Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Three easy steps for exporting .NET functionality to VBA:
1. Write a source file:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace InteropTest
{
[Guid("BEB2C62D-5646-4B08-81DF-670314BFEE4A")]
public class InteropTestClass
{
public void Help()
{
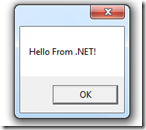
MessageBox.Show("Hello From .NET!");
}
}
}
The GUID needs to be unique.
2. Generate a strong key to sign the assembly:
sn -k MyKey.snk
3. Compile the C# file using CSC:
csc /target:library /out:tstint.dll MyClass.cs /keyfile:MyKey.snk
We now have a DLL that can be exported to another machine with the .NET Framework installed. On the target machnie, the assembly needs to be registered:
regasm tstint.dll /codebase /tlb:tstint.tlb
Now the library can be used in Office by selecting it from the list of references in VBA:
Comments
- Anonymous
November 13, 2015
But I want to use .NET just because I don't want the final user install anithing apart from Office!