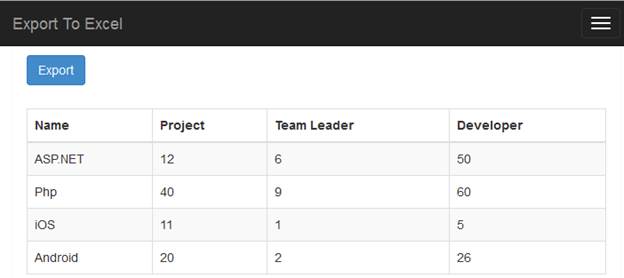
The application runs and shows results as follows.
Figure 3: Listing for Data
Now, we write the action method to call the export to Excel functionality. This action method returns an exported Excel file. The action method returns FileContentResult which is used when we have a byte array and return as a file. The following code snippet is used for the same.
[HttpGet]
public FileContentResult ExportToExcel()
{
List<Technology> technologies = StaticData.Technologies;
string[] columns = {"Name","Project","Developer"};
byte[] filecontent = ExcelExportHelper.ExportExcel(technologies, "Technology", true,columns );
return File(filecontent, ExcelExportHelper.ExcelContentType, "Technologies.xlsx");
}
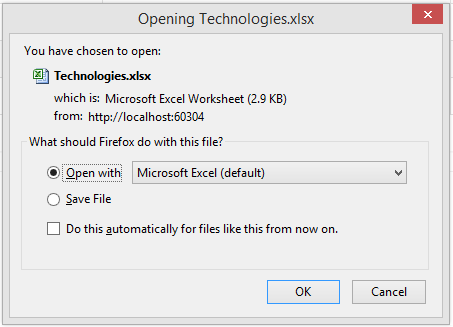
Now, click The Export button. The button calls the above action method and the result is as shown in the figure.
Figure 4: Dialog for Excel
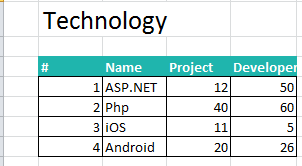
The resulted Excel file has the data. It has only those columns that we exported rather than all the columns of the collection.
Figure 5: Excel with Data
Download
You can download the complete solution source code from the code gallery using the following URL.
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/Export-To-Excel-In-ASPNET-cf17ea0d